Products
I/O Systems
-
 IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All
IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBN1-354XXX
IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Metal Housing Metal Thread / Bayonet LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBN1-310XXX
IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Metal Housing Metal Thread LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP1-372XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 2A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP2-364XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 2A/channel Plastic Housing Metal Thread/Bayonet LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP1-372XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP1-351XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Metal Thread/Bayonet LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP2-330XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 2A/channel Metal Housing Metal Thread LockingView All
-

P/N: ALM-MPA1-051XXX
IO Link Master Multiprotocol Plastic Housing 7/8 Power ConnectorView All -

P/N: ALM-ECA1-010XXX
IO Link Master EtherCAT Single ProtocolView All -

P/N: ALM-MPA1-041XXX
IO Link Master Multiprotocol Plastic Housing M12 L-Codedd Power ConnectorView All -

P/N: ALM-MPA1-030XXX
IO Link Master Multiprotocol Metal Housing M12 L-Codedd Power ConnectorView All -

P/N: ALM-PNA1-010XXX
IO Link Master Profitnet Single ProtocolView All
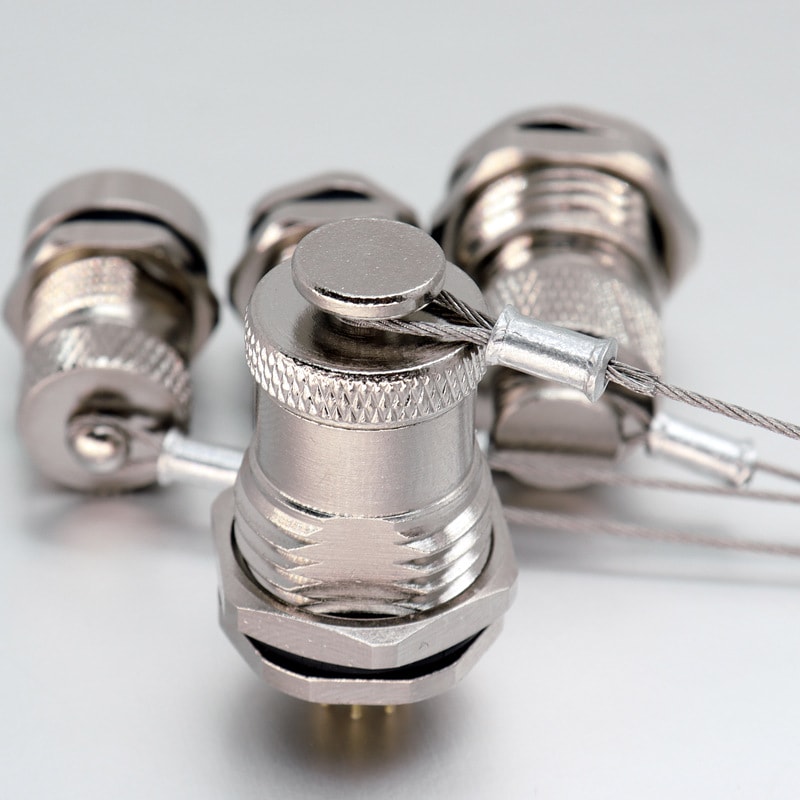
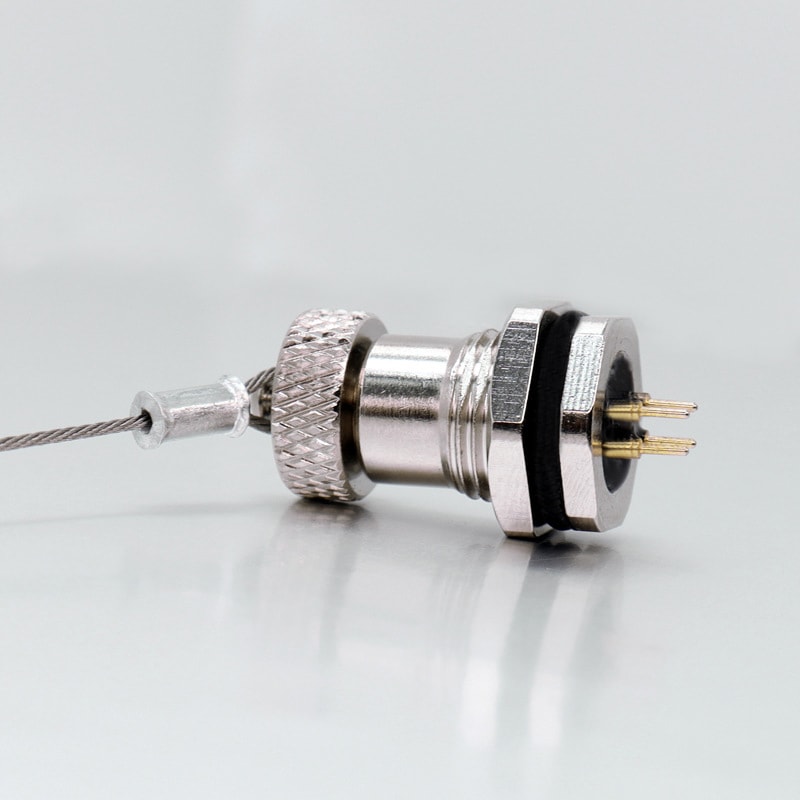
Circular Connectors
-
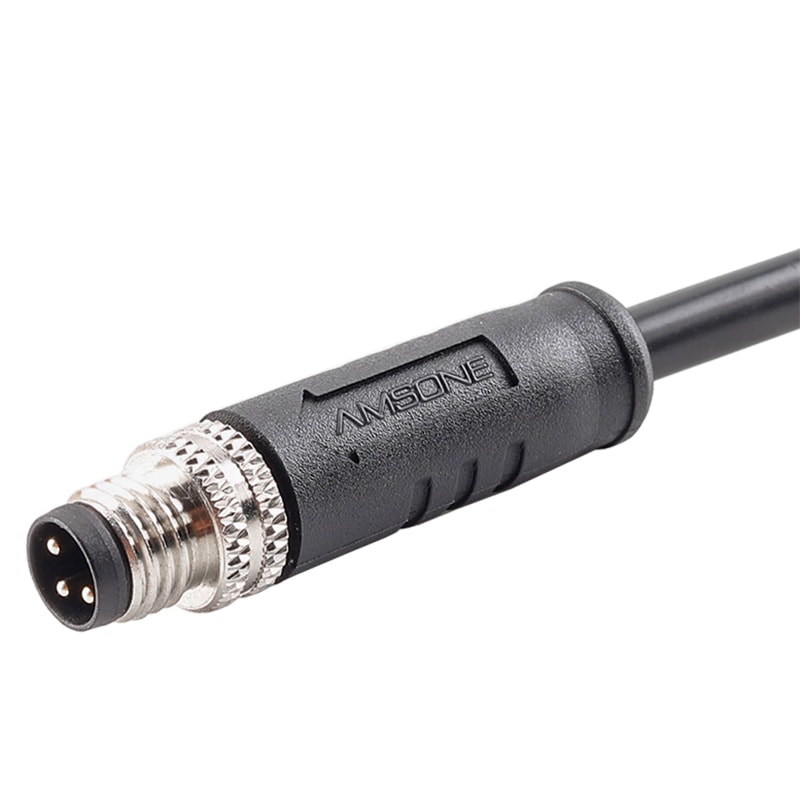

P/N: AM08M0411AXX1-XXX
M8 4Pin Pre-molded Cable Male Straight M8 ConnectorView All -
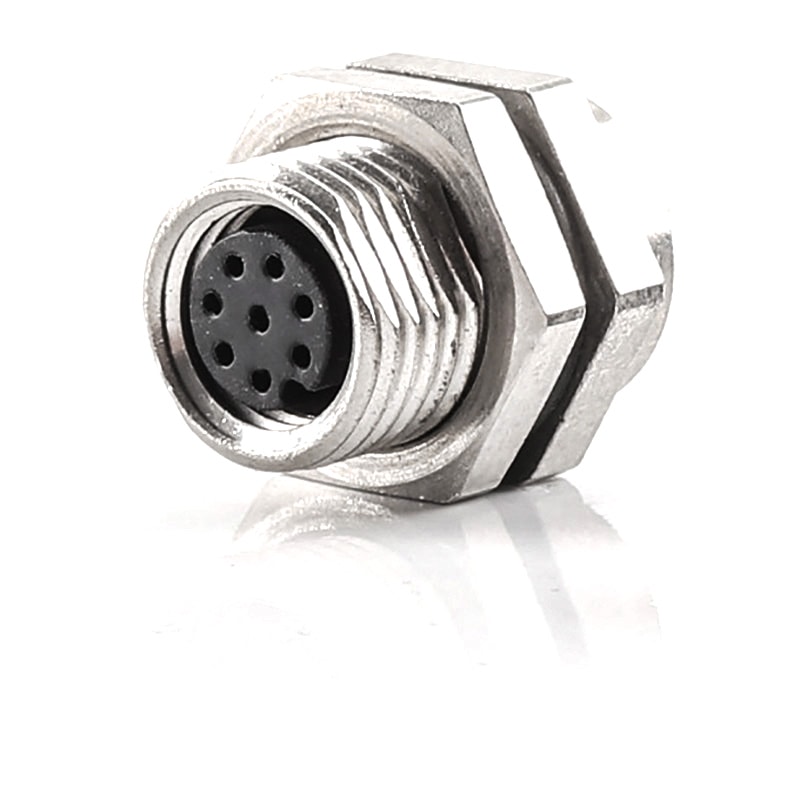

P/N: AM08F0822A001
M8 Device Connector Panel Rear Mount M8 8P Female ReceptacleView All -
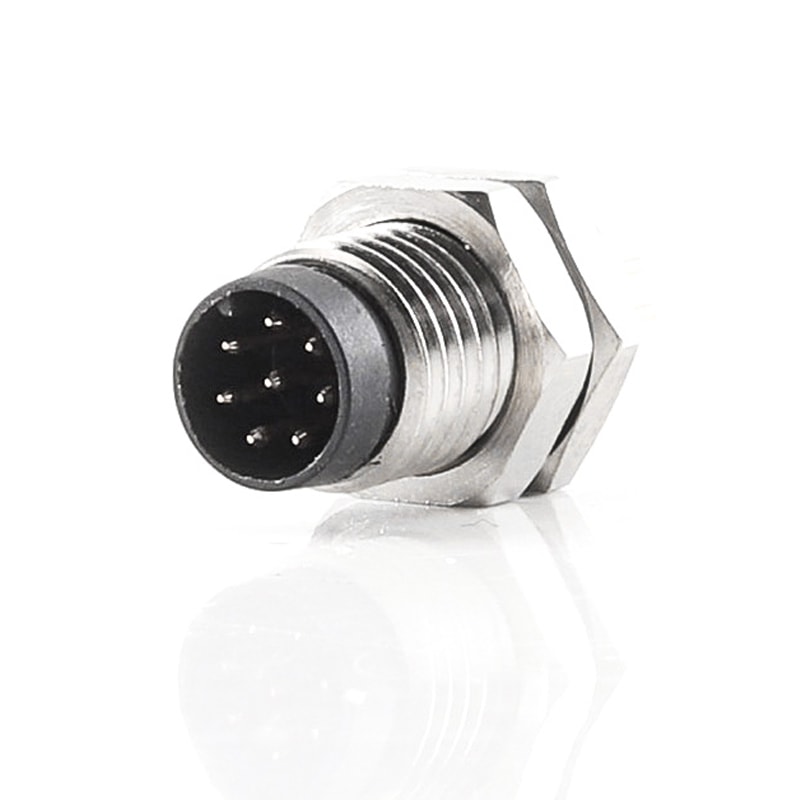

P/N: AM08M0622A001
M8 Device Connector Panel Rear Mount M8 6P Male ReceptacleView All -
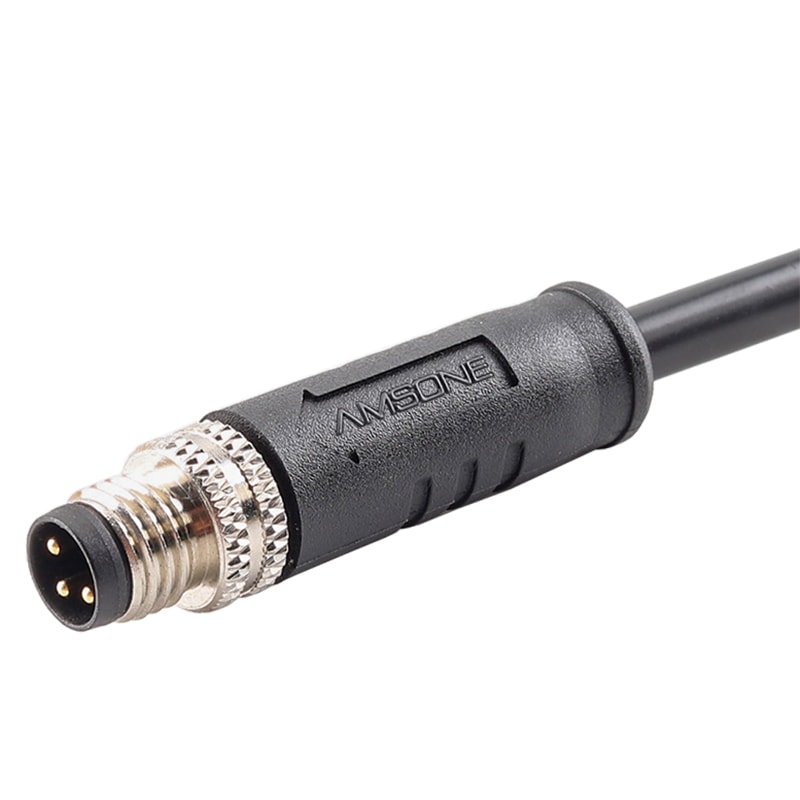

P/N: AM08M0811AXX1-XXX
M8 8Pin Pre-molded Cable Male Straight M8 ConnectorView All -
P/N: AM08M0822A003
M8 Device Connector Male 8Pin PCB Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Right Angled ShieldedView All -
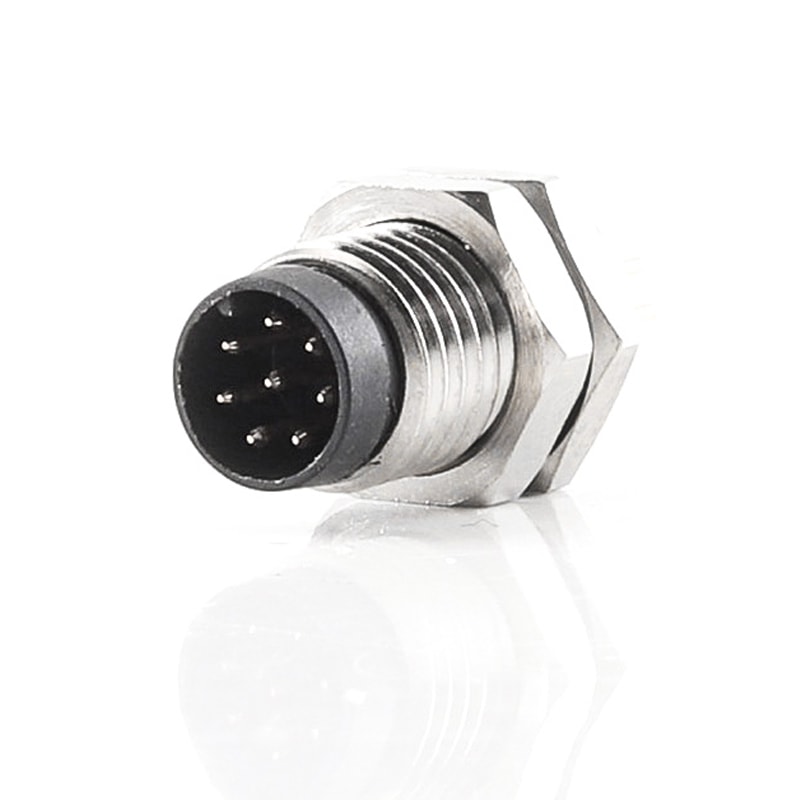

P/N: AM08M0822A001
M8 Device Connector Panel Rear Mount M8 8P Male ReceptacleView All -
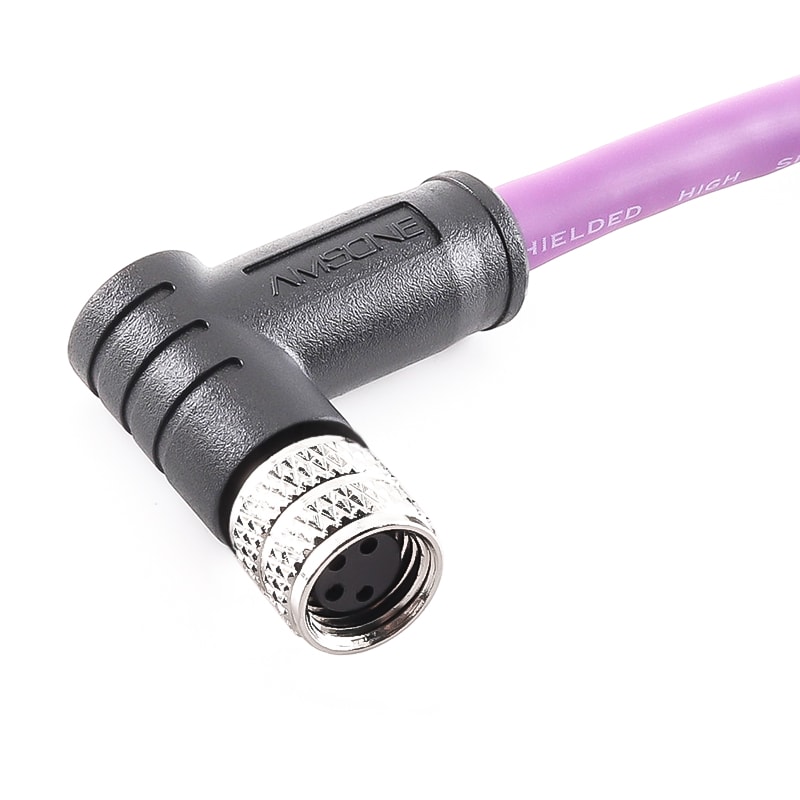

P/N: AM08F0811AXX3-XXX
M8 8P Female Shield Connector Pre-molded Cable Right Angled IP67View All -

P/N: AM08M0811AXX3-XXX
M8 Connector 8P Male Shield Pre-molded Cable Right Angled IP67View All
-

P/N: AM12F1211AXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts: 12,solder connection, A code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0822A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts: 8, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0522A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts: 5, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
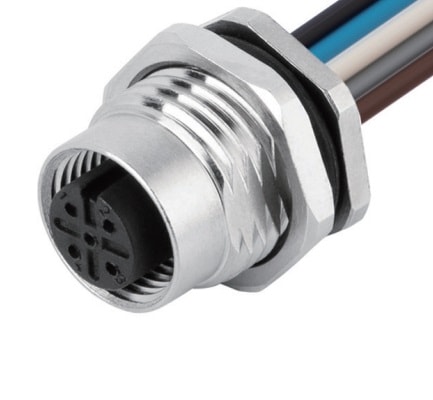

P/N: AM12F0512AXX1-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts: 5, solder connection for wires, A code, straight, IP67View All -
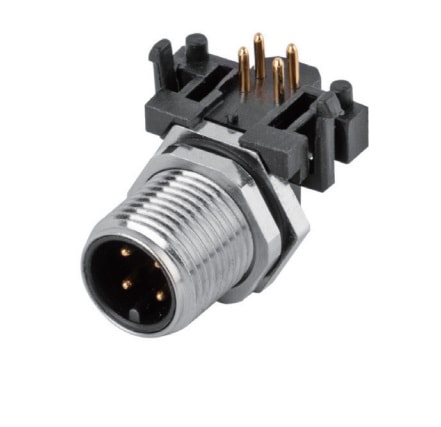

P/N: AM12M0422A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts: 4, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
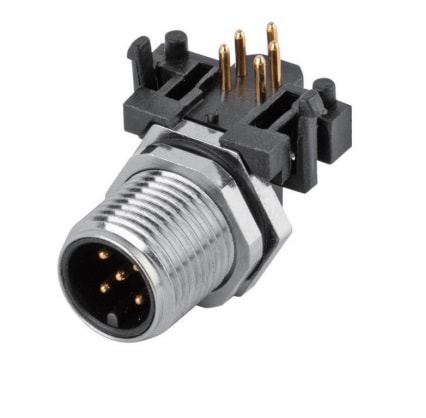

P/N: AM12M0522A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts: 5, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
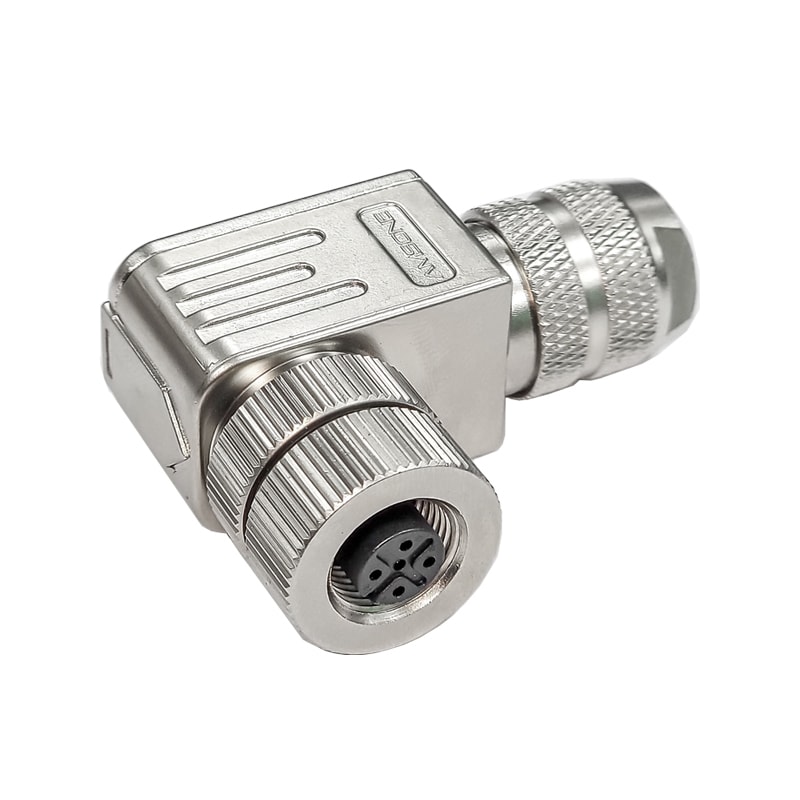

P/N: AM12F0534A007
M12 cable connector, female, contacts:5, field assembly type, screw connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
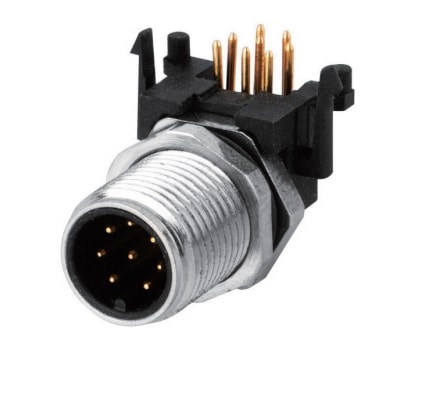

P/N: AM12M0822A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts: 8, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All
-
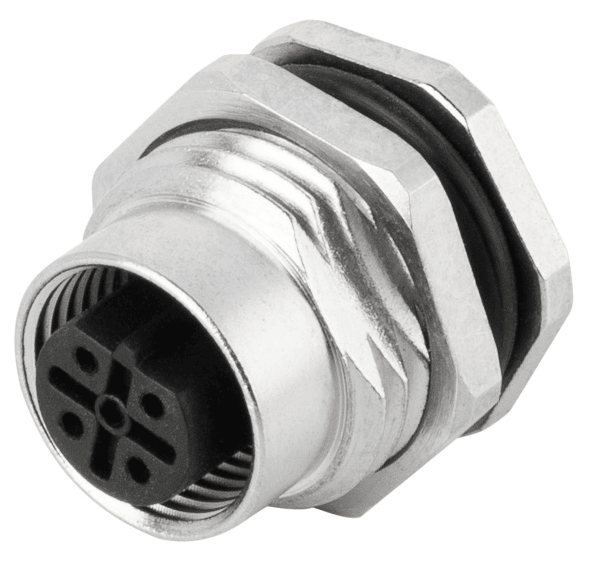

P/N: AM12F0522B001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:5, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -
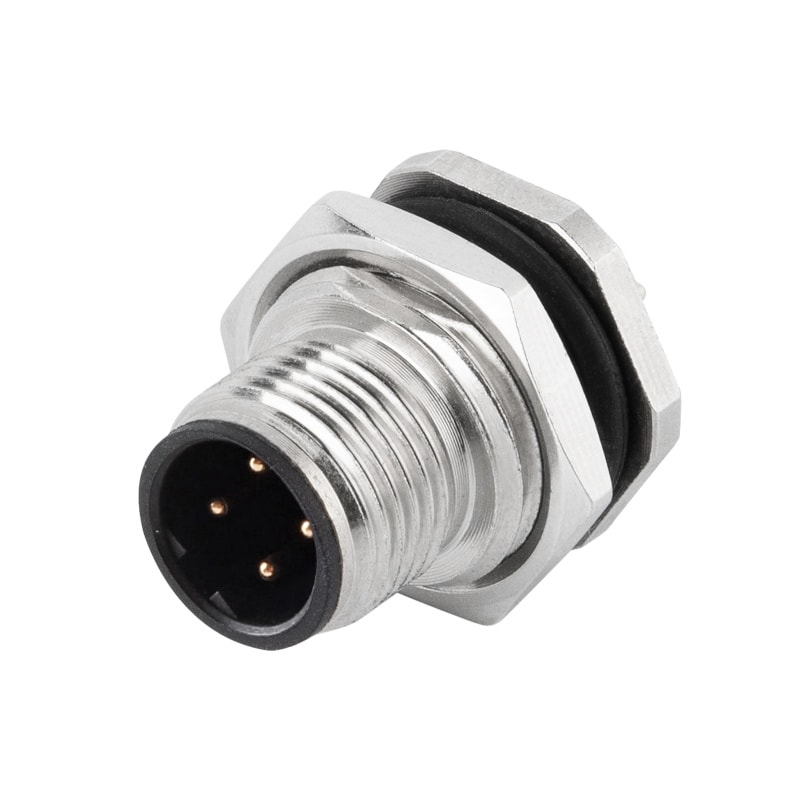

P/N: AM12M0522B001
M12 B Code Male Panel Rear Mount Receptacle PCB Connector PG9View All -
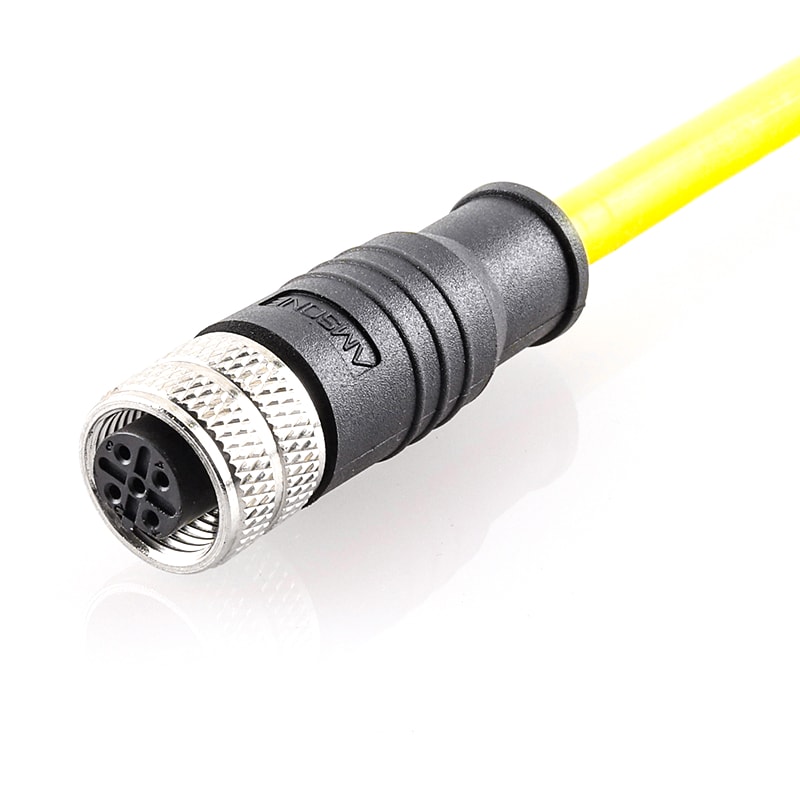

P/N: AM12F0511BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:5, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -
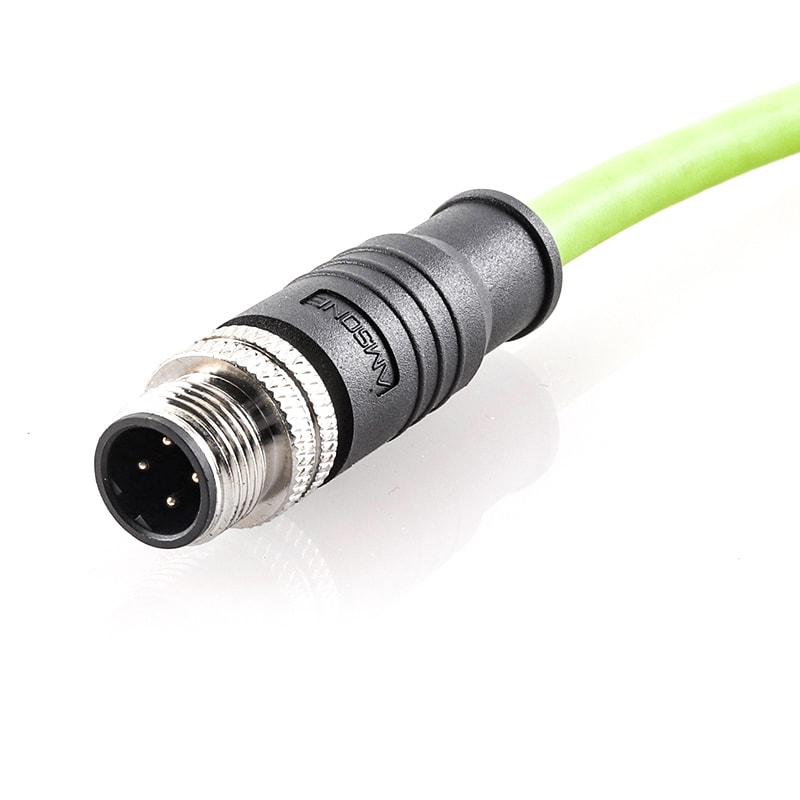

P/N: AM12M0511BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:5, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -
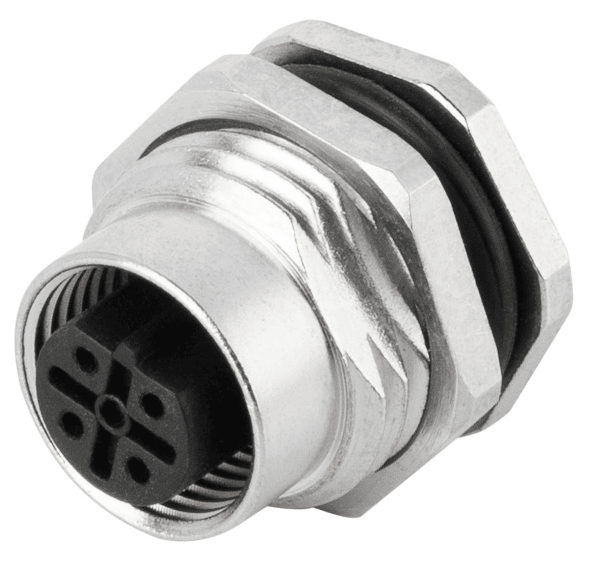

P/N: AM12F0422B001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -
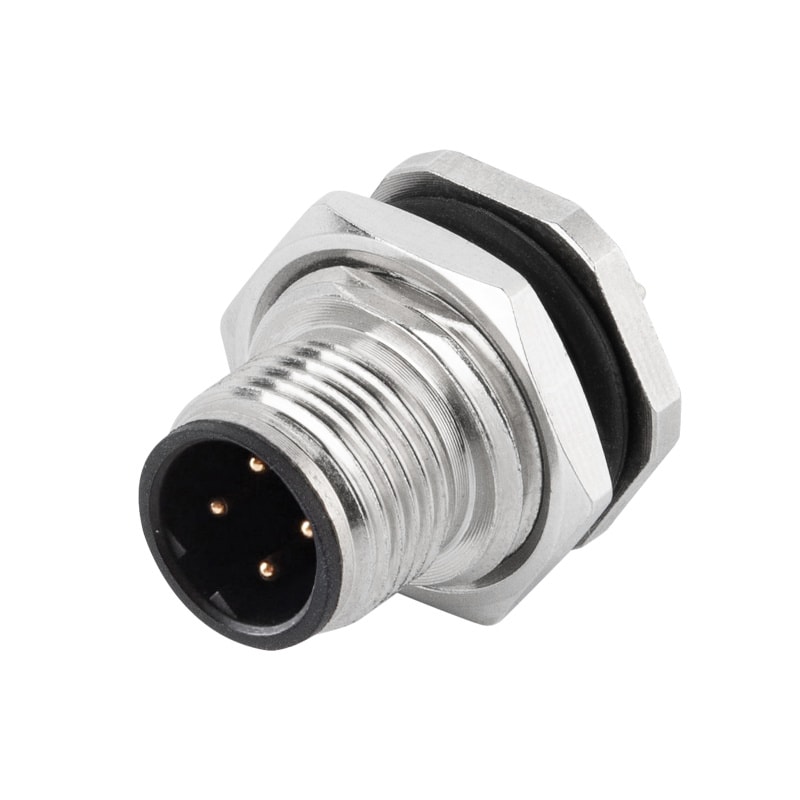

P/N: AM12M0422B001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -
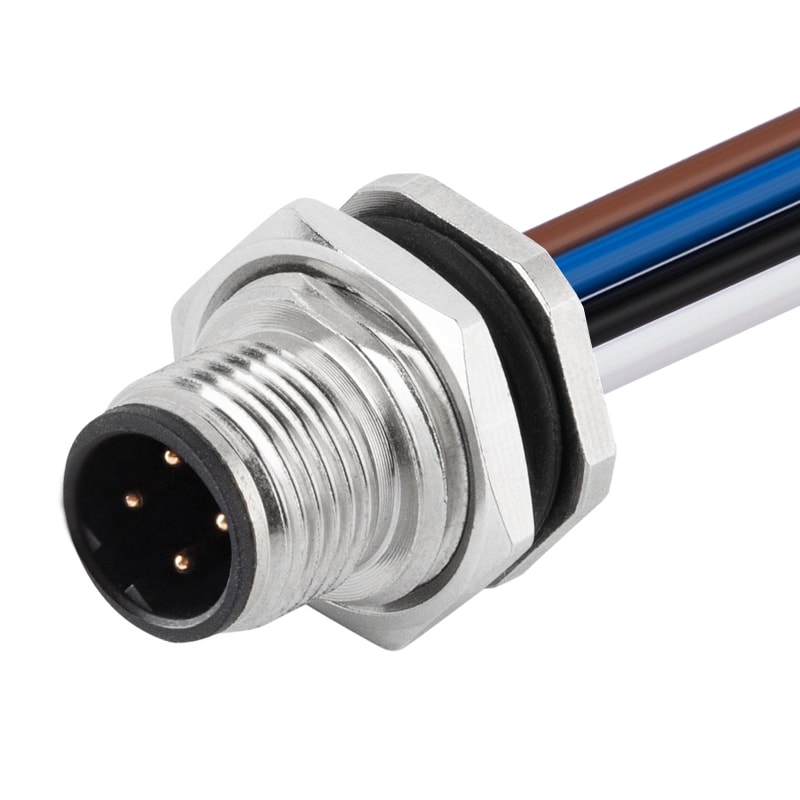

P/N: AM12M0512B002
M12 5P Male B Code Panel Rear Mount Receptacle Wires Solder Connector M16*1.5View All -
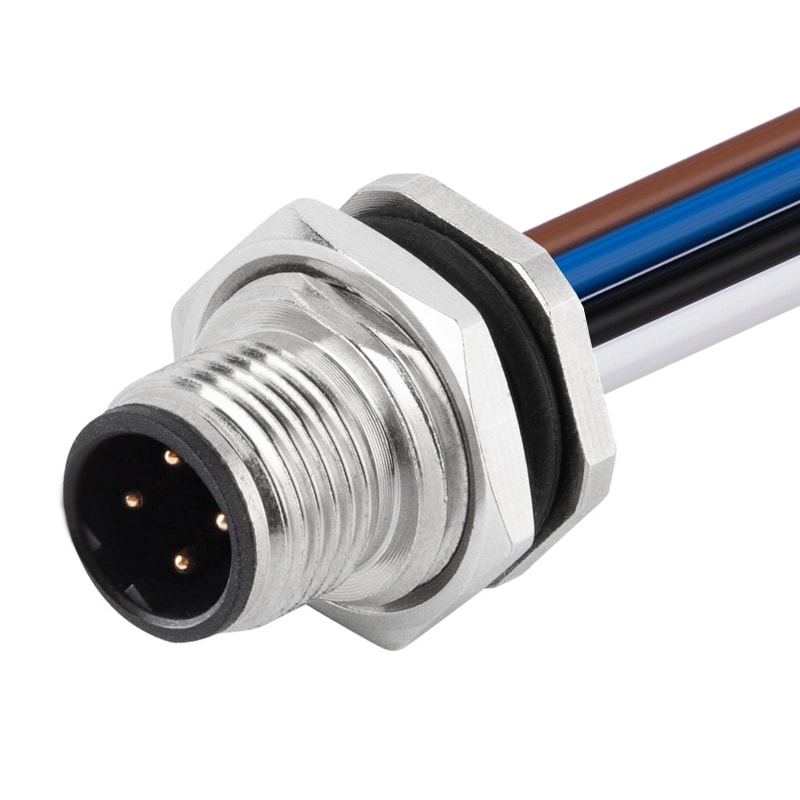

P/N: AM12M0512B001
M12 5P Male B Code Panel Rear Mount Receptacle Wires Solder Connector PG9View All
-
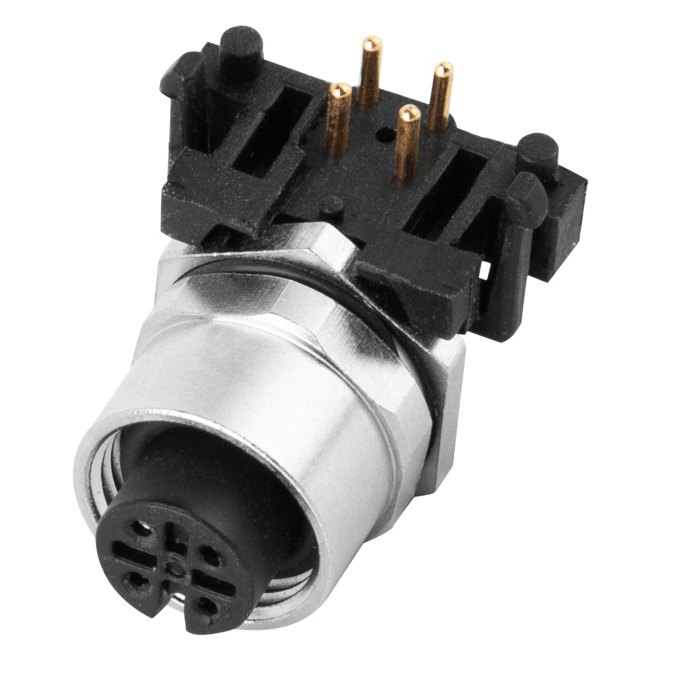
P/N: AM12F0422D006
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, D code, right angled, IP67View All -
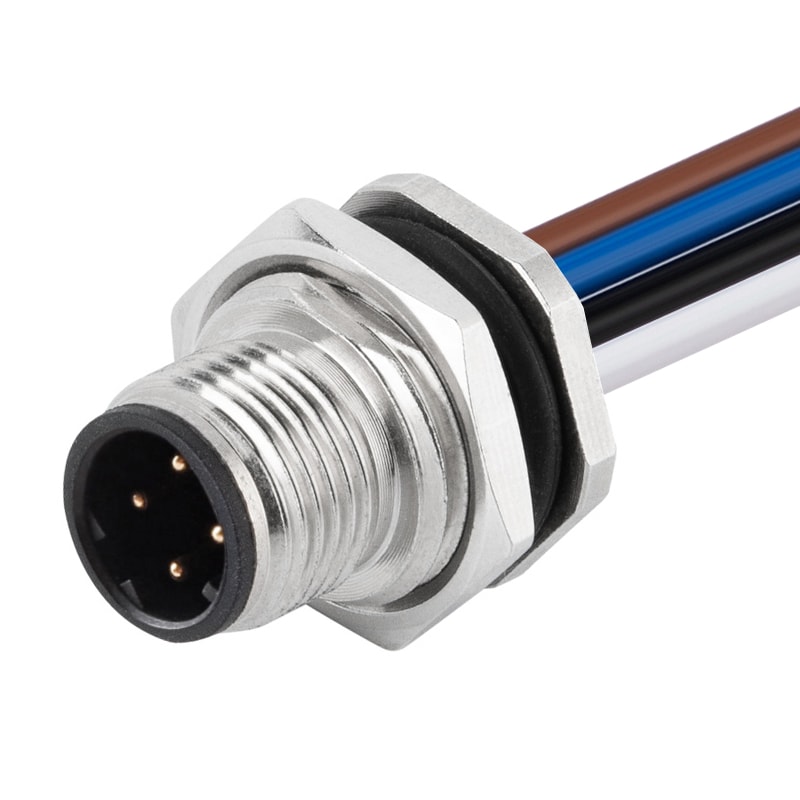

P/N: AM12M0412D001
M12 D Code Male Panel Rear Mount Receptacle For Wires Solder Connector PG9View All -
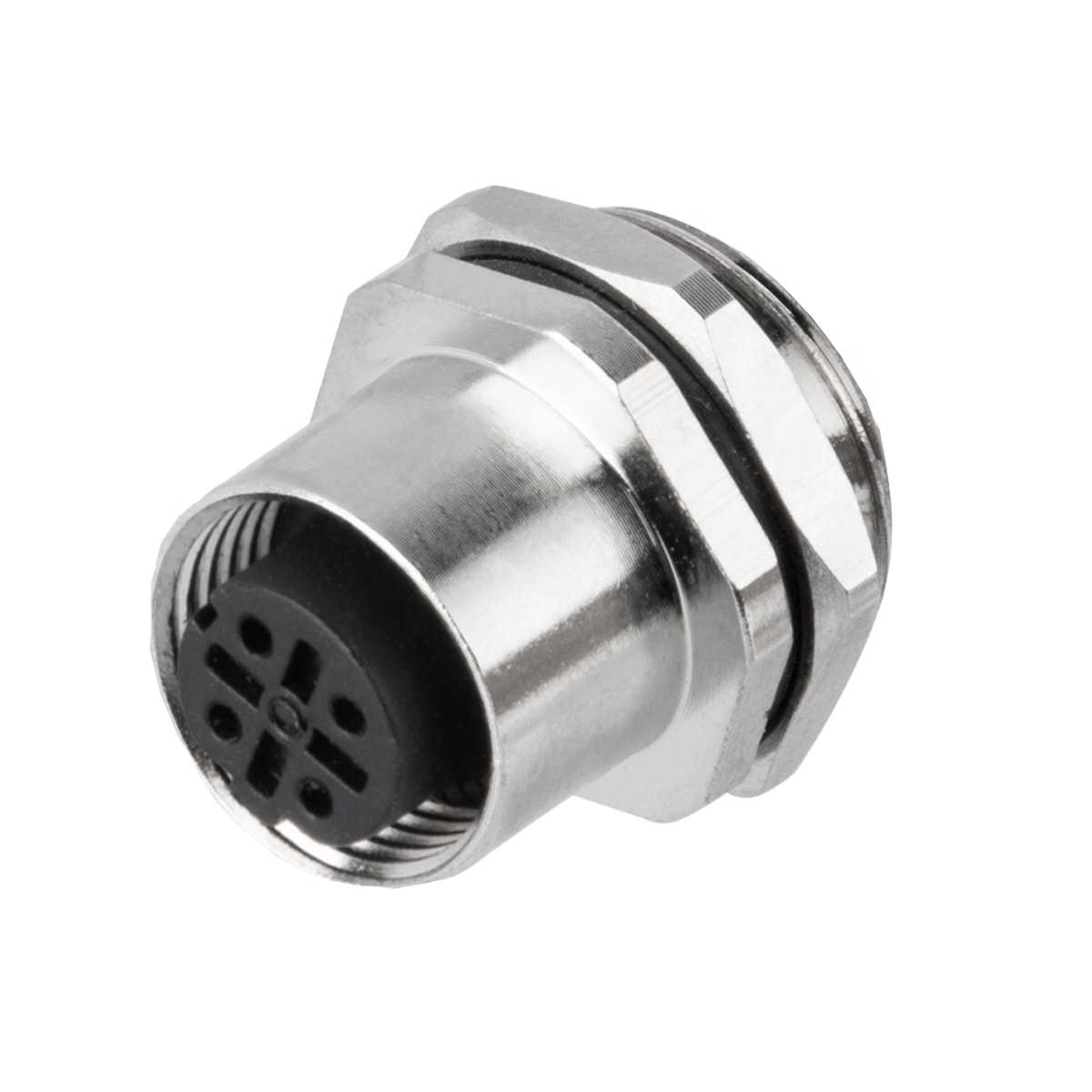

P/N: AM12F0413D001
M12 panel receptacle, front mount, female, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, D code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0413D351-005
M12 Panel Receptacle Front Mount Male 4Pin Solder Connection For Wires D Code Straight IP67View All -
P/N: AM12F0422D001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, D code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0422D001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, D code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0411D241-010
M12 4P D Code Pre-molded Cable Connector Female Straight IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0411D241-010
M12 pre-molded cable connector male solder connection D code straight IP67View All
-
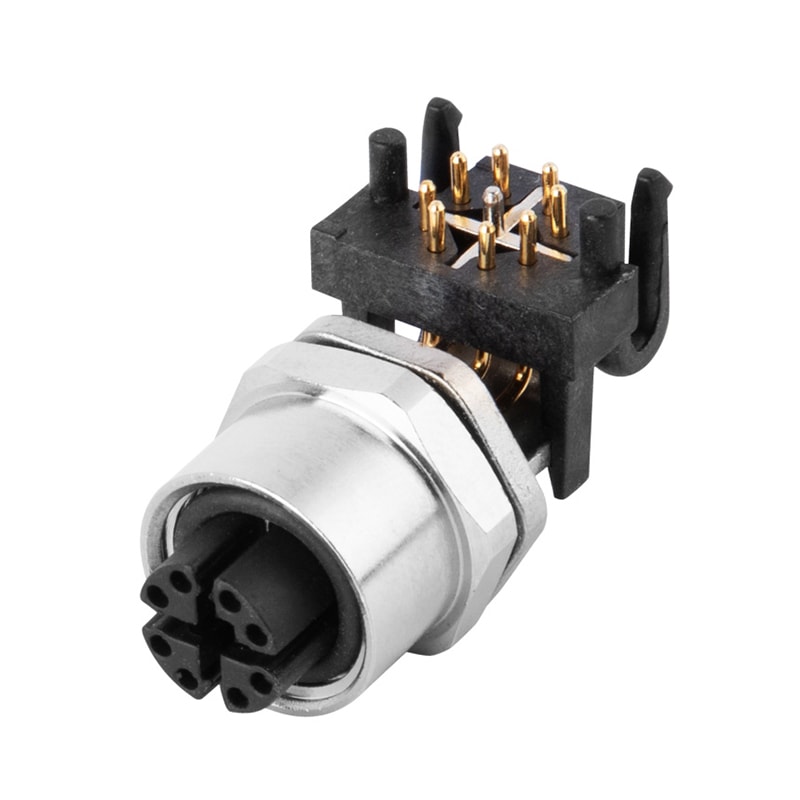

P/N: AM12F0822X008
M12 X Code 8Pole Panel Receptacle Rear Mount Female PCB Dip-solder Connection Right Angled IP67View All -
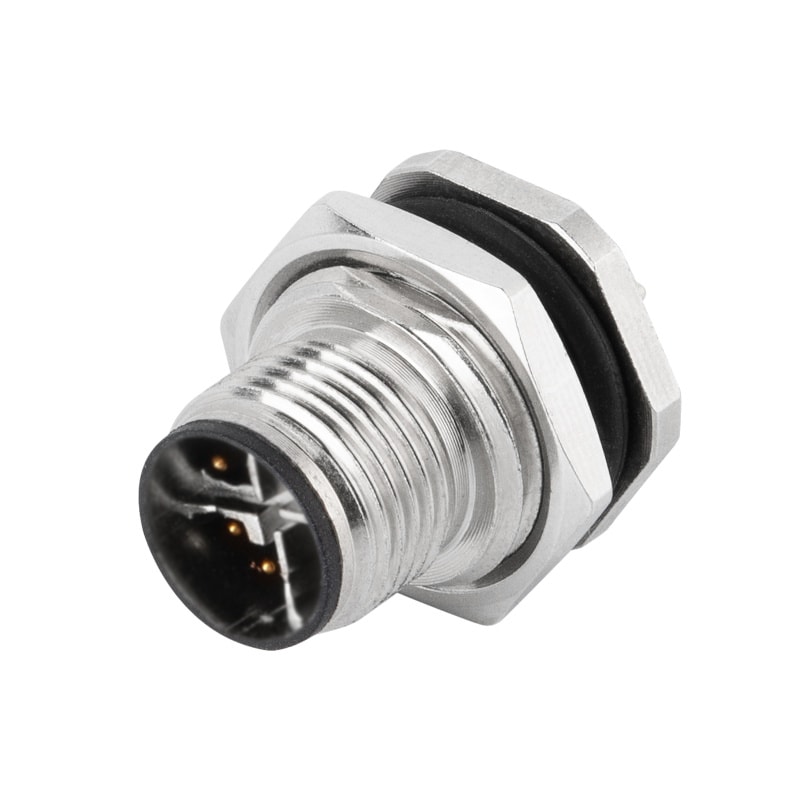

P/N: AM12M0822X001
M12 Panel Receptacle Rear Mount Male PCB DIP Solder X Code StraightView All -
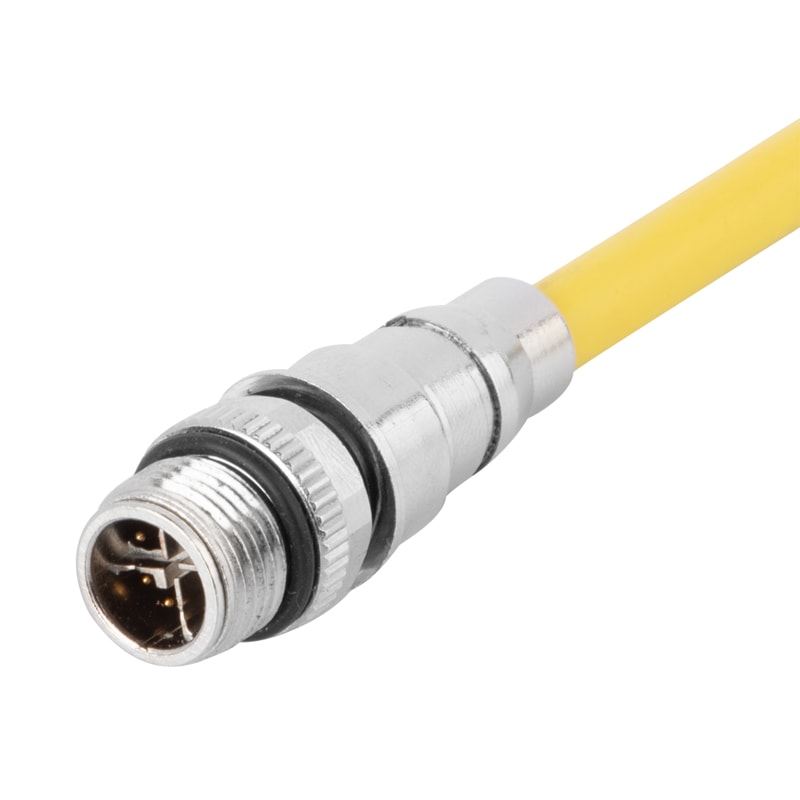

P/N: AM12M0811X003
M12 data cable connector, contact: 8P, male, for pre-molding , X code, straight, 360 EMC shielding, solder connection, 0.5A/60VView All -
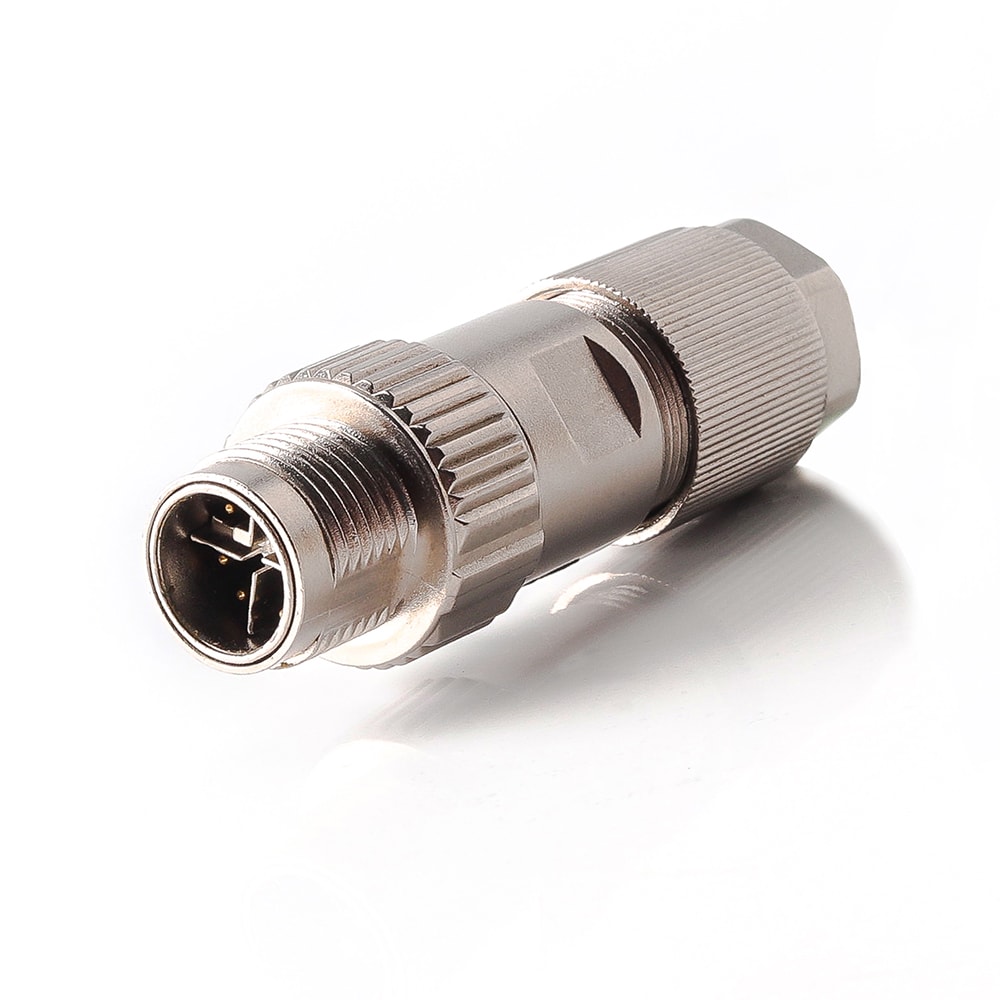

P/N: AM12M0844X003
M12 X Code Field Assembly Connector Male EMC Shielded Straight IP67 Crimp ContactsView All -
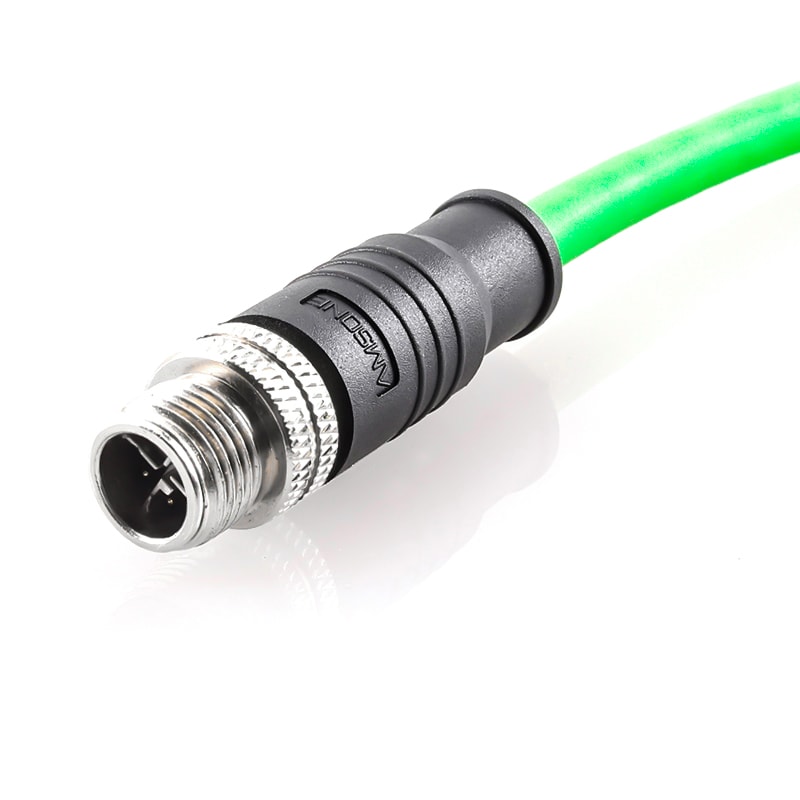

P/N: AM12M0811X233-100
M12 Pre-molded Cable Connector 8Pole Male X Code EMC Profinet/Ethernet Cable StraightView All -
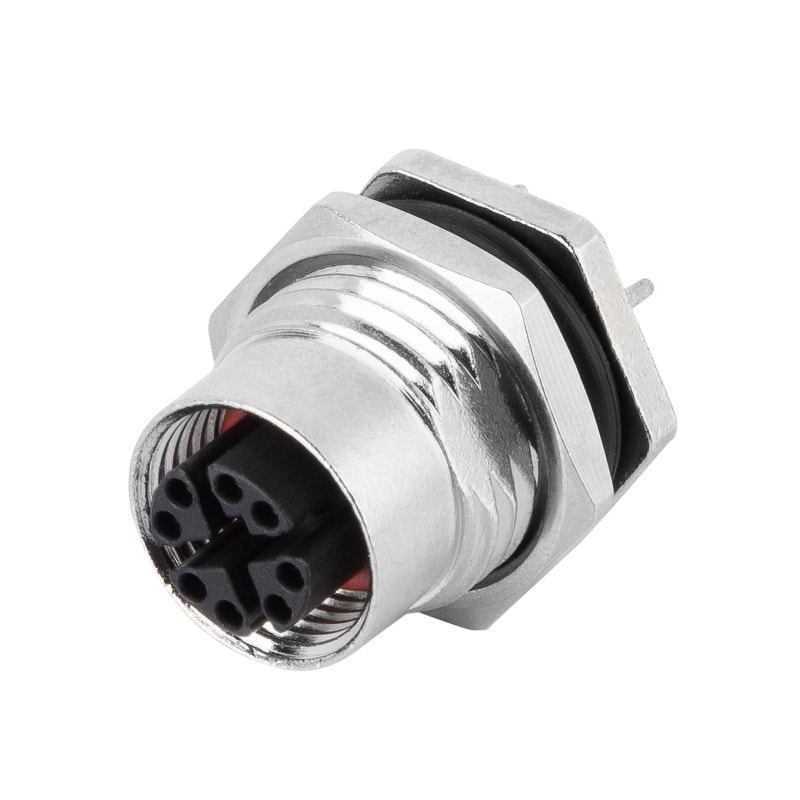

P/N: AM12F0822X002
M12 X Code Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female PCB DIP Connection M16*1.5View All -
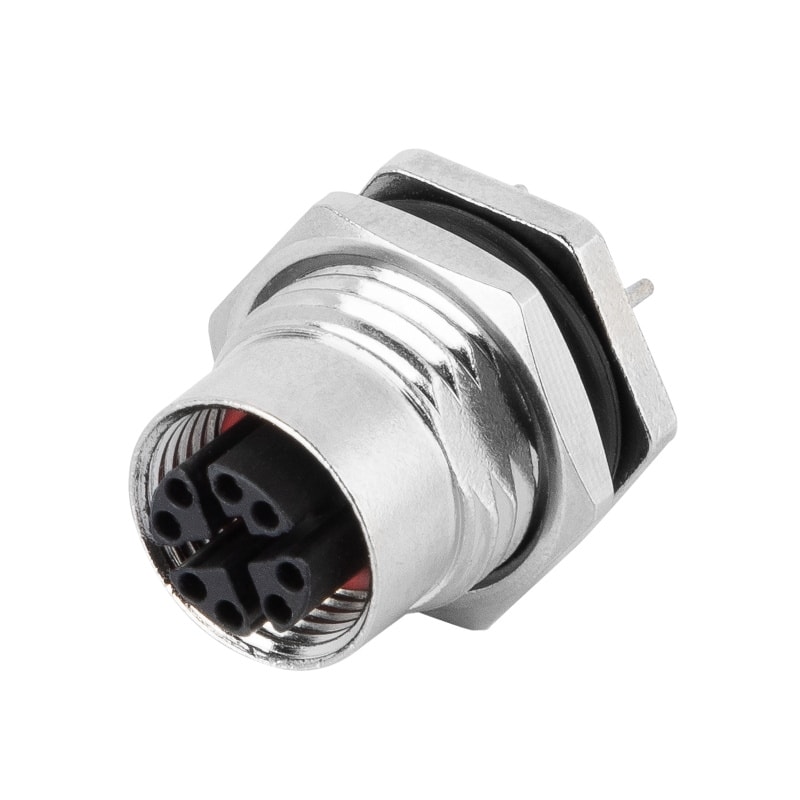

P/N: AM12F0822X001
M12 X Code Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female PCB DIP Connection PG9View All -
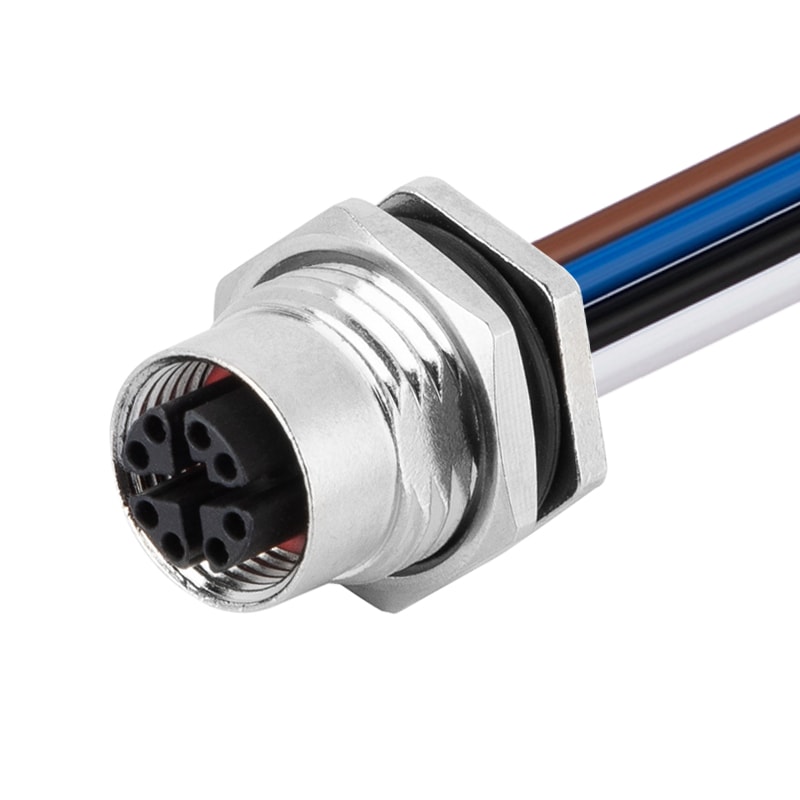

P/N: AM12F0812X001
M12 X Code Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female For Solder Wires ConnectionView All
-
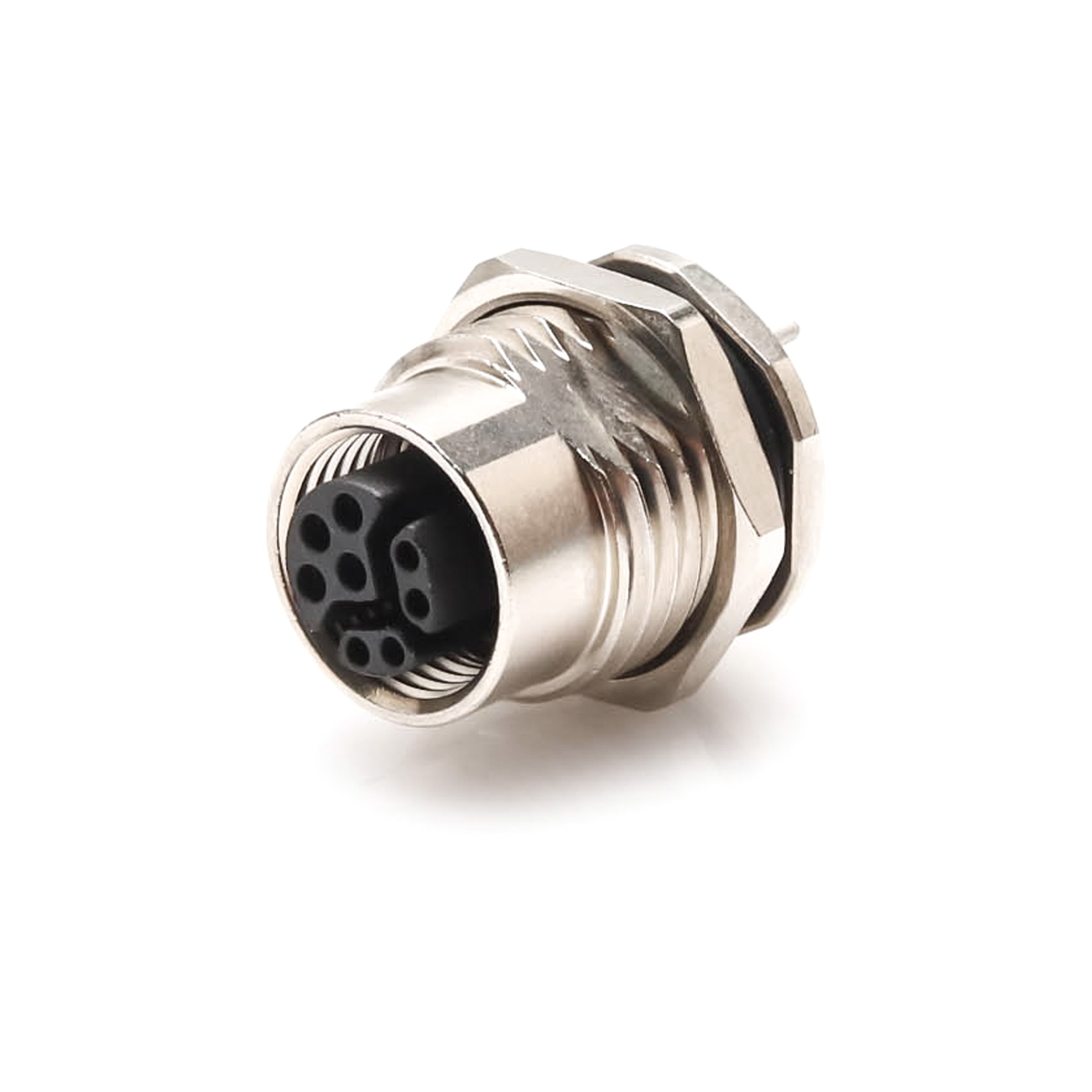

P/N: AM12F0822Y002
M12 Hybrid Connector,Y Code,Female,Panel Mount Receptacle,M12 Device ConnectorView All -
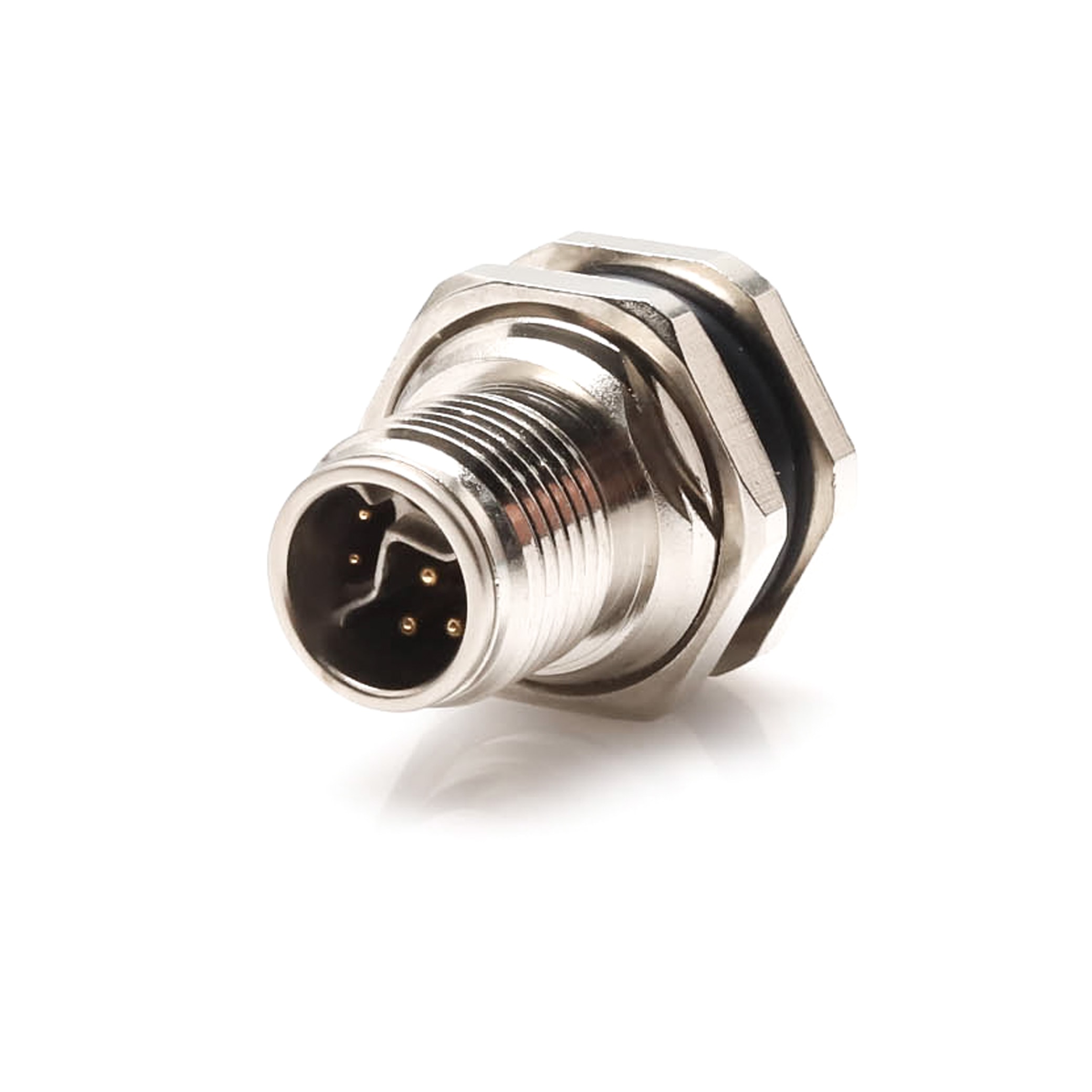

P/N: AM12M0822Y002
M12 Hybrid Connector,Y Code,Male,Panel Mount Receptacle,M12 Device ConnectorView All -
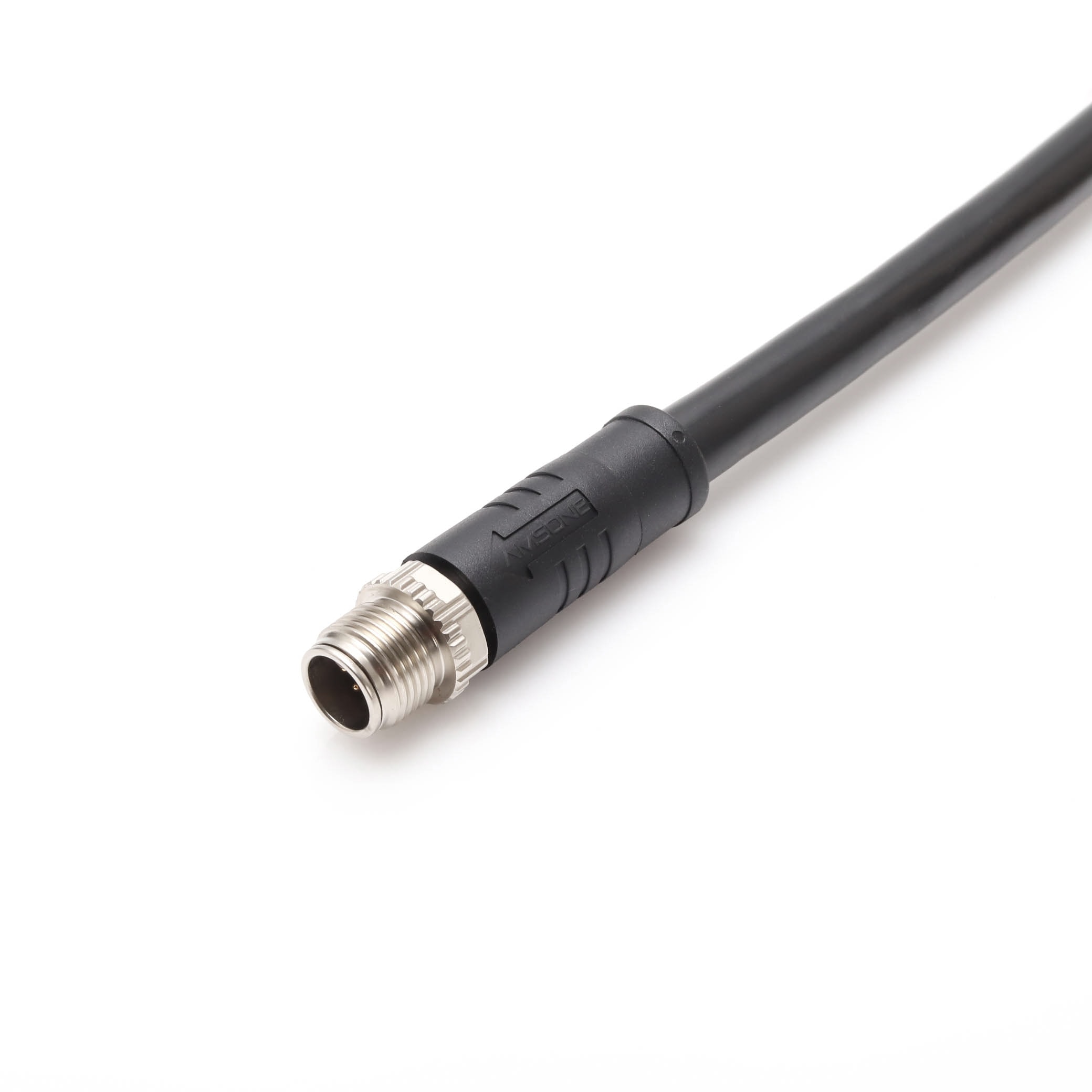

P/N: AM12M0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Male,M12 Y-Coded Power Signal Ethernet CableView All -
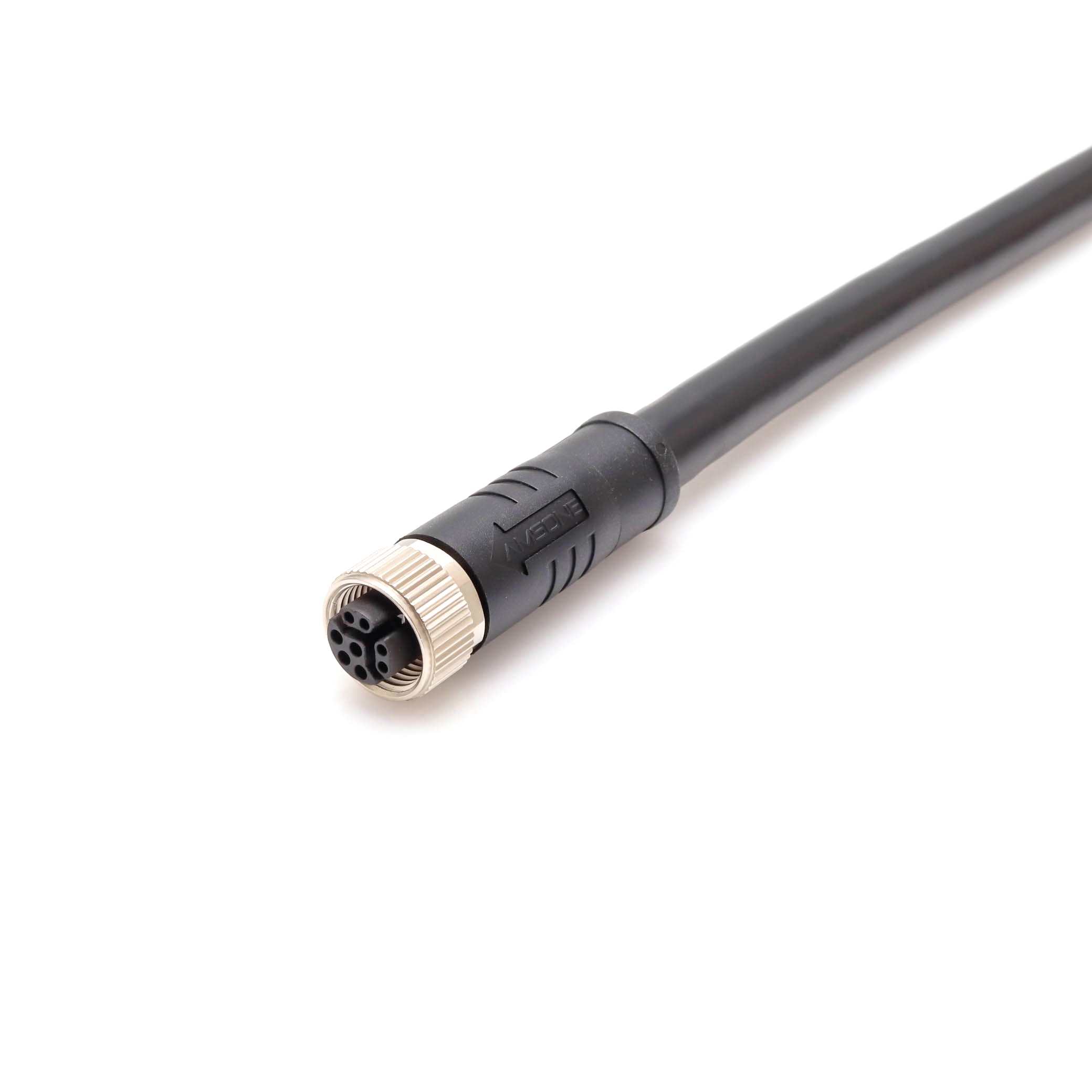

P/N: AM12F0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Power Signal,M12 Y-Coded CablesView All -
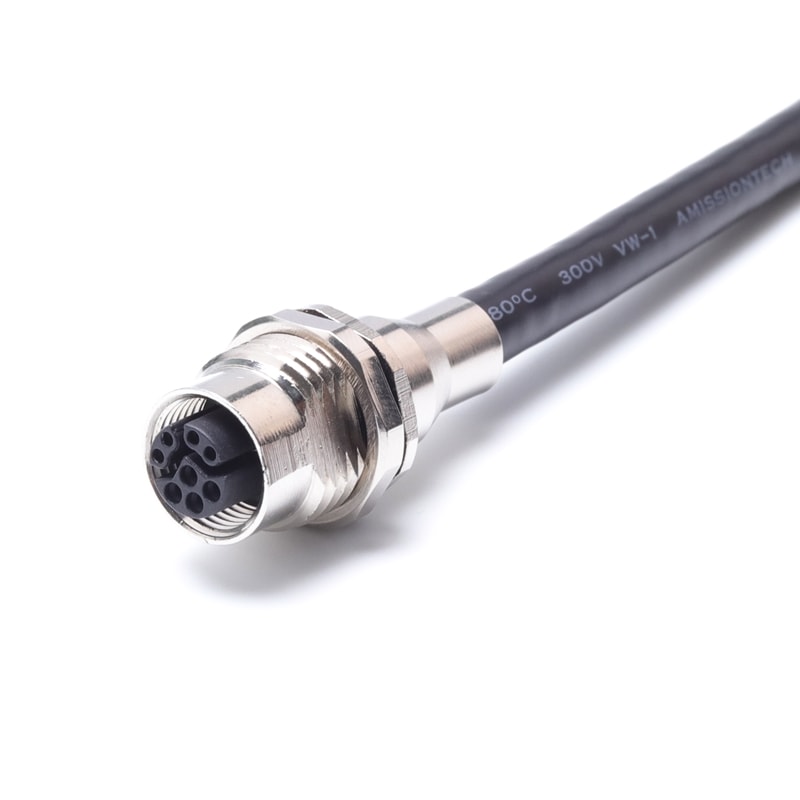

P/N: AM12F0812Y003
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Panel Mount Shielded,M12 Y-CodedView All
-
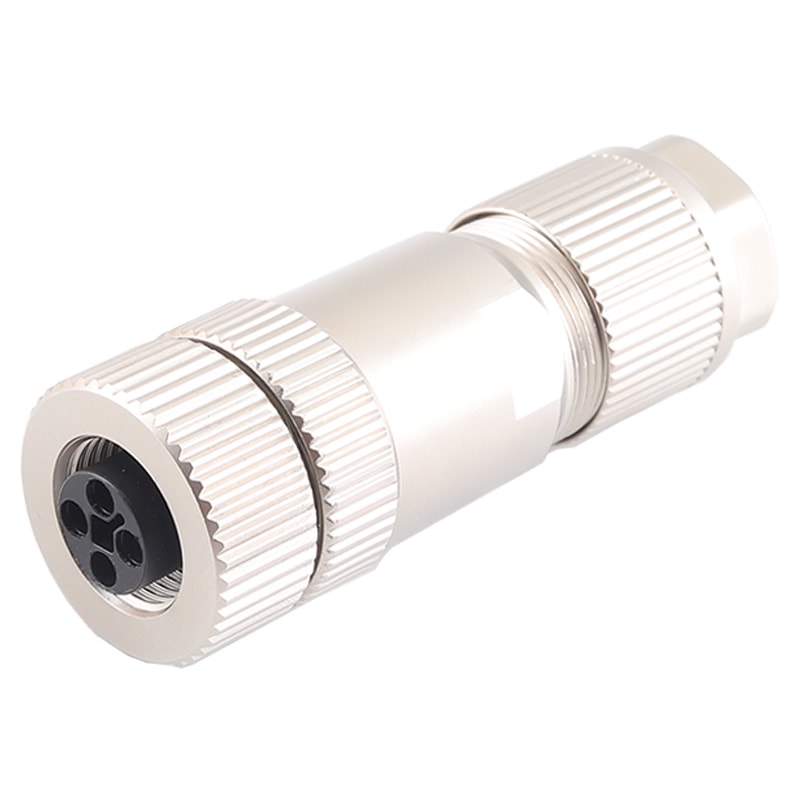

P/N: AM12F0434T001
M12 cable connector, female, contacts: 4, field assembly type, screw connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -
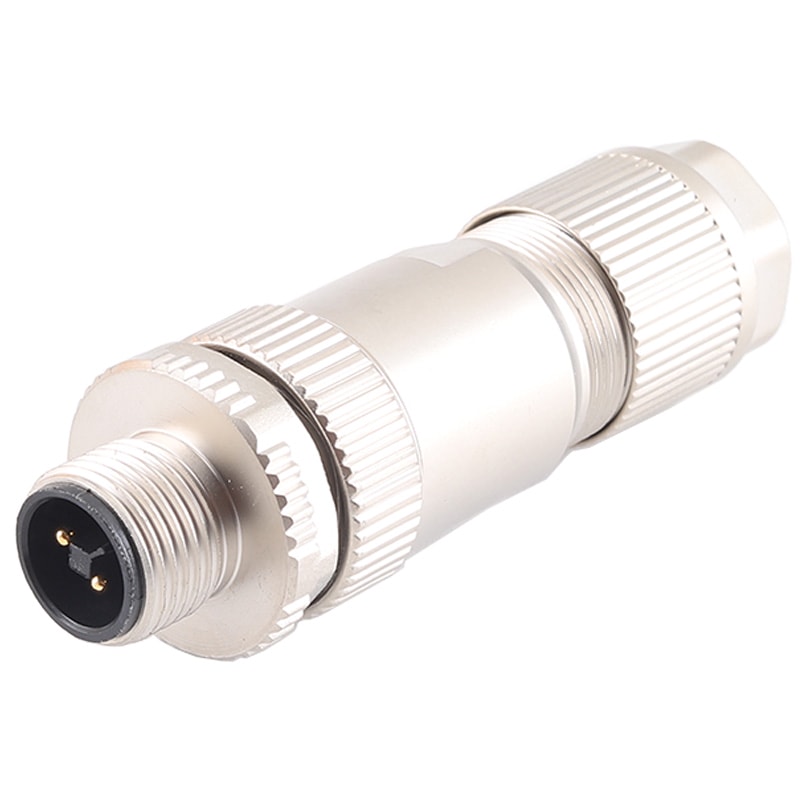

P/N: AM12M0434T001
M12 cable connector, male, contacts: ,4, field assembly type, screw connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -
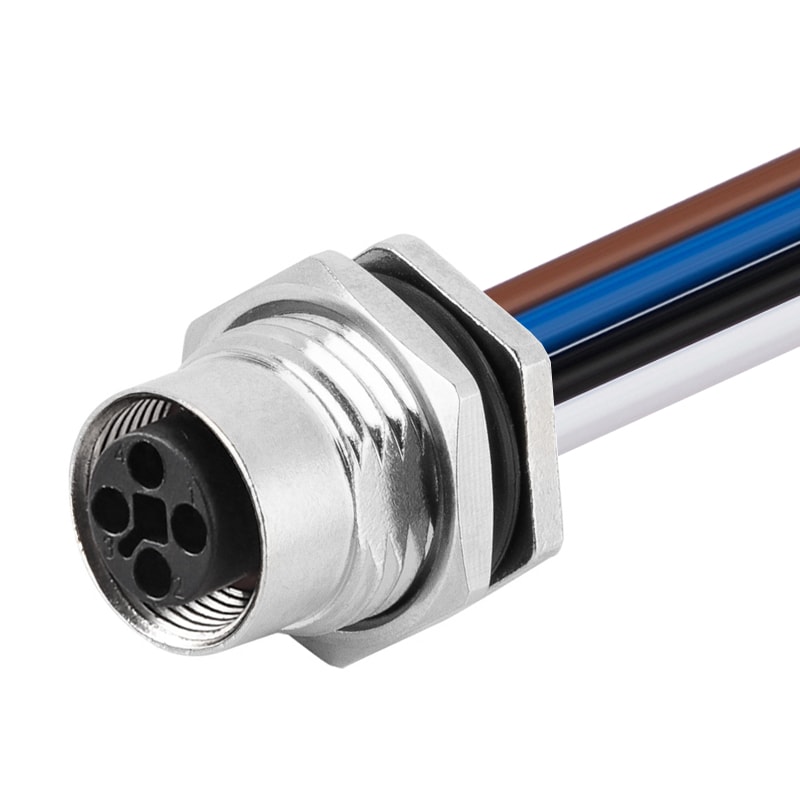

P/N: AM12F0412T171 -XXX
M12 panel receptacle, female, contacts: 4, solder connection for wires, T code, straight, IP67View All -
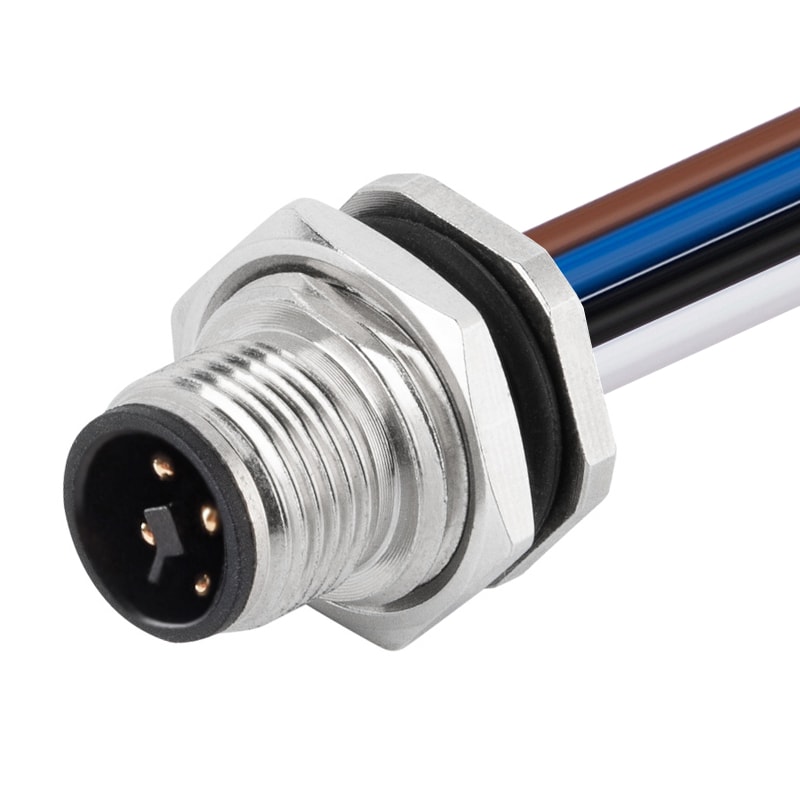

P/N: AM12M0412T171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, male, contacts: 4, solder connection for wires, T code, straight, IP67View All -
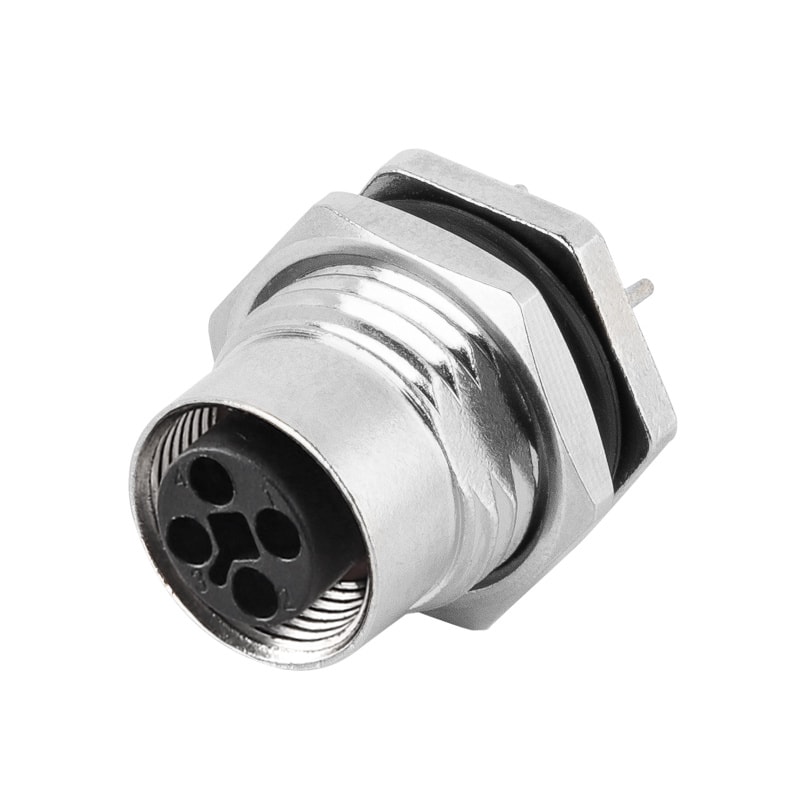

P/N: AM12F0322T001
M12 panel receptacle, female, contacts: 3,PCB dip-solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -
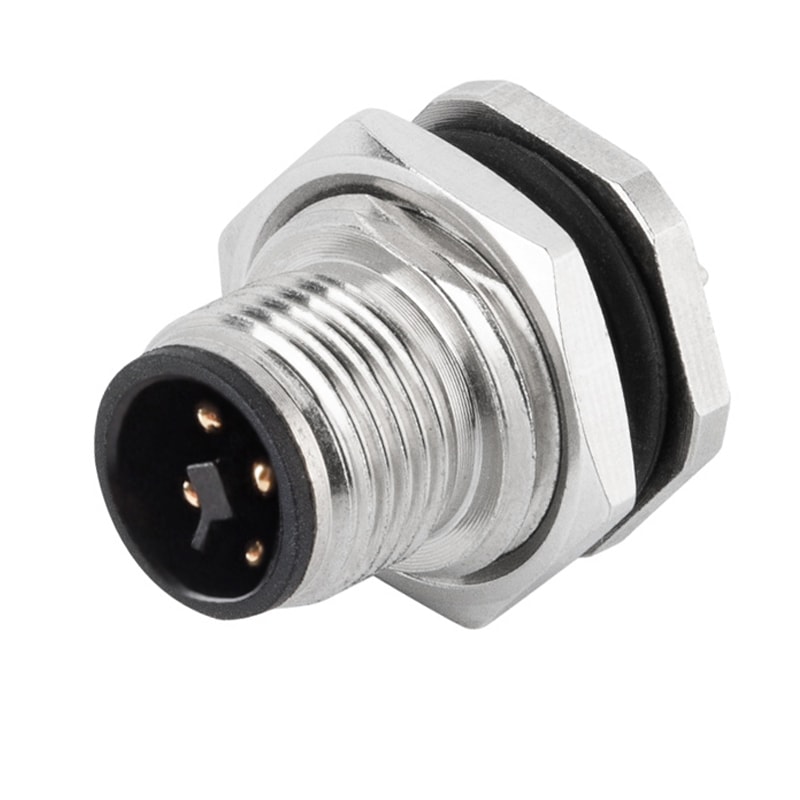

P/N: AM12M0322T001
M12 panel receptacle, male, contacts: 3,PCB dip-solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -
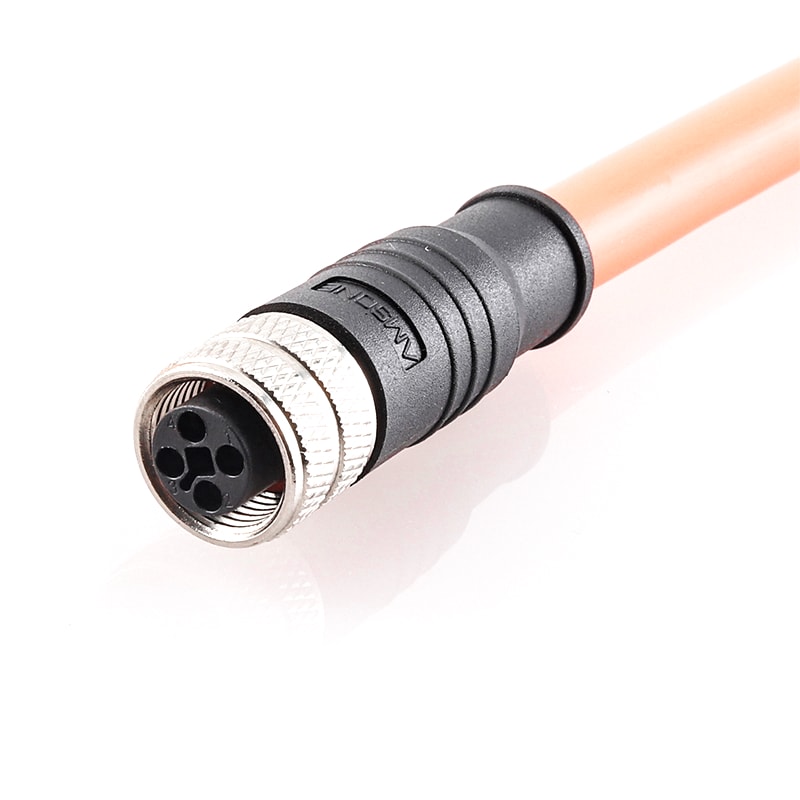

P/N: AM12F0311TXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts: 3,solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -
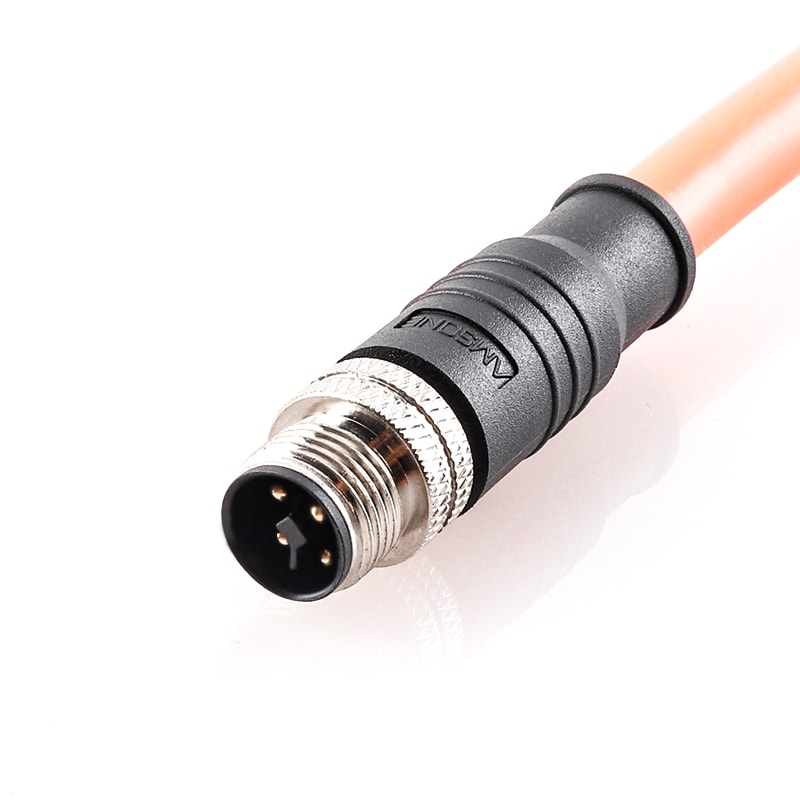

P/N: AM12M0311TXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:3, solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All
-
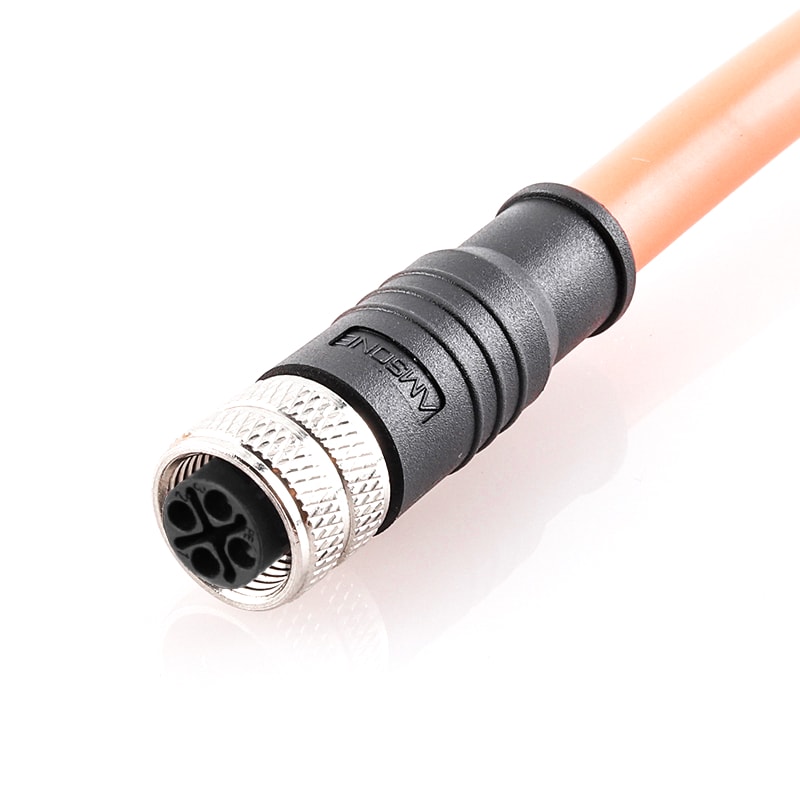

P/N: AM12F0411SXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4(3+PE), solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -
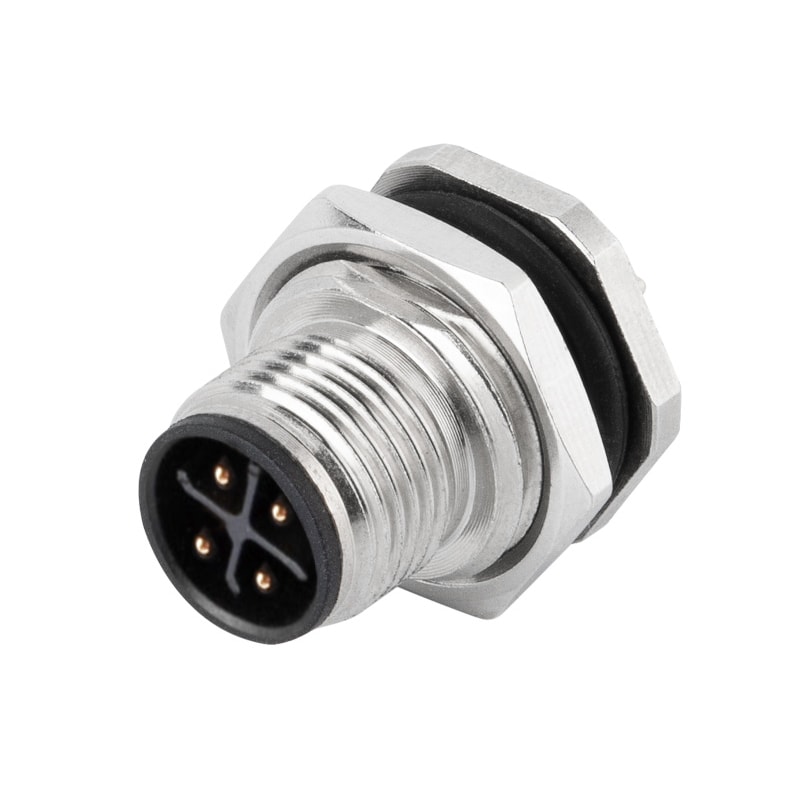

P/N: AM12M0322S001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:3(2+PE),PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0412S171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, S code, straight, IP67View All -
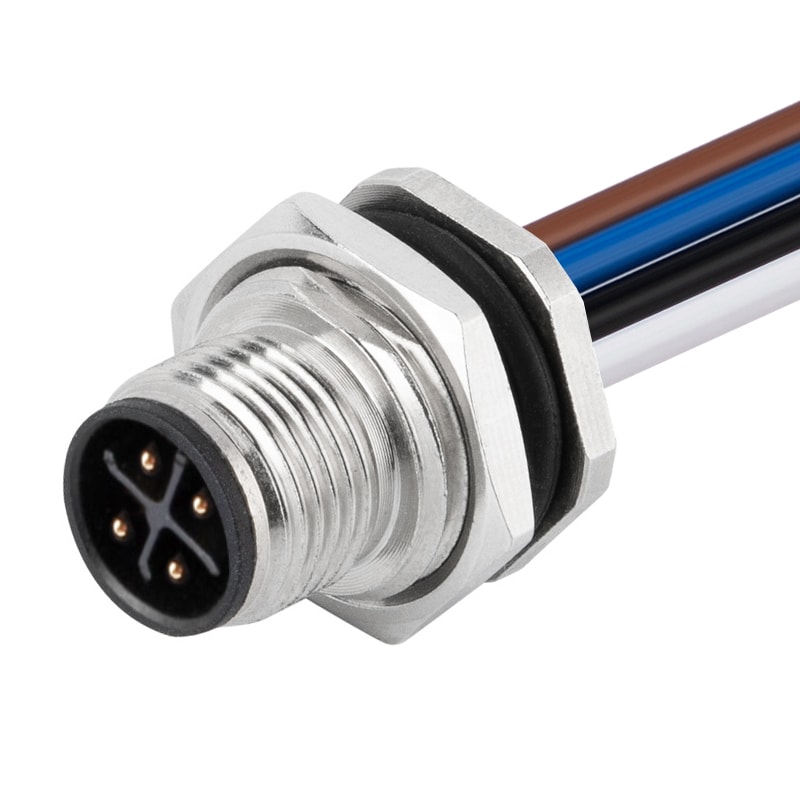

P/N: AM12M0412S171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, S code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0322S001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:3(2+PE),PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0422S001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:,4(3+PE), PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0311SXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:3(2+PE), solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0322S002
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:3(2+PE), PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All
-

P/N: AM12M0511Lxx1-xxx
M12 L Coded Power 5P Connector Male Drag Chain Pre-Molded CableView All -

P/N: AM12M0412L171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0522L001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:5, PCB dip-solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0411LXX2-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0411LXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:4, solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0322L001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:3, PCB dip-solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0422L001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4,PCB dip-solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0311LXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:3, solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All
-
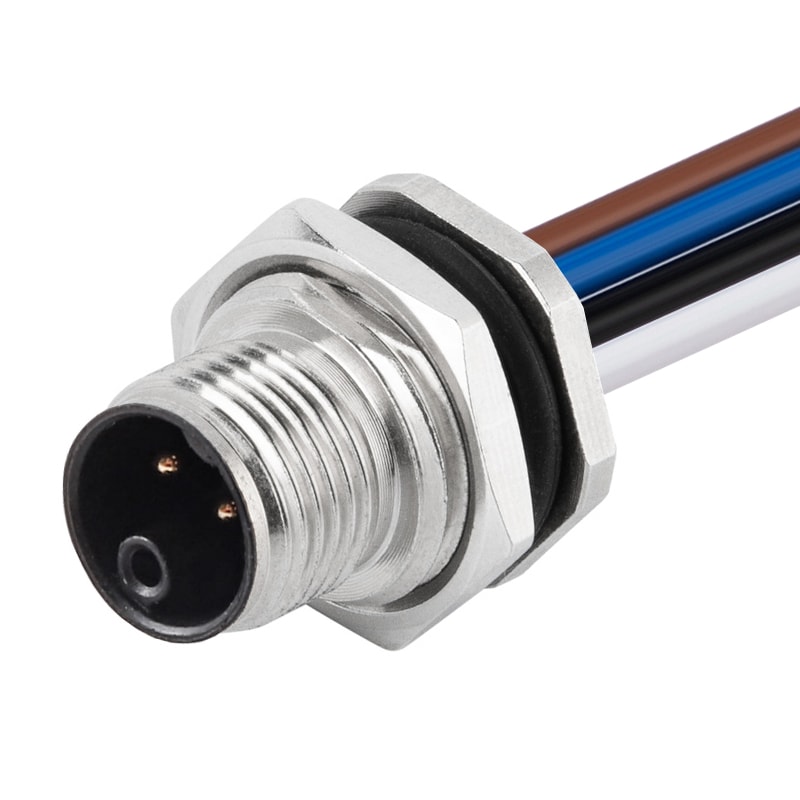

P/N: AM12M0312K171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:3,solder connection for wires, K code, straight, IP67View All -
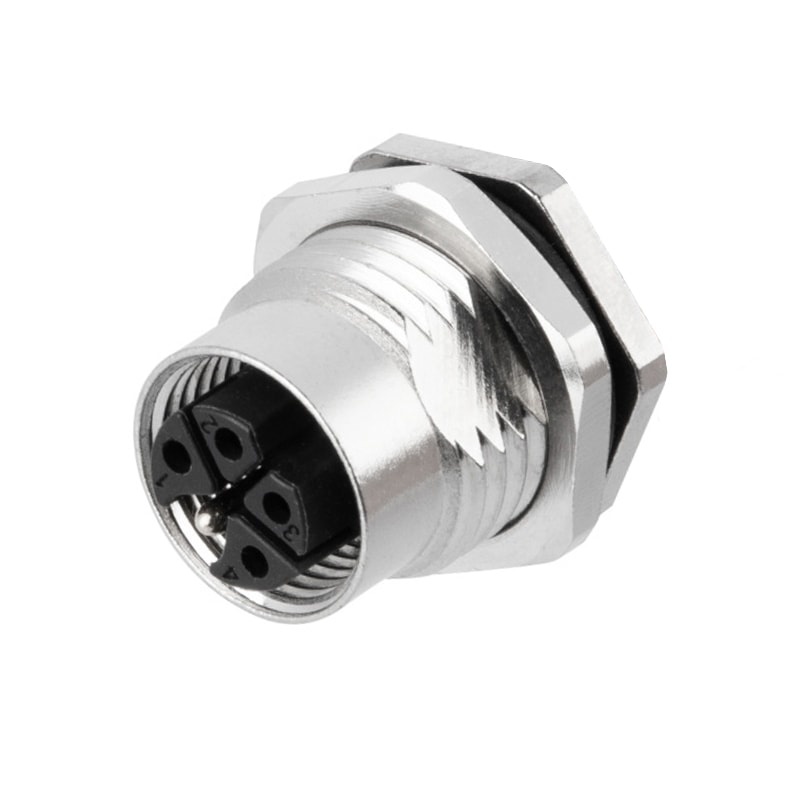

P/N: AM12F0522K001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:5, PCB dip-solder connection, K code, straight, IP67View All -
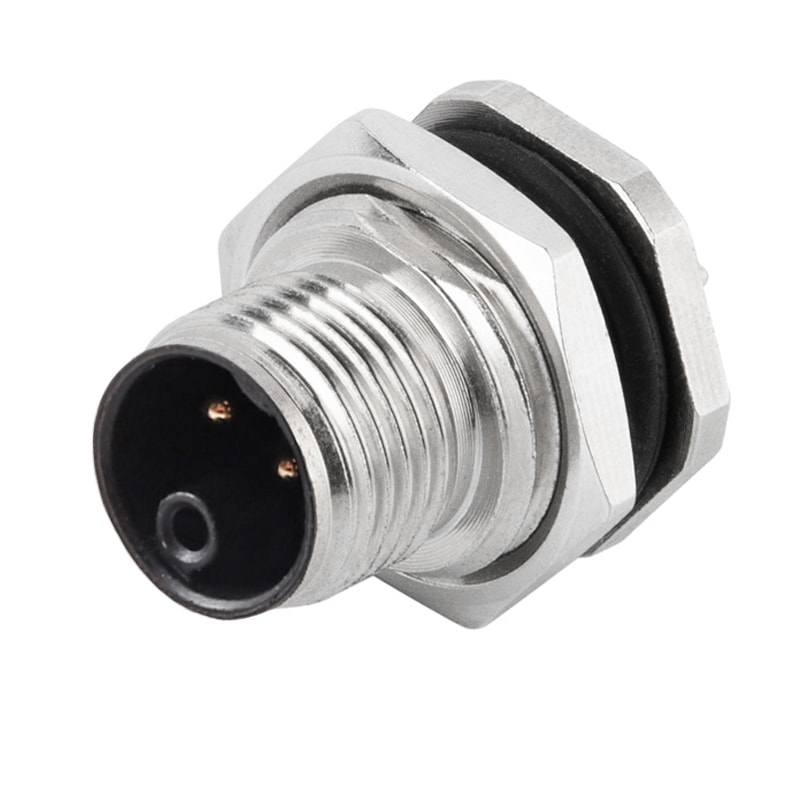

P/N: AM12M0522K001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:5,PCB dip-solderconnection, K code, straight, IP67View All -
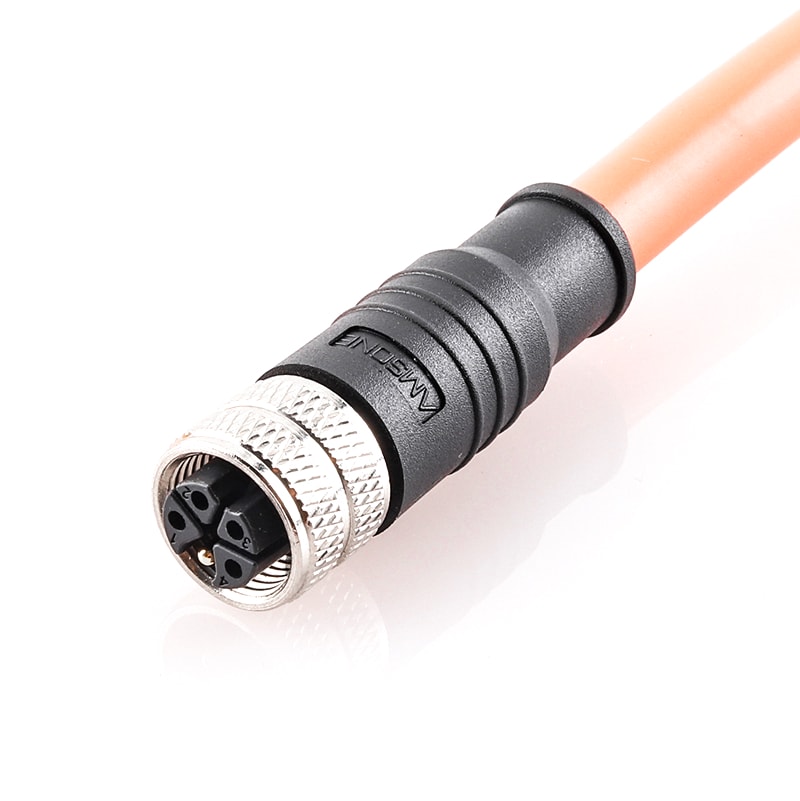

P/N: AM12F0311KXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:3, solder connection, K code, straight, IP67View All -
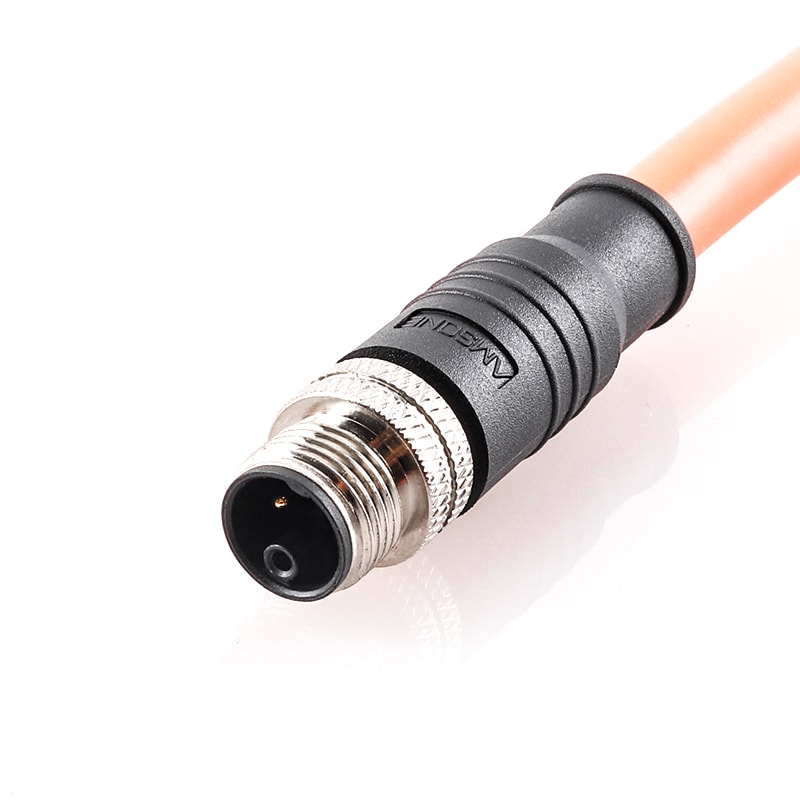

P/N: AM12M0311KXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:3, solder connection, K code, straight, IP67View All -
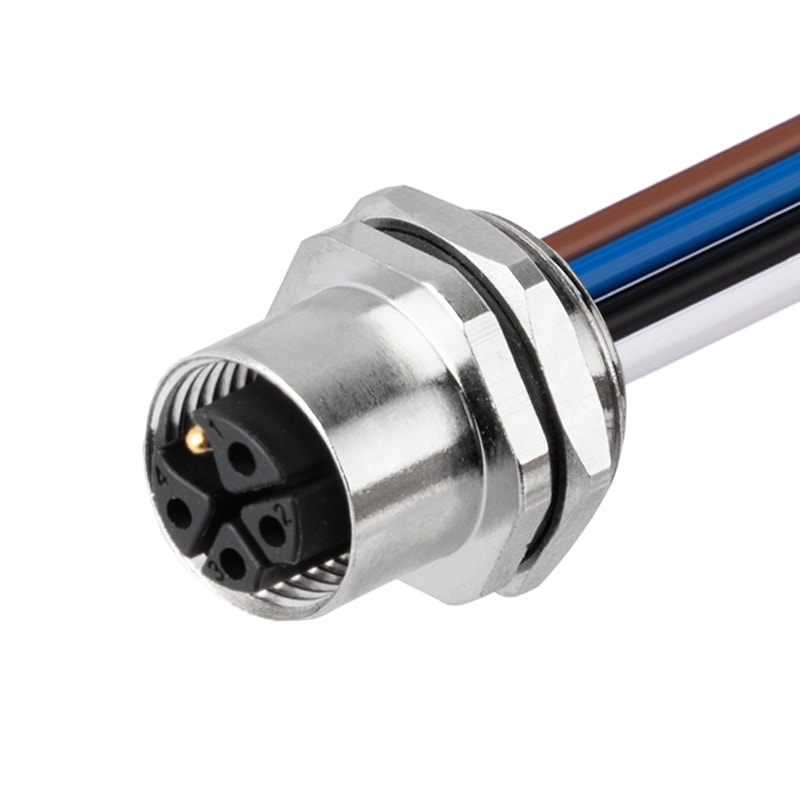

P/N: AM12F0513K371-005
M12 K Code 5P(4+PE) Female Panel Front Mount Receptacle ConnectorView All -
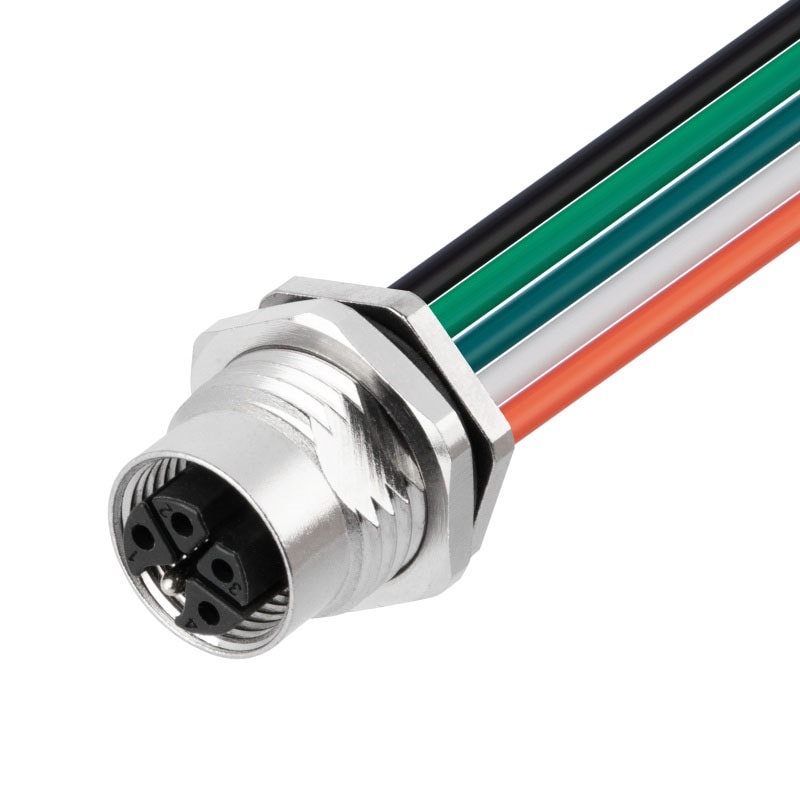

P/N: AM12F0312K171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:3, solder connection for wires, K code, straight, IP67View All
-
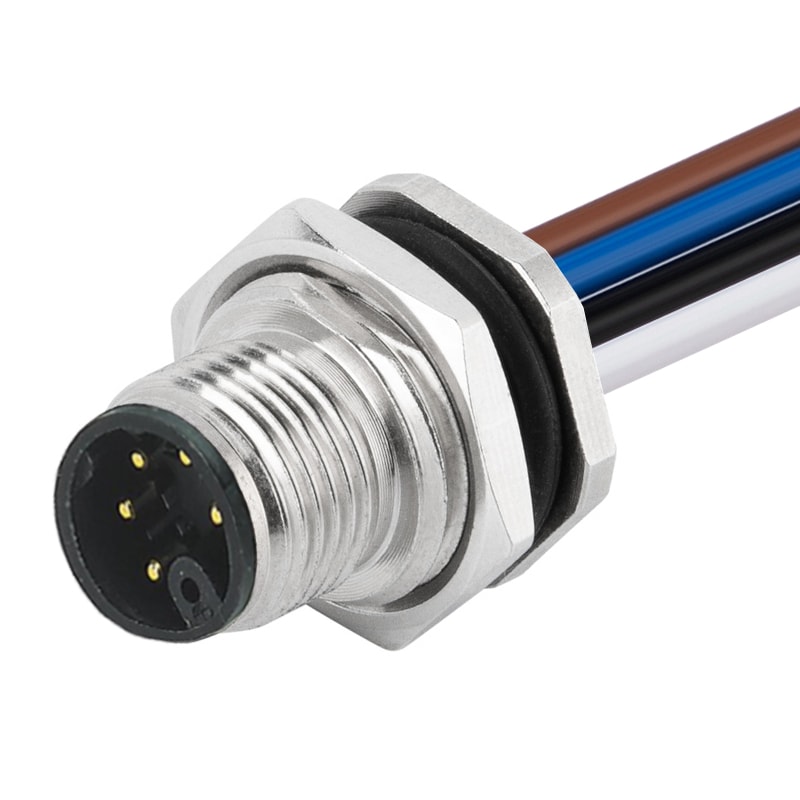

P/N: AM12M0512M371-XXX
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Male 5Pin Connector For WiresView All -
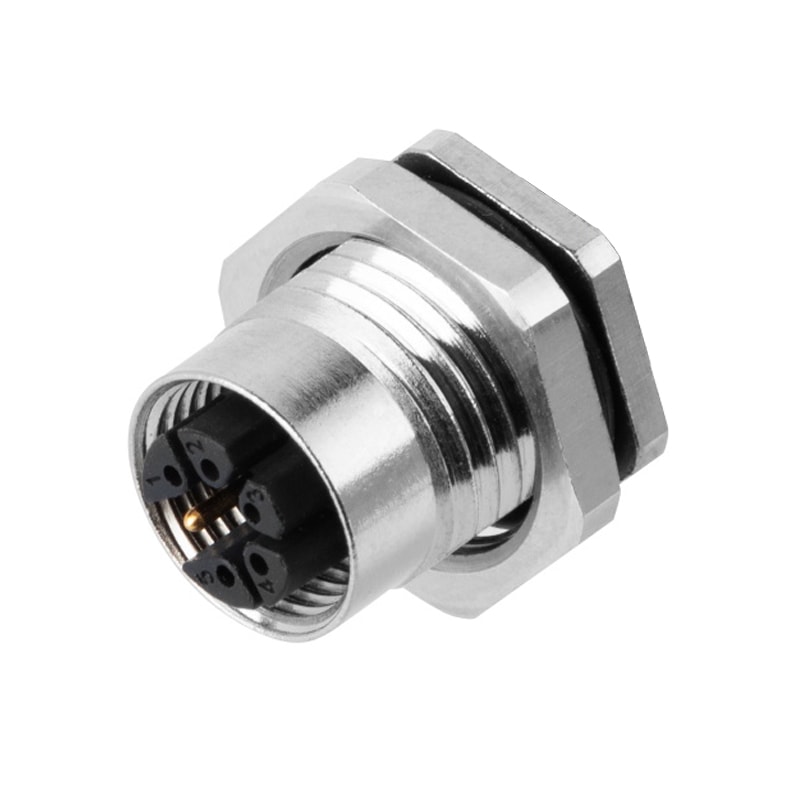

P/N: AM12F0322M001
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Female 3Pin PCB ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM12F0612M171-XXX
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Female 6Pin Connector For WiresView All -

P/N: AM12M0612M371-XXX
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Male 6Pin Connector For WiresView All -
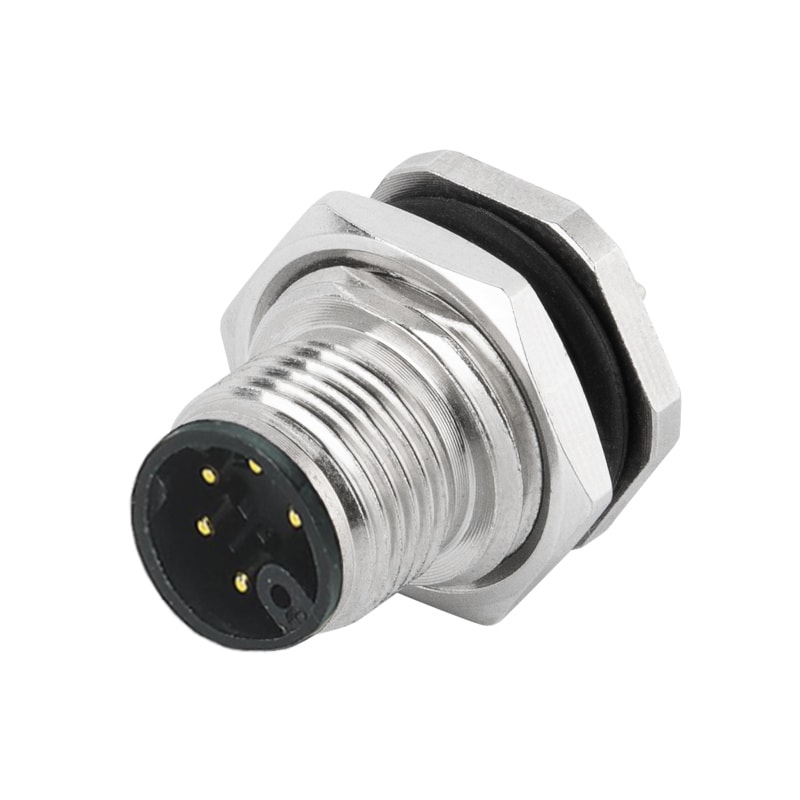

P/N: AM12M0522M001
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Male 5Pin PCB ConnectorView All -
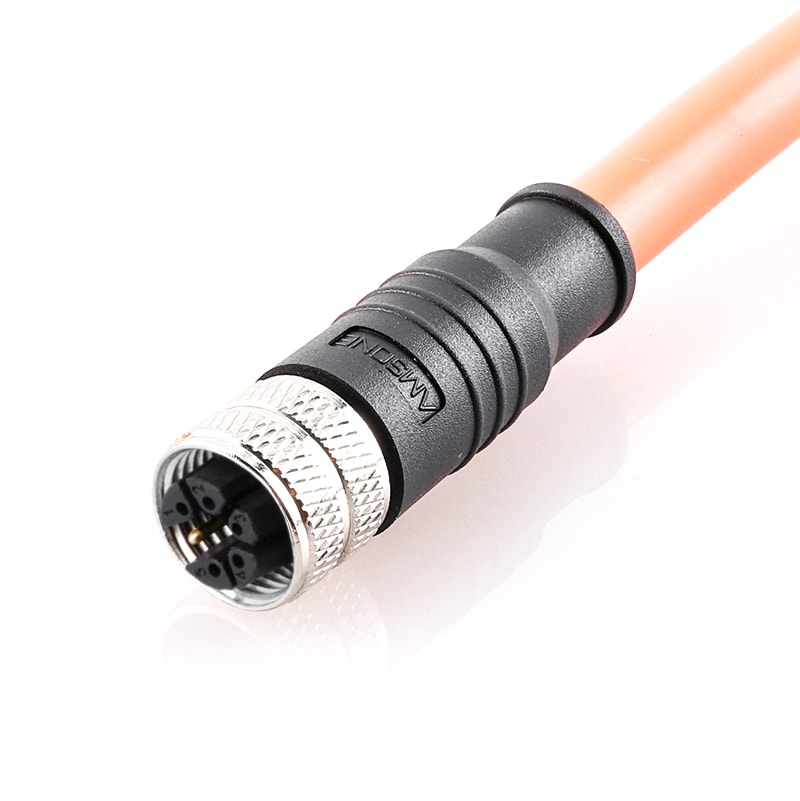

P/N: AM12F0611MXX1-XXX
M12 M Code 5+PE Pre-molded Cable 6Pin Female Straight ConnectorView All -
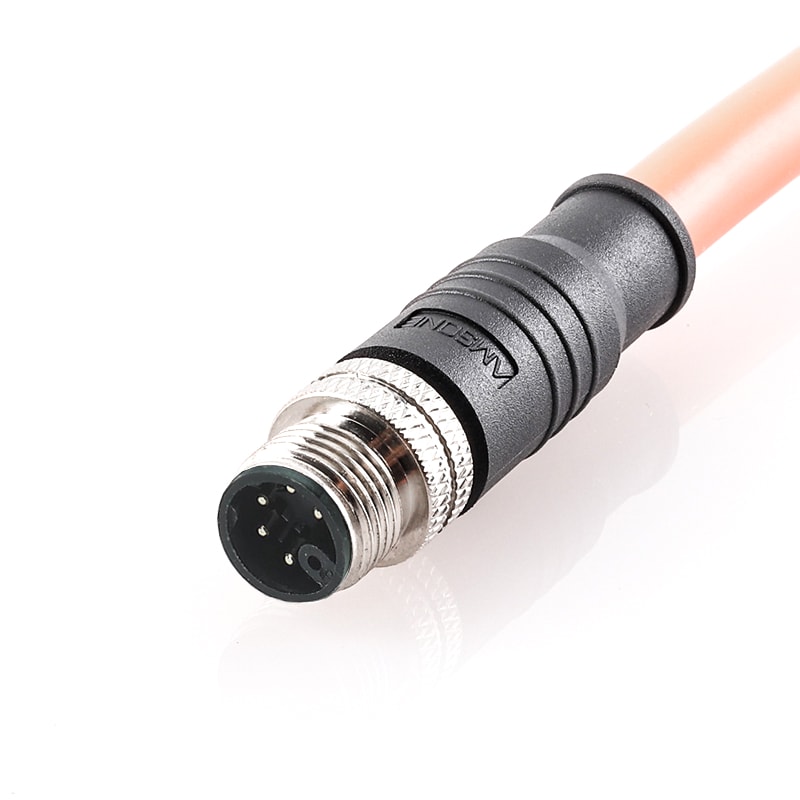

P/N: AM12M0611MXX1-XXX
M12 M Code 5+PE Pre-molded Cable 6Pin Male Straight ConnectorView All -
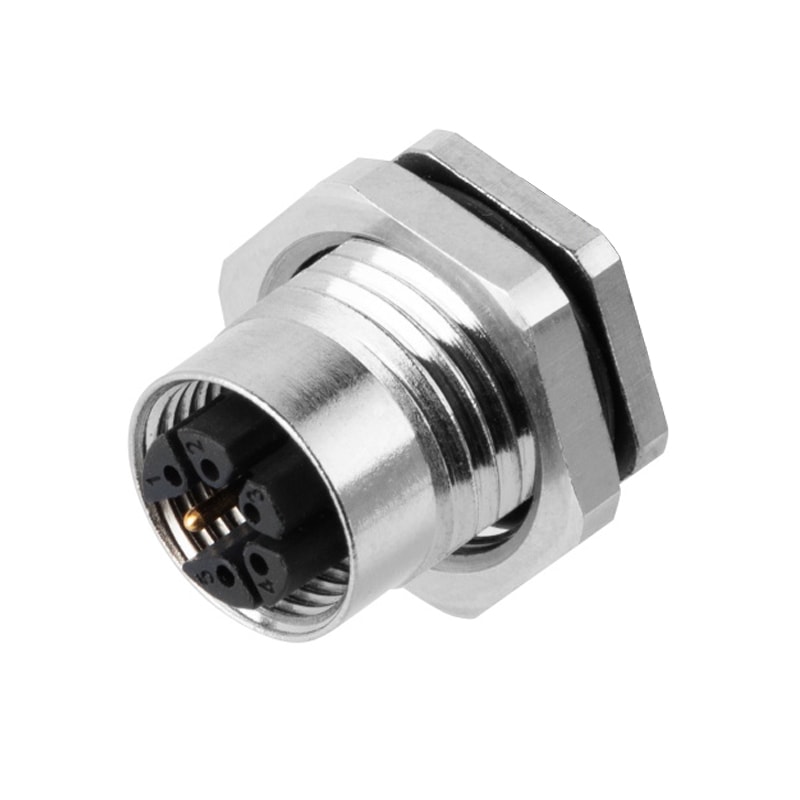

P/N: AM12F0522M001
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Female 5Pin PCB ConnectorView All
-
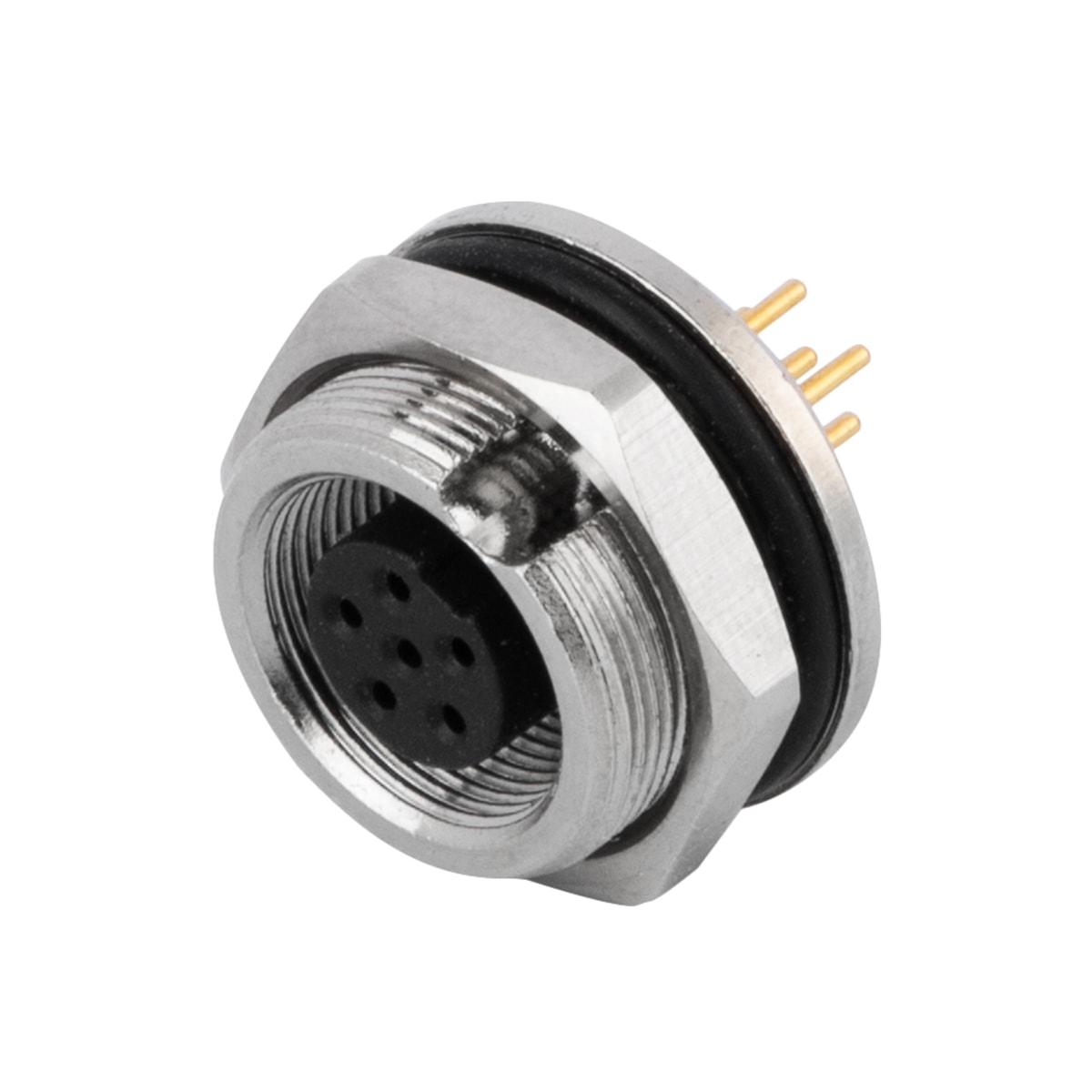

P/N: AM09F0522A001
M9 Connector Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female 5Pole PCB Dip-solderView All -
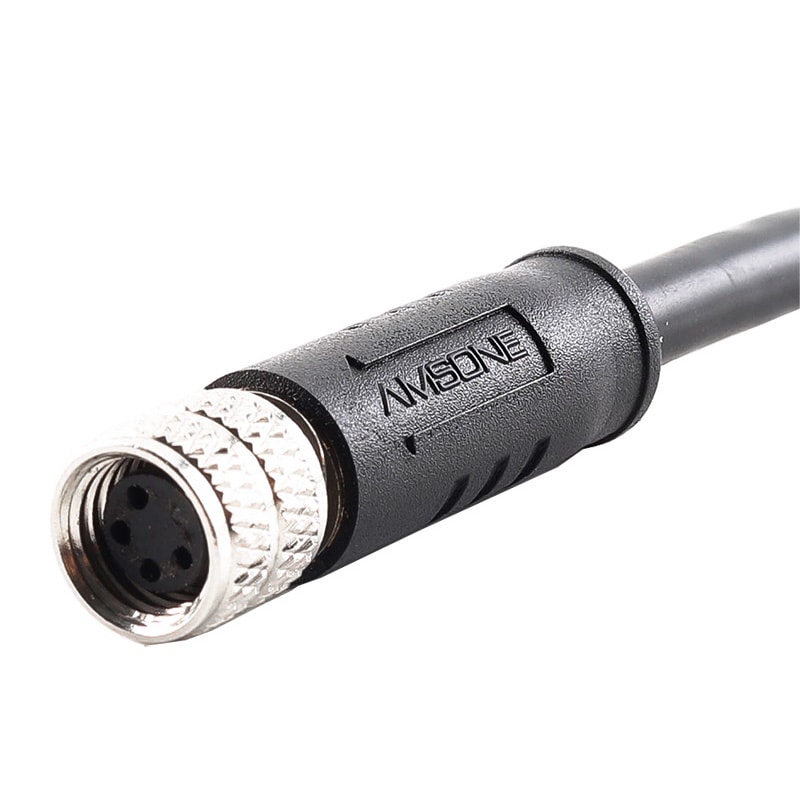

P/N: AM09F0411A001
M9 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM09F0311A001
M9 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts: 3, solder connection, straight, IP67View All -
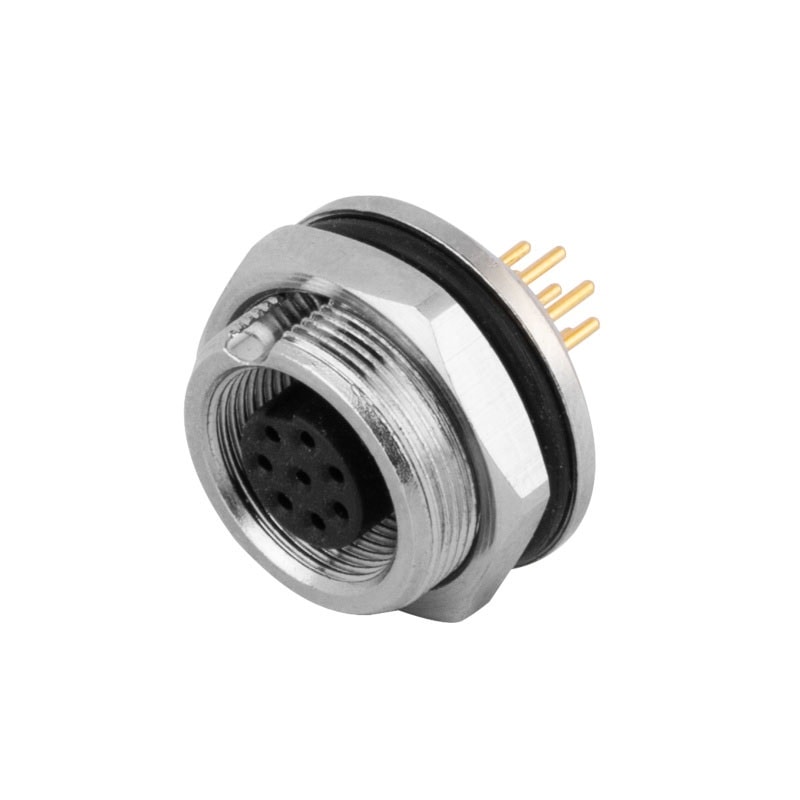

P/N: AM09F0822A001
M9 Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle 8Pin PCB Waterproof ConnectorView All -
P/N: AM09F0422A001
M9 4P Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle PCB Waterproof ConnectorView All -
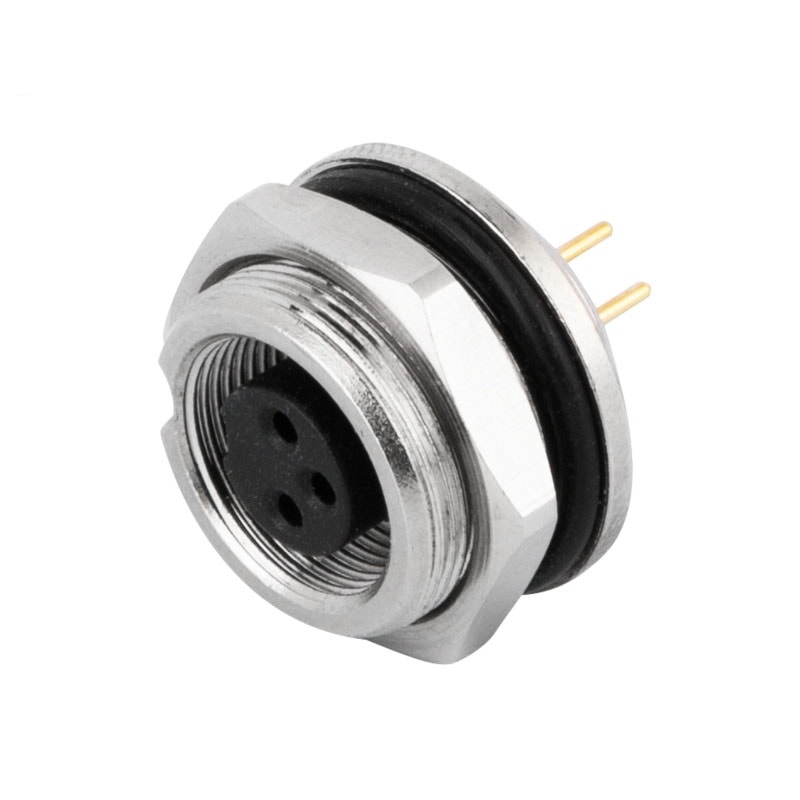

P/N: AM09F0322A001
M9 3Pole Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle PCB Waterproof ConnectorView All -
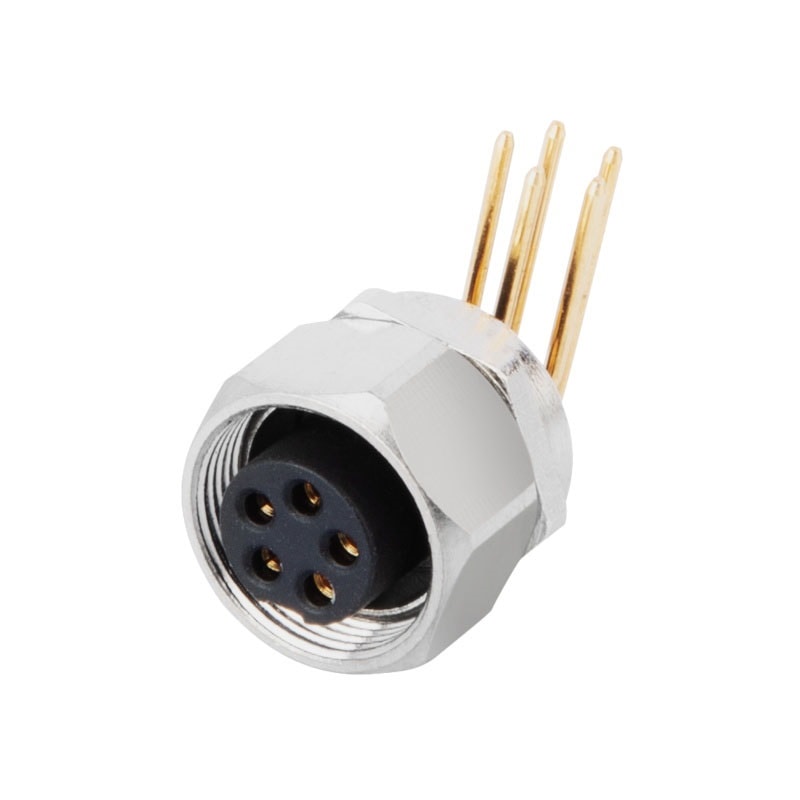

P/N: AM09F0522A201
M9 Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle 5Pin PCB Connector Right AngledView All
-
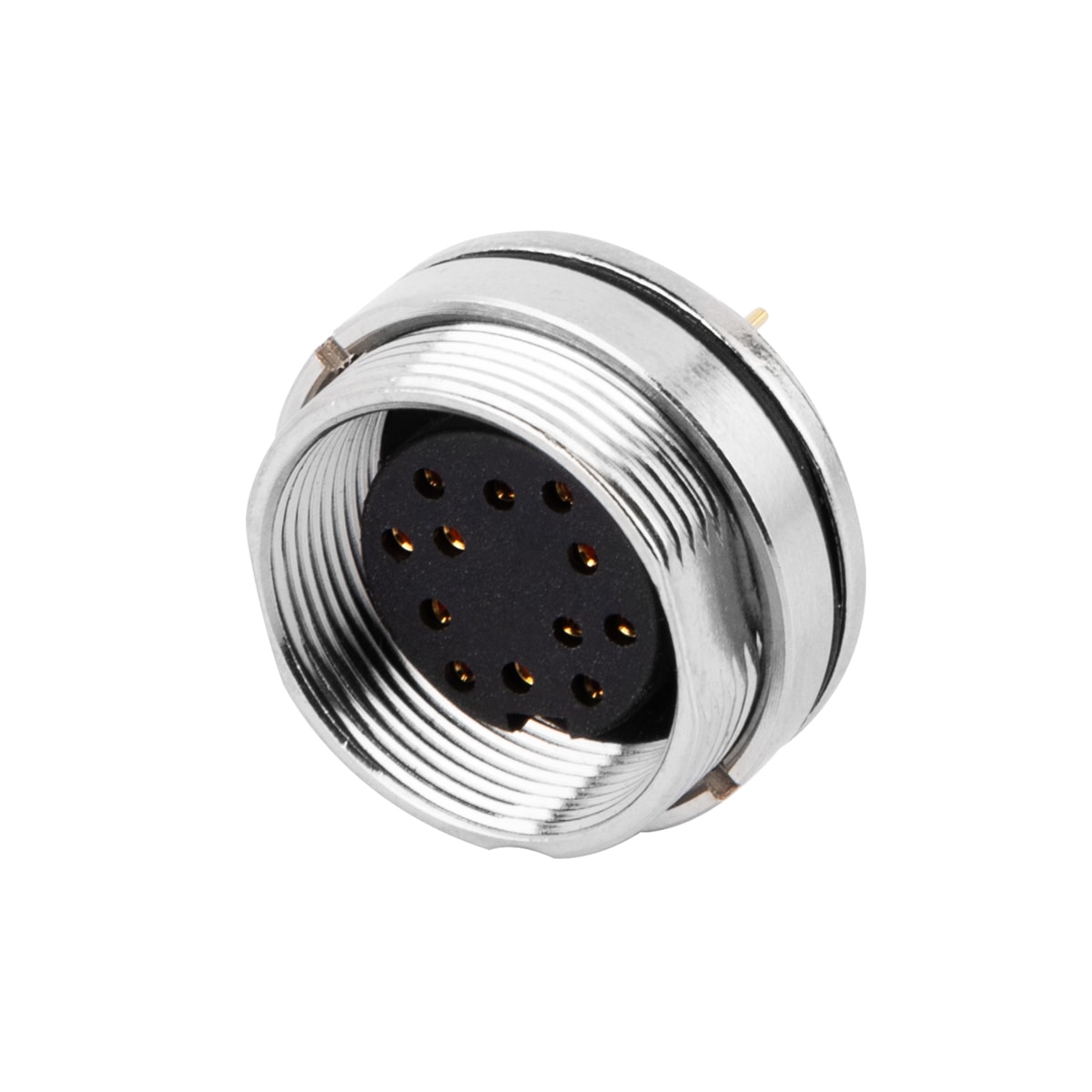

P/N: AM16F2422A001
M16 panel receptacle,rear mount,Female, contacts:24, PCB dip- solder connection,straight,IP67,UL certifiedView All -
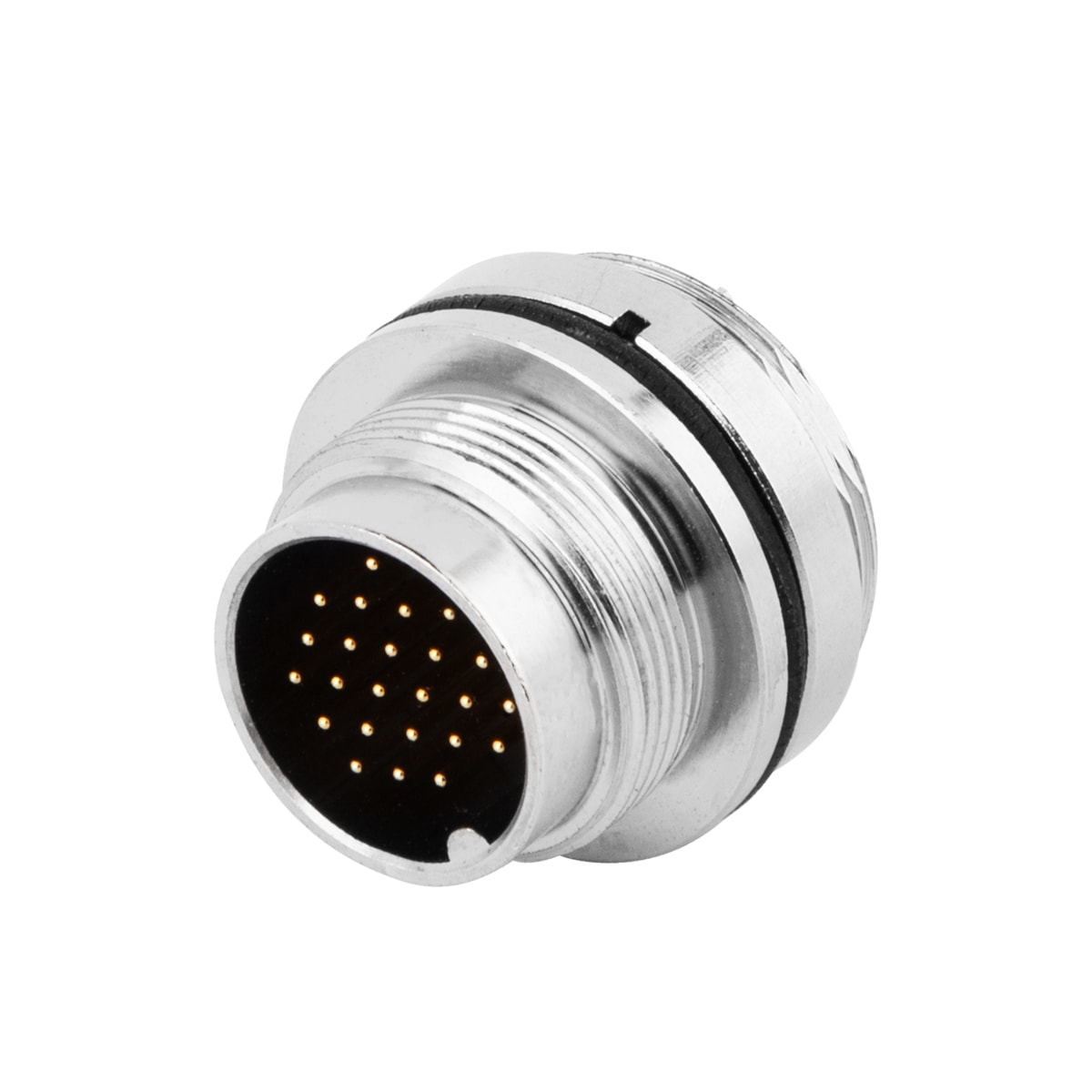

P/N: AM16M2422A001
M16 panel receptacle,rear mount,male, contacts:24, PCB dip- solder connection,straight,IP67,UL certifiedView All -
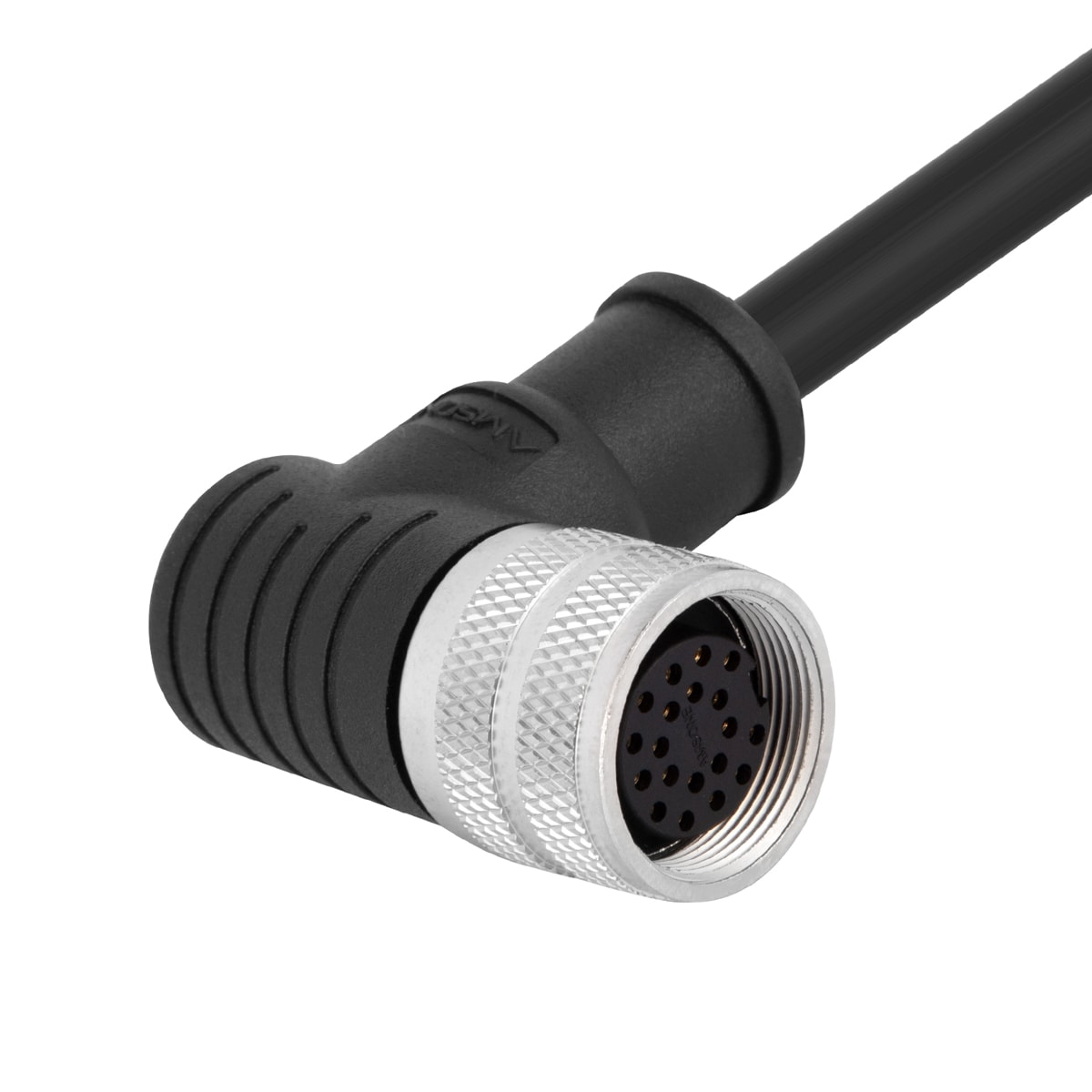

P/N: AM16F2411AXX2-XXX
M16 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:24, solder connection, right angled, IP67, shieldable, UL certifiedView All -
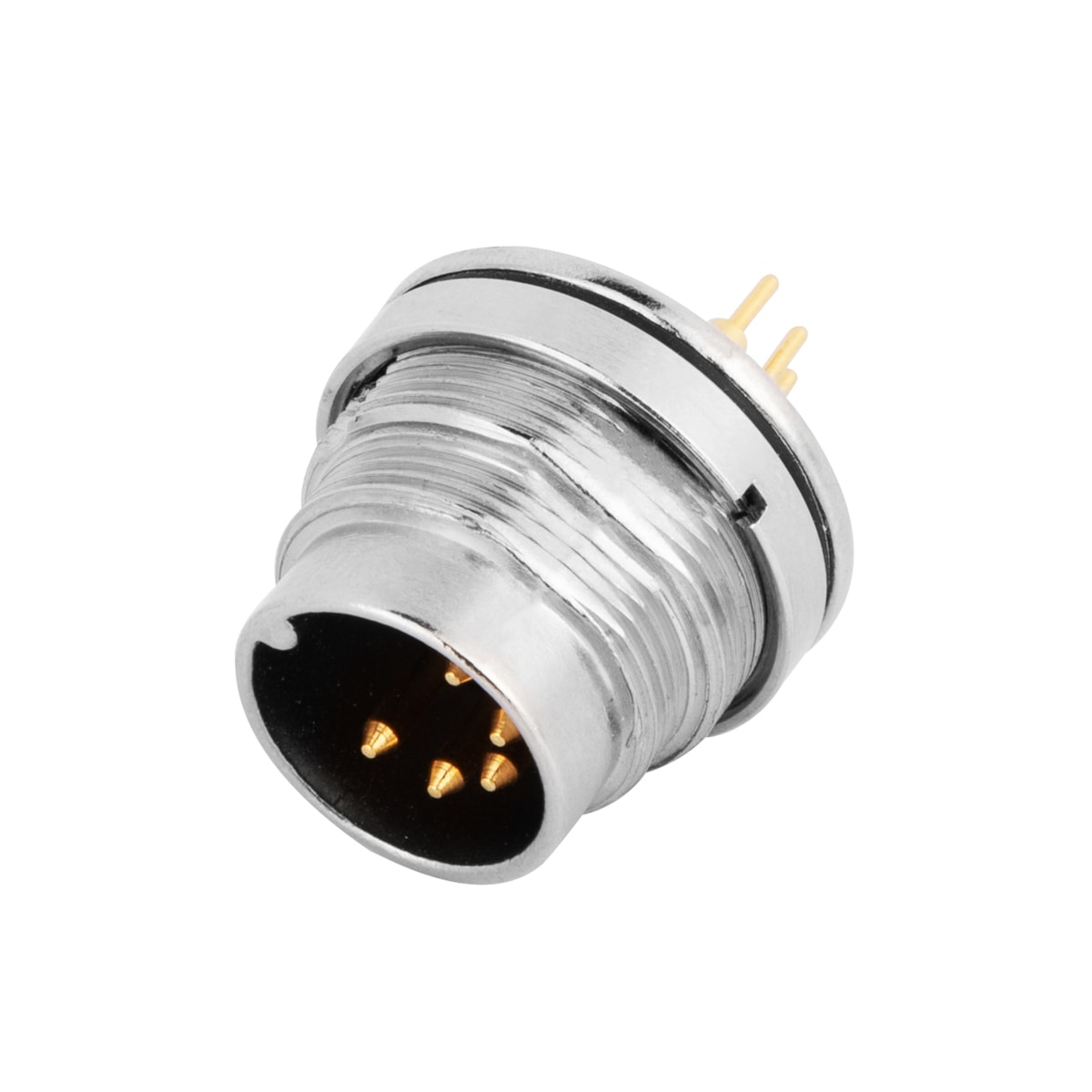

P/N: AM16M0522B001
M1M16 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:5, PCB dip-solderconnection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All -
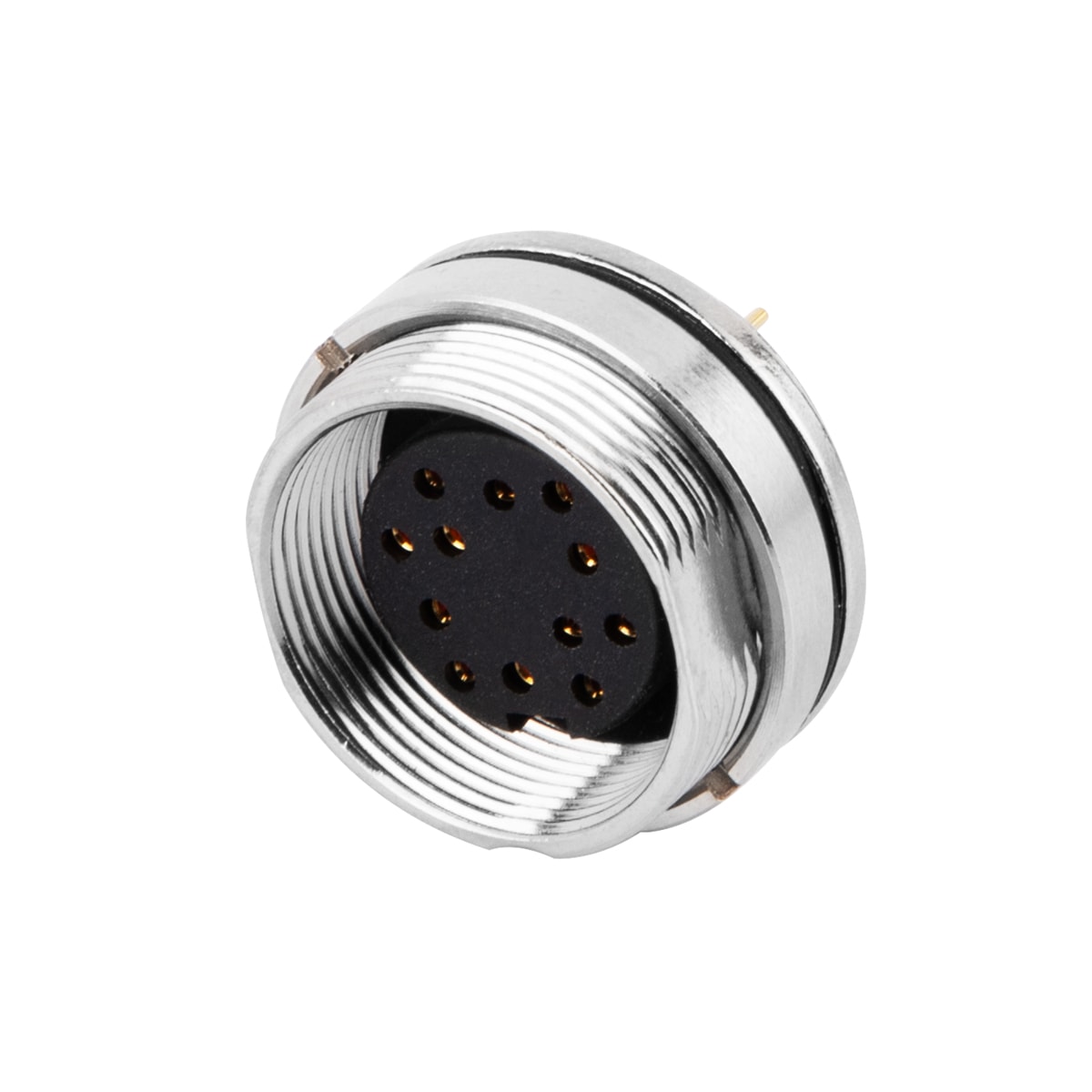

P/N: AM16F1222A001
M16 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:12,PCB connection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All -
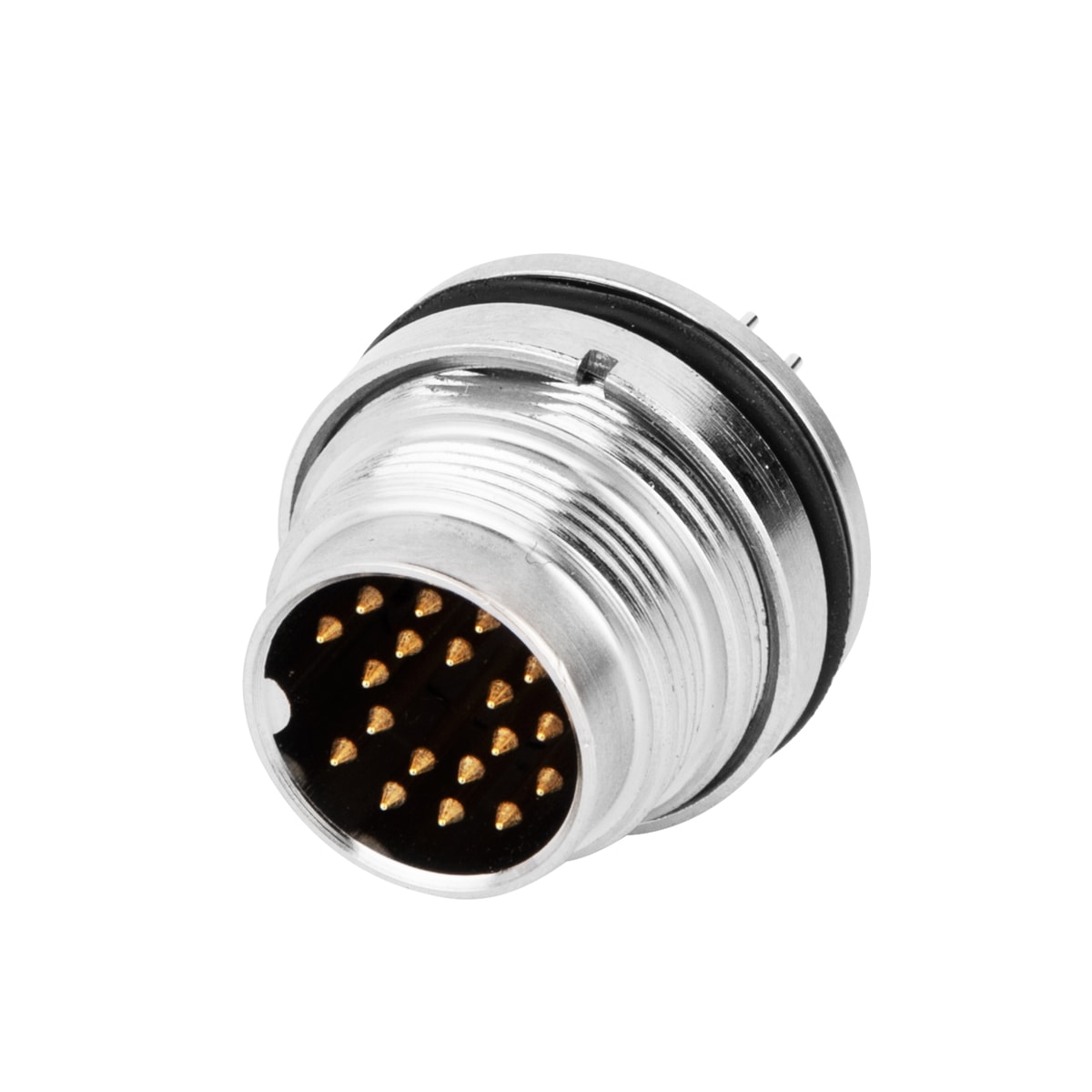

P/N: AM16M1222A001
M16 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:12,PCB dip-solder connection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All -

P/N: AM16M2411AXX1-XXX
M16 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:24, solder connection, straight, IP67, shieldableView All -
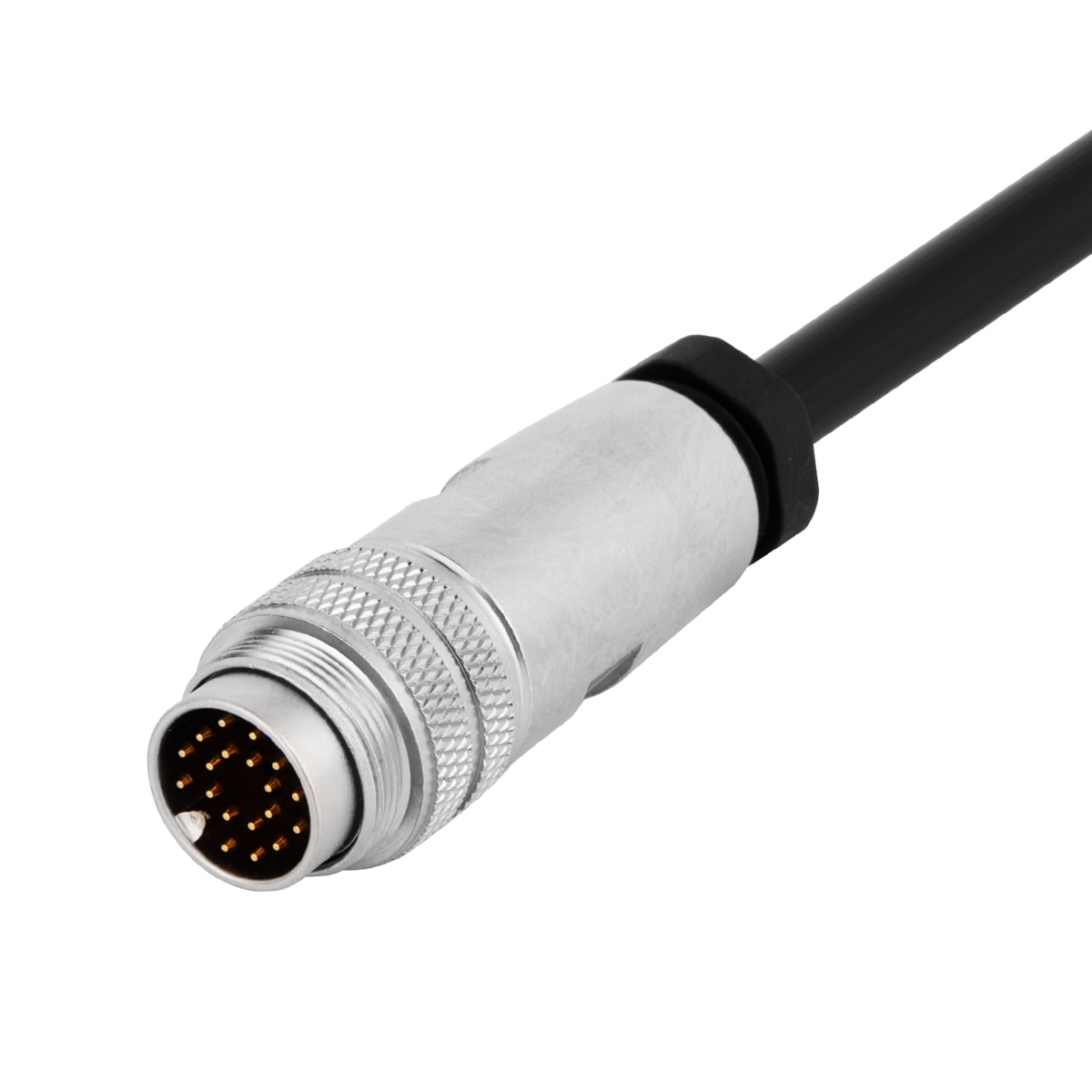

P/N: AM16M1214A001
M16 cable connector, male, contacts:12,field assembly type, solder connection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All
-
P/N: AM78F0511A162-010
MINI-Change 7/8View All -
P/N: AM78M0522A001
MINI-Change 7/8-16UNF Panel Rear Mount Receptacle Male 5Pin PCB ConnectorView All -
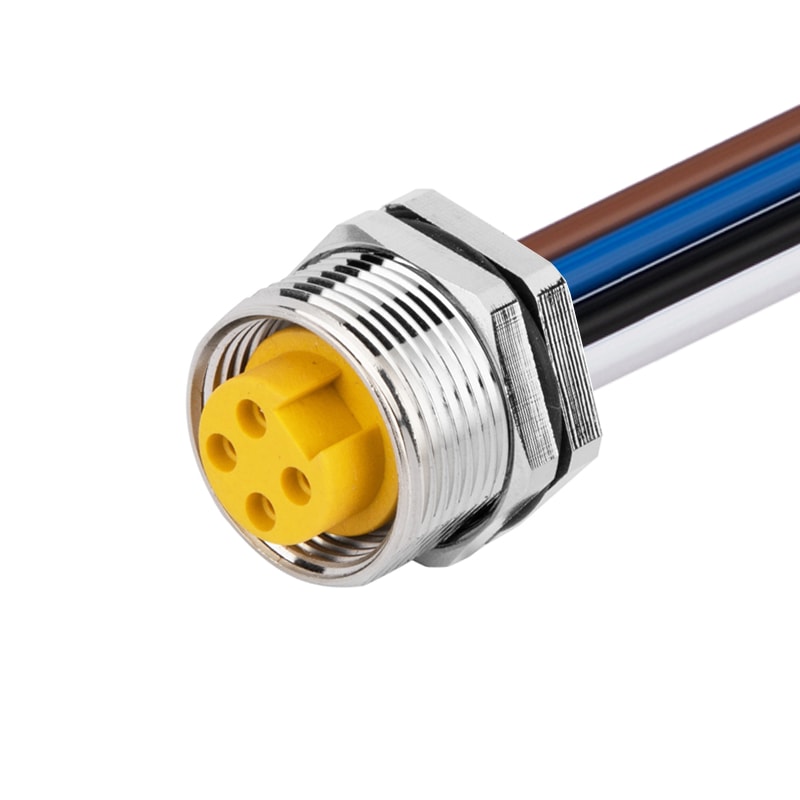

P/N: AM78F0412A371-050
7/8View All -
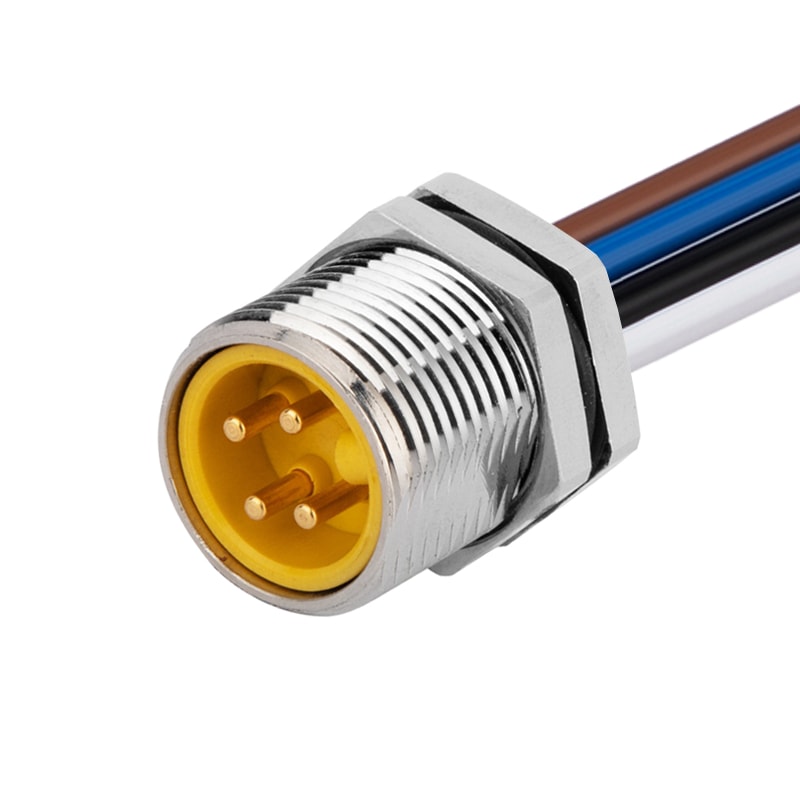

P/N: AM78M0412A371-050
7/8View All -
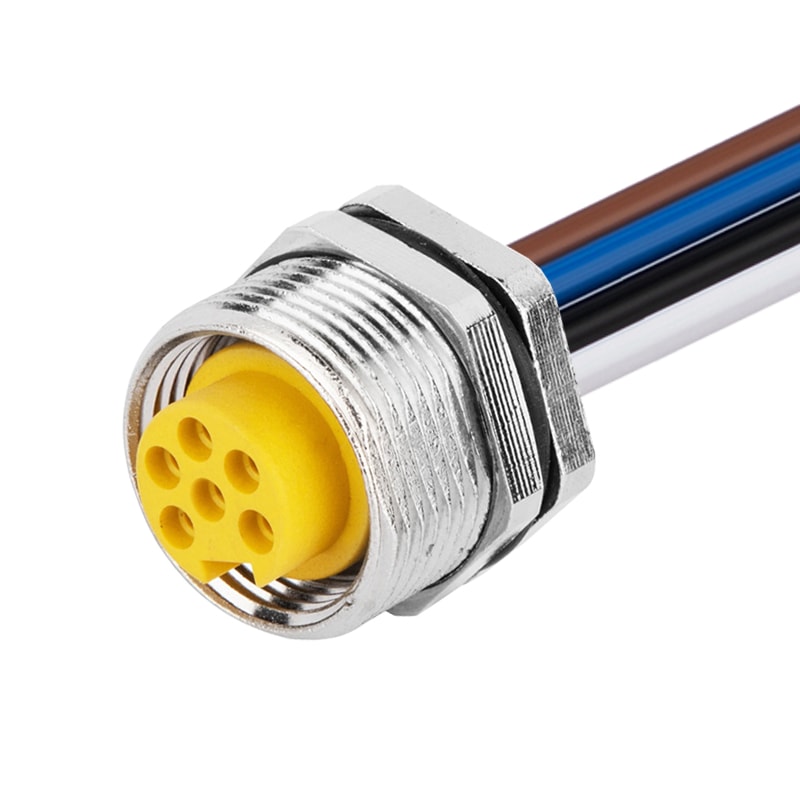

P/N: AM78F0512A371-050
7/8View All -
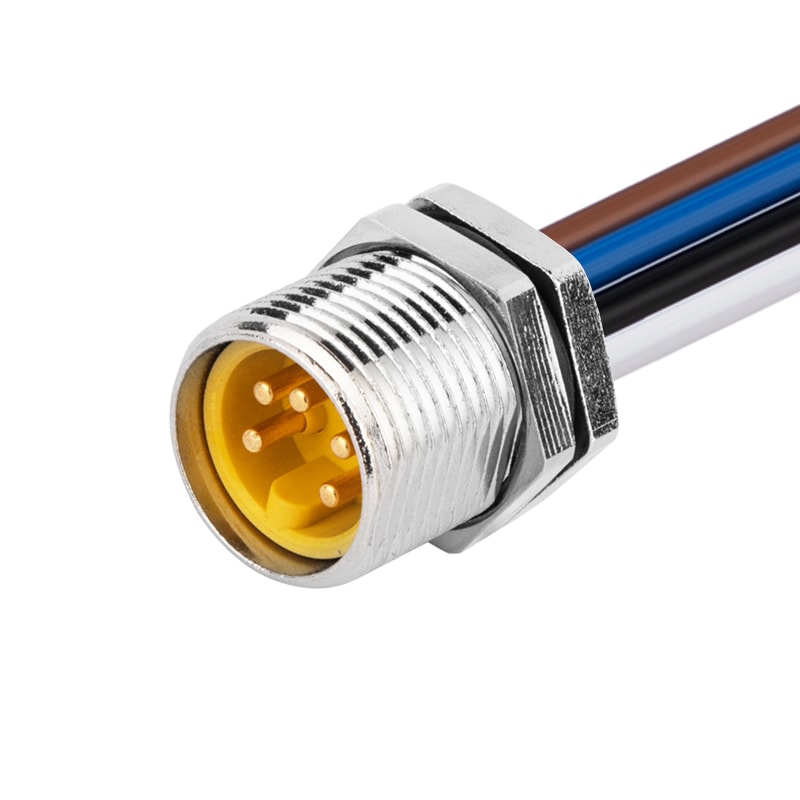

P/N: AM78M0512A371-050
7/8View All -
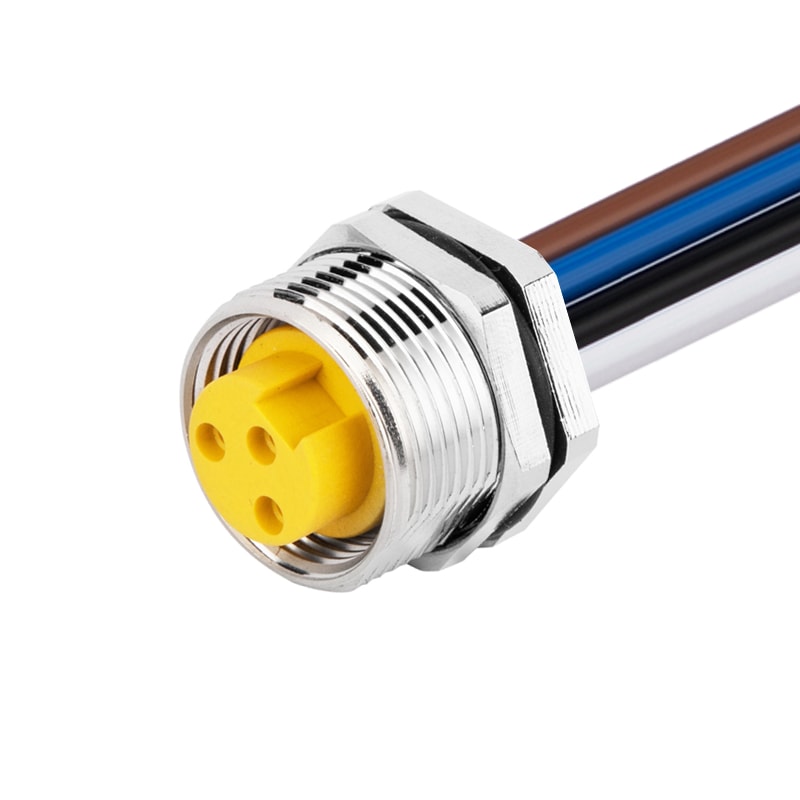

P/N: AM78F0312A371-050
7/8View All -
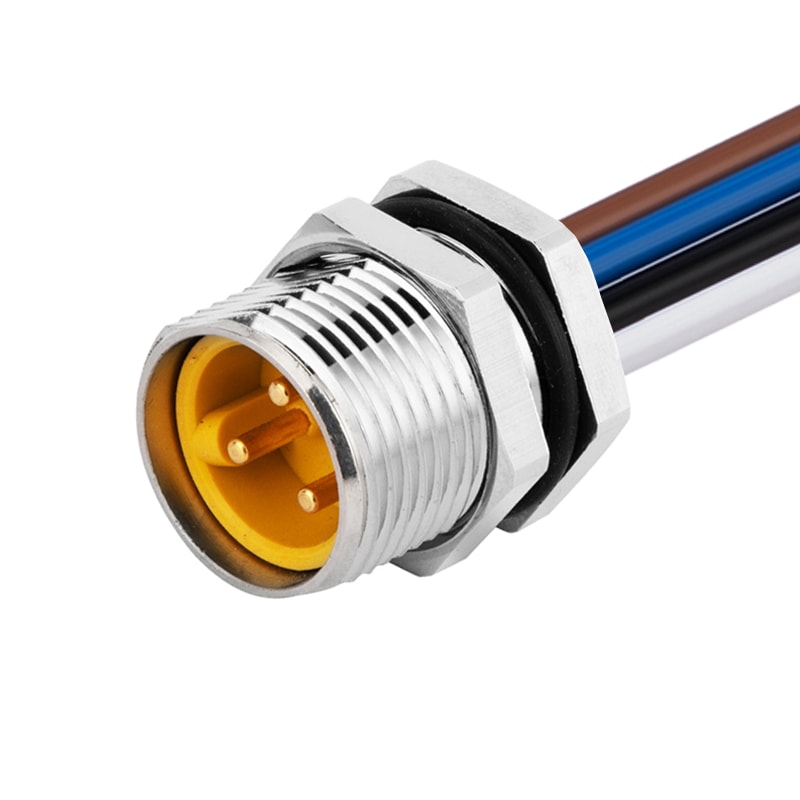

P/N: AM78M0312A371-050
7/8View All
-
P/N: AM23M1912A002
M23 Panel Receptacle Rear Mount Male 19P(16+3) Solder Connection For Wires Straight IP67View All -
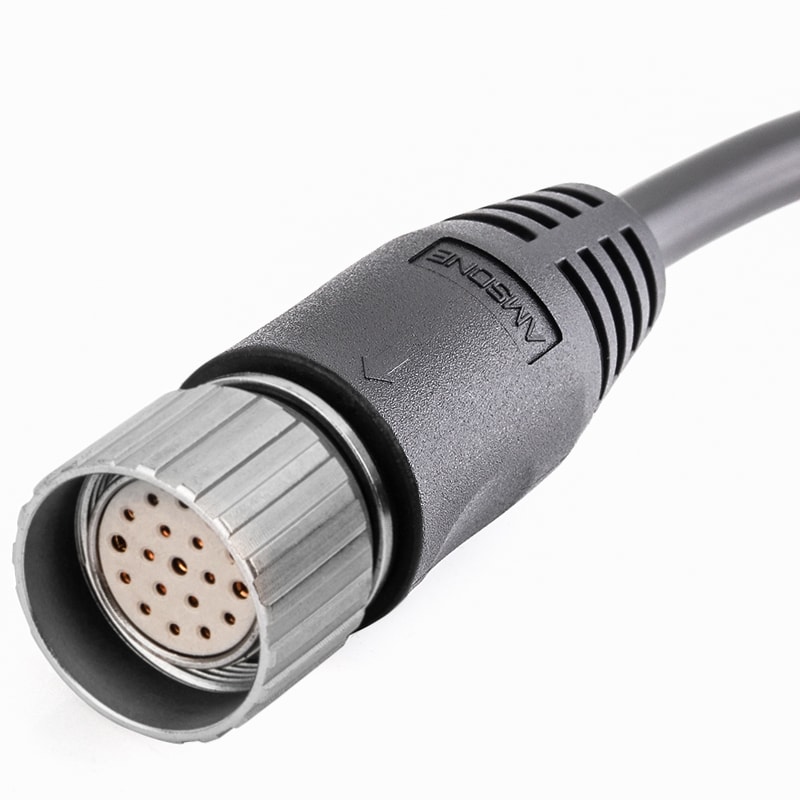

P/N: AM23F1911AXX1-XXX
M23 Pre-molded Cable Connector Female 19P(16+3) Solder Connection Straight IP67View All -
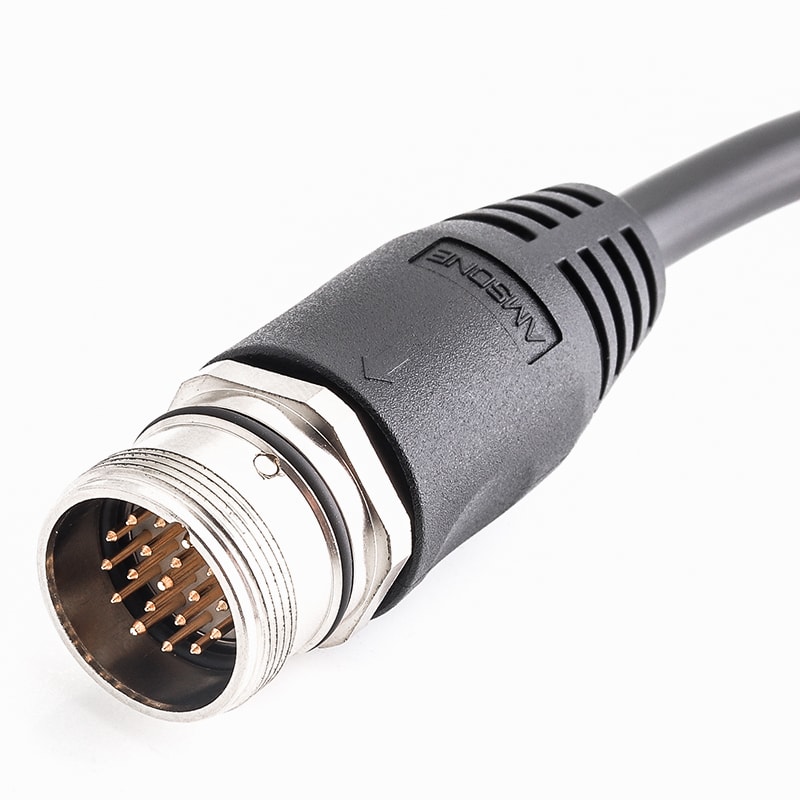

P/N: AM23M1911AXX1-XXX
M23 Pre-molded Cable Connector Male 19P(16+3) Solder Connection Straight IP67View All
-
P/N: BM24F0212A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 2P Receptacle Panel Mount Solder ConnectView All -
P/N: BM24M0214A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 2P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24M0314A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 3P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24F0312A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 3P Receptacle Panel Mount Solder ConnectView All -
P/N: BM24M0414A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 4P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24F0412A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 4P Receptacle Panel Mount Solder ConnectView All -
P/N: BM24M1214A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 12P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24F1222A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 12P Receptacle Panel Mount PCB ConnectView All
Industrial Cable Harnesses
-

P/N: AM12F0411D241-010
M12 4P D Code Pre-molded Cable Connector Female Straight IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0411D241-010
M12 pre-molded cable connector male solder connection D code straight IP67View All -
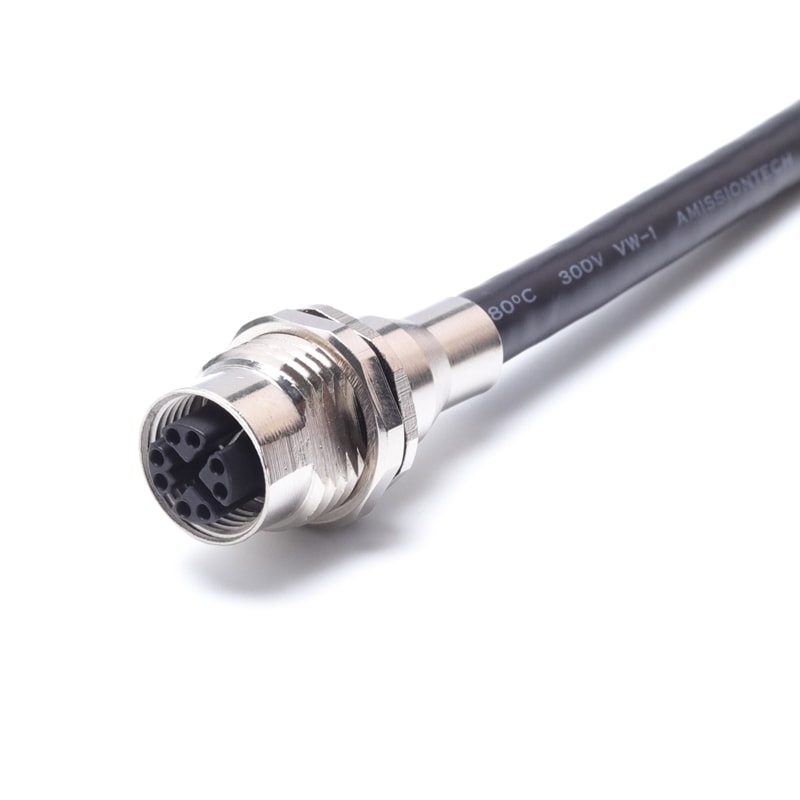

P/N: AM12F0812X003
M12 Device Connector X Code Female EMC Shielded Panel Rear Mount ReceptacleView All -
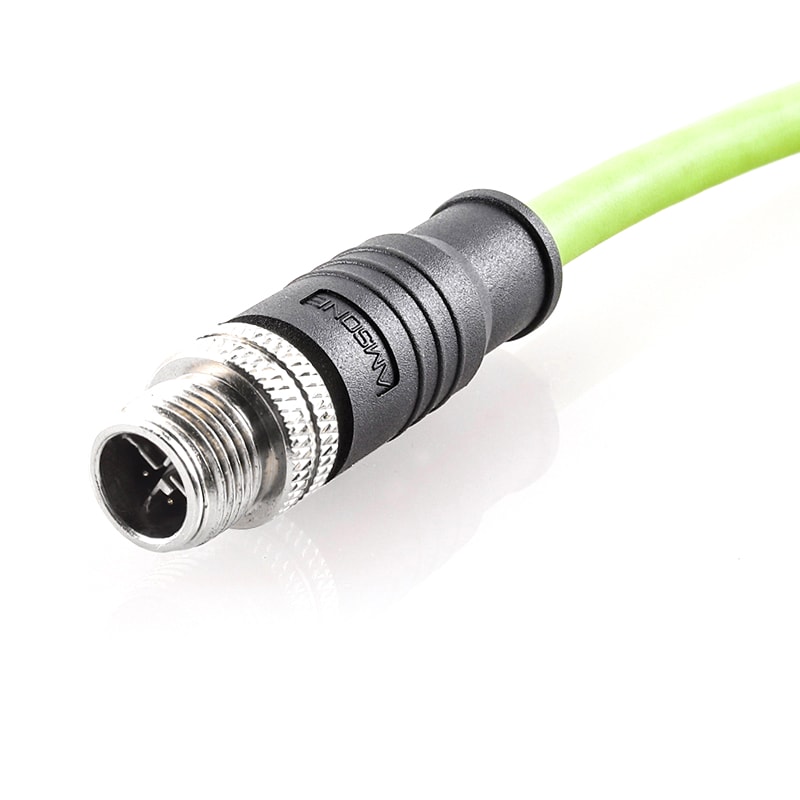

P/N: AM12M0811X231-030
M12 Pre-molded Cable Connector 8Pole Male X Code Cable StraightView All -
P/N: AM12F0411BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -
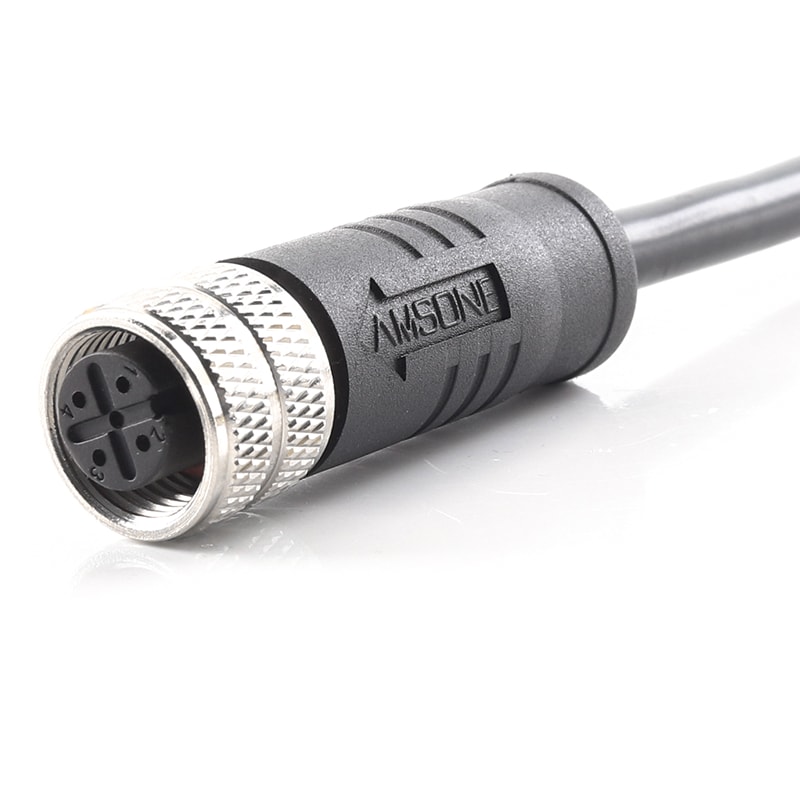

P/N: AM12F0511A241-010
M12 FieldBUS Cable Industrial Automation DeviceNet CanOpen CableView All -
P/N: EhterNet Cable
EhterNet Cable CAT5/CAT6/CAT7 PROFIBUS Industrial Network cableView All -

P/N: AM12M0814X221-010
M12 X Code Male ProfiNET/EtherNET Cable M12 Connector X CodedView All
-

P/N: AM12F0411D241-010
M12 4P D Code Pre-molded Cable Connector Female Straight IP67View All -

P/N: AM78M0411A272-050
DeviceNET 7/8View All -
P/N: AM12F0411BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0511A241-010
M12 FieldBUS Cable Industrial Automation DeviceNet CanOpen CableView All -

P/N: AM78M0511A172-030
MINI-Change 7/8View All
-

P/N: AM12M0411D241-010
M12 pre-molded cable connector male solder connection D code straight IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0812X003
M12 Device Connector X Code Female EMC Shielded Panel Rear Mount ReceptacleView All -

P/N: AM12M0811X231-030
M12 Pre-molded Cable Connector 8Pole Male X Code Cable StraightView All -
P/N: EhterNet Cable
EhterNet Cable CAT5/CAT6/CAT7 PROFIBUS Industrial Network cableView All -

P/N: AM12M0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Male,M12 Y-Coded Power Signal Ethernet CableView All -

P/N: AM12F0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Power Signal,M12 Y-Coded CablesView All -

P/N: AM12F0812Y003
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Panel Mount Shielded,M12 Y-CodedView All
-

P/N: AM78H0511A433-XXX
Electrical Automation Power Supply Connector Cable 7/8-16UNF Pre-molded H-SplitterView All -

P/N: AM12H0811AXX1-XXX
M12 A Code 8P/4P Connector Y-Splitter Industrial Automation Sensor CableView All -

P/N: AM08Y0411A001-000
M8 Y-Splitter Electrical Automation Sensor Connector AdapterView All
Underwater Connectors and Cables
-

P/N: RMK5F
RMK5F 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 And 8 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: MCDLS-F
MCDLS-F 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 8 contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: MCBH5MTI
MCBH5MTI 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 And 8 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: HPBH9M
HPBH9M 9 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: HF75 50CXBH6F
HF75 50CXBH6F 6 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: DMCIL13F M
DMCIL13F M 13 contacts Underwater cable connectorView All -

P/N: AWQ7-42
AWQ7-42 24, 28, 32, 36, 42 contacts Underwater cable connectorView All -

P/N: 1L25F M
1L25F M Circular 12, 16, 25 Contacts Underwater ConnectorView All
company
News
-
 Amissiontech to Showcase Smart Interconnection Solutions at SPS 2025 in NurembergView All
Amissiontech to Showcase Smart Interconnection Solutions at SPS 2025 in NurembergView All -
 2025 Tokyo International Manufacturing Expo: A Perfect ConclusionView All
2025 Tokyo International Manufacturing Expo: A Perfect ConclusionView All -
 Amissiontech to Showcase Advanced Industrial Connectors and I/O Solutions at Manufacturing World Japan 2025View All
Amissiontech to Showcase Advanced Industrial Connectors and I/O Solutions at Manufacturing World Japan 2025View All -
 Amissiontech Reflects on a Successful Participation at ProPak China 2025View All
Amissiontech Reflects on a Successful Participation at ProPak China 2025View All -
 Amissiontech Team-Building Activity at Hailing IslandView All
Amissiontech Team-Building Activity at Hailing IslandView All -
 Dragon Boat Festival Greetings: Celebrating Tradition with AmissiontechView All
Dragon Boat Festival Greetings: Celebrating Tradition with AmissiontechView All -
 Celebrating Women at Amissiontech on International Women’s DayView All
Celebrating Women at Amissiontech on International Women’s DayView All -
 Amissiontech Invites You to HANNOVER MESSE 2025View All
Amissiontech Invites You to HANNOVER MESSE 2025View All
-
 Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All
Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All -
 What is an M12 A coded connector?View All
What is an M12 A coded connector?View All -
 What Do You Know M12 B Coded?View All
What Do You Know M12 B Coded?View All -
 Revolutionizing Field I/O Signal Transmission with Amissiontech's IO-Link HUBView All
Revolutionizing Field I/O Signal Transmission with Amissiontech's IO-Link HUBView All -
 Exploring the Technology Behind Underwater Connectors and CablesView All
Exploring the Technology Behind Underwater Connectors and CablesView All -
 Amissiontech's IO-LINK Modules Shine at HANNOVER MESSE 2024View All
Amissiontech's IO-LINK Modules Shine at HANNOVER MESSE 2024View All -
 Circular ConnectorView All
Circular ConnectorView All -
 IO-Link Module - Connects Future Digital CommunicationsView All
IO-Link Module - Connects Future Digital CommunicationsView All
-
 Understanding Ethernet MHz Speed and Its Impact on Network PerformanceView All
Understanding Ethernet MHz Speed and Its Impact on Network PerformanceView All -
 Top 10 Cable Types and Their UsesView All
Top 10 Cable Types and Their UsesView All -
 HDMI vs VGA: Understanding the Key Differences for Industrial & Custom Cable ApplicationsView All
HDMI vs VGA: Understanding the Key Differences for Industrial & Custom Cable ApplicationsView All -
 Complete Guide to Ethernet Cable CategoriesView All
Complete Guide to Ethernet Cable CategoriesView All -
 Wire Harness Production ExplainedView All
Wire Harness Production ExplainedView All -
 Industrial HDMI Shielded Cable Technology InterpretationView All
Industrial HDMI Shielded Cable Technology InterpretationView All -
 Revolutionize Automation with DeviceNet-Compatible ToolsView All
Revolutionize Automation with DeviceNet-Compatible ToolsView All -
 Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All
Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All
Industries and Solutions
Solutions
Industries
News And Events
Cat6 vs Cat7: Understanding the Differences in Ethernet Cables
When selecting the right Ethernet cable, it's crucial to understand the differences between Cat6 and Cat7. Whether for a home network or a business environment, both types of cables have their own advantages and suitable applications. This article will delve into the features of Cat6 and Cat7, helping you make an informed decision based on your needs.
Basics of Cat6 and Cat7
Cat6 Cable
Cat6 (Category 6) cable is an advanced option compared to the older Cat5 cable. It consists of four pairs of twisted copper wires designed to reduce crosstalk and interference, supporting higher transmission speeds. Key features of Cat6 cables include:
Speed: Supports speeds of up to 10 Gbps over short distances (up to 55 meters); for lengths of up to 100 meters, the speed drops to 1 Gbps.
Frequency Bandwidth: Supports a maximum frequency of 250 MHz, capable of meeting modern bandwidth demands, especially for applications like 4K video streaming and online gaming.
Compatibility: Cat6 is backward compatible with older Cat5 and Cat5e devices, making it convenient for upgrading existing networks.
Cat7 Cable
Cat7 (Category 7) cable takes performance a step further from Cat6, specifically designed for high-speed and high-interference environments. Key features of Cat7 cables include:
Speed: Supports speeds of up to 40 Gbps, suitable for long-distance transmission (up to 100 meters), making it ideal for data centers and high-demand network environments.
Frequency Bandwidth: Supports a maximum frequency of 600 MHz, catering to future higher-speed needs.Shielding Design: Each pair of wires is individually shielded (S/FTP), effectively reducing external interference and enhancing signal stability and integrity.

Comparison of Cat6 and Cat7
Performance Comparison
| Feature | Cat6 | Cat7 |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Speed | 10 Gbps | 40 Gbps |
| Frequency Support | 250 MHz | 600 MHz |
| Shielding | None or shielded | Shielded for each pair |
| Cost | $0.25 - $0.35/foot | $0.40 - $0.60/foot |
As the table shows, Cat7 outperforms Cat6 in speed and frequency support, but it also comes with a higher cost. For home users, Cat6 typically meets everyday needs such as web browsing and video streaming. For data centers or enterprises that handle large amounts of data, Cat7 provides a better performance guarantee.
Installation and Compatibility
During installation, Cat6 is more flexible and suitable for most home and office environments. While the thickness and rigidity of Cat7 may complicate running it through conduits and ducts, its enhanced interference resistance is crucial in electromagnetically noisy environments.
Both cables use RJ45 connectors, and Cat7 can also utilize GG45 connectors, which are designed to support higher performance expectations. Although GG45 can plug into RJ45 sockets, the reverse is not true, potentially limiting Cat7's compatibility with older network devices.
Cost-effectiveness and Future-proofing
Cat6’s lower cost makes it an attractive choice for budget-conscious users. For those who only need to meet basic network demands at home, Cat6 is an economical option. However, as internet speeds continue to rise, investing in Cat7 can be viewed as a future-proof choice. Although the initial cost is higher, it may save future upgrade costs in the long run.
When to Choose Cat6 or Cat7?
Choosing between Cat6 and Cat7 cables depends on your specific needs and budget:
Home Users: If you primarily engage in web browsing, streaming, or occasional online gaming, Cat6 is typically sufficient for these tasks. It offers great value and compatibility.
Small Offices: For offices needing to support multiple devices and higher bandwidth, Cat6 remains an ideal choice. However, if you anticipate increased data transmission demands in the future, Cat7 would provide better assurance.
Data Centers and Enterprise Environments: For environments that require handling large data streams, Cat7 is undoubtedly the better option. Its high speed and shielding design can effectively support high-density networks and low-latency requirements.
Conclusion
When choosing between Cat6 and Cat7 cables, consider the specific demands of your network. Cat6 is suitable for most home users and small offices, while Cat7 offers an ideal solution for those needing high performance and interference resistance. Regardless of which cable you choose, ensuring your network devices can support the respective speeds is key to achieving optimal performance.
Ultimately, whether upgrading a home network or building a new enterprise network, understanding the characteristics and applicable scenarios of these two cables is essential for ensuring network stability and efficiency. We hope this article helps you make an informed decision between Cat6 and Cat7.
If you are looking for high-quality Ethernet solutions, Amissiontech offers a range of exceptional networking products to help you optimize performance and meet future demands. To learn more, visit our website or contact our professional team—we're here to assist you!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the key performance differences between Cat6 and Cat7 cables?
Cat6 supports a maximum bandwidth of 250 MHz, while Cat7 supports up to 600 MHz, offering better performance in high-traffic environments.
2. How do they compare in data transmission speed?
Both cables can handle speeds up to 10 Gbps, but Cat7 can achieve higher speeds under certain conditions.
3. Is there a noticeable improvement in latency for gaming with Cat7?
While Cat7 might offer slight latency improvements, overall performance is influenced by your internet service and router.
4. Which cable type is best for home network setups?
Cat6 is typically sufficient for home use, but consider Cat7 for future-ready solutions.






































