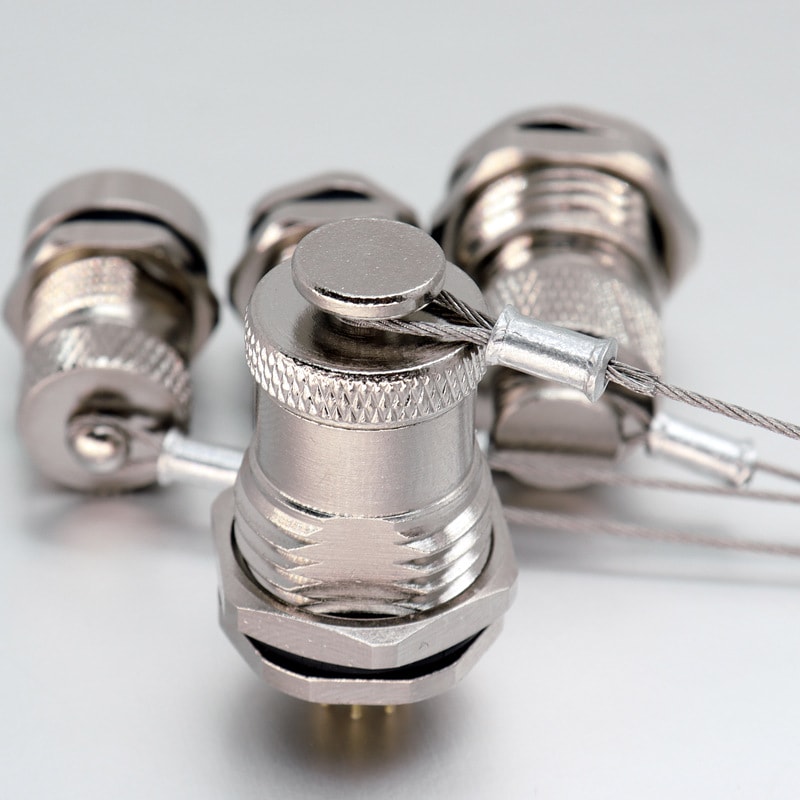
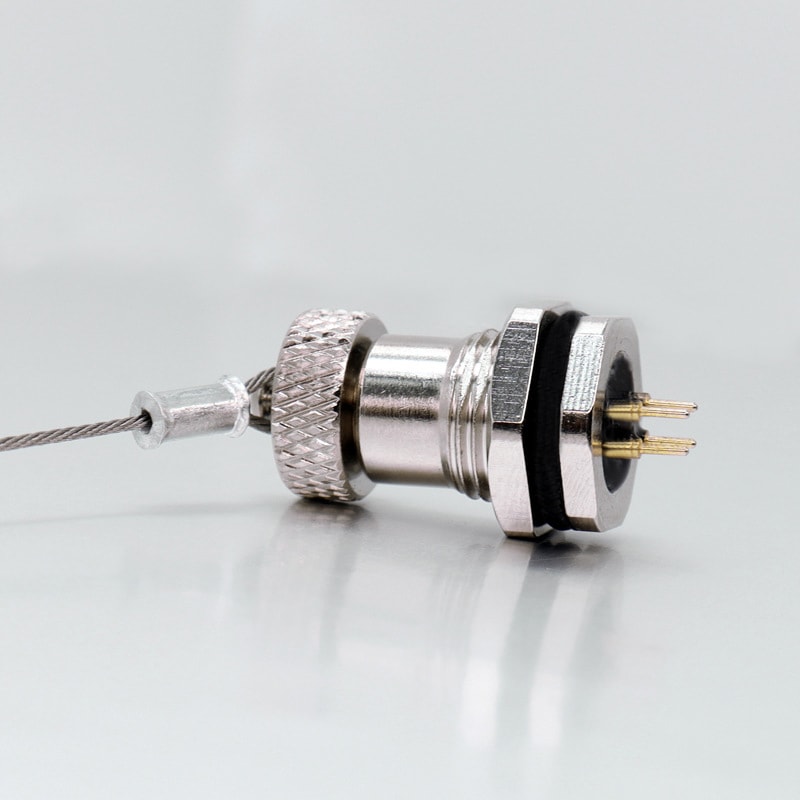
Products
I/O Systems
-
 IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All
IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBN1-354XXX
IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Metal Housing Metal Thread / Bayonet LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBN1-310XXX
IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Metal Housing Metal Thread LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP1-372XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 2A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP2-364XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 2A/channel Plastic Housing Metal Thread/Bayonet LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP1-372XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP1-351XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Metal Thread/Bayonet LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP2-330XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 2A/channel Metal Housing Metal Thread LockingView All
-

P/N: ALM-MPA1-051XXX
IO Link Master Multiprotocol Plastic Housing 7/8 Power ConnectorView All -

P/N: ALM-ECA1-010XXX
IO Link Master EtherCAT Single ProtocolView All -

P/N: ALM-MPA1-041XXX
IO Link Master Multiprotocol Plastic Housing M12 L-Codedd Power ConnectorView All -

P/N: ALM-MPA1-030XXX
IO Link Master Multiprotocol Metal Housing M12 L-Codedd Power ConnectorView All -

P/N: ALM-PNA1-010XXX
IO Link Master Profitnet Single ProtocolView All
Circular Connectors
-
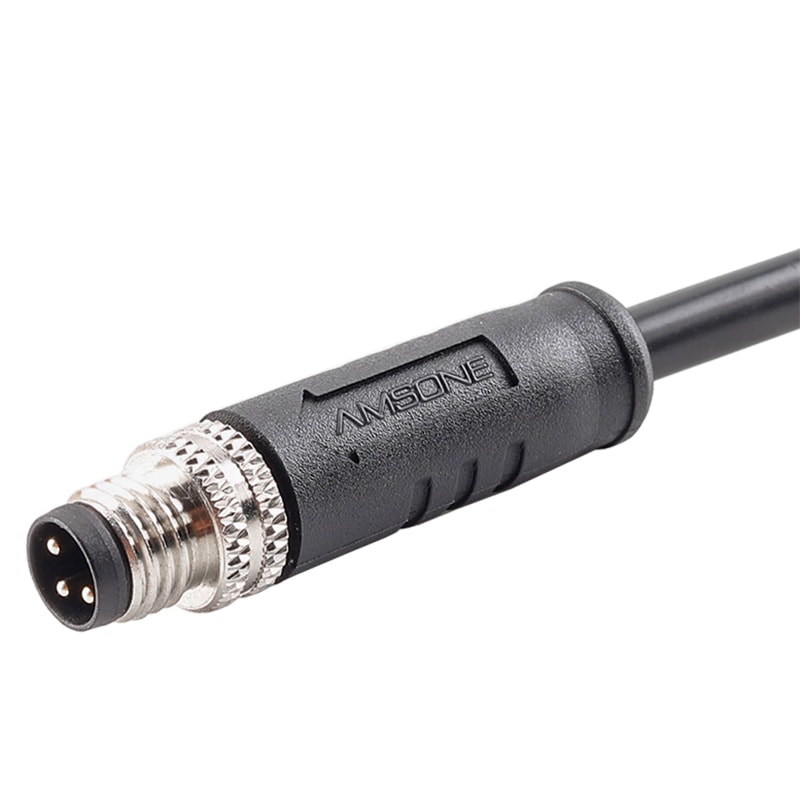

P/N: AM08M0411AXX1-XXX
M8 4Pin Pre-molded Cable Male Straight M8 ConnectorView All -
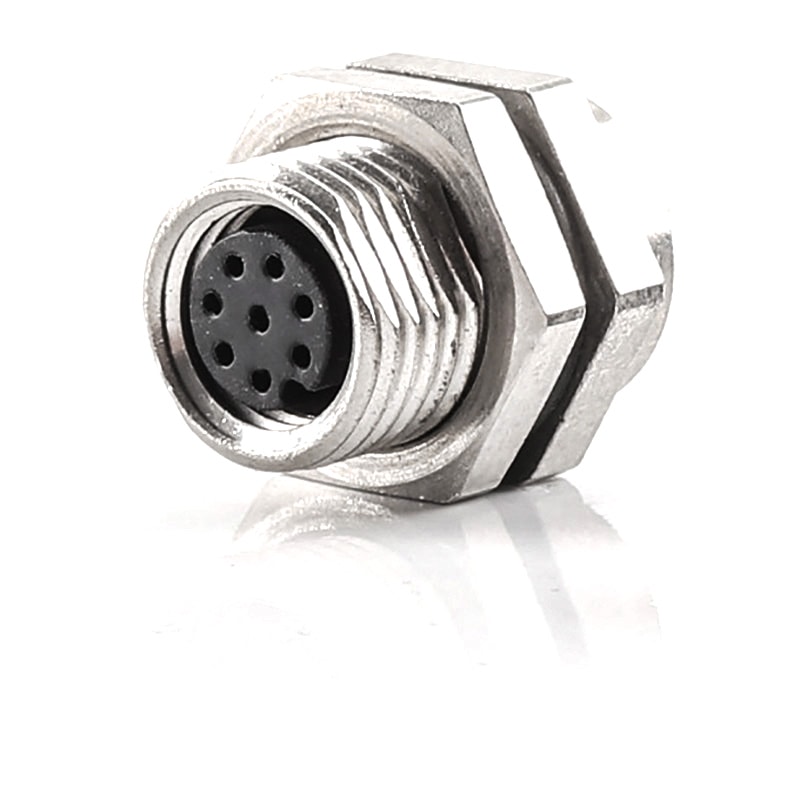

P/N: AM08F0822A001
M8 Device Connector Panel Rear Mount M8 8P Female ReceptacleView All -
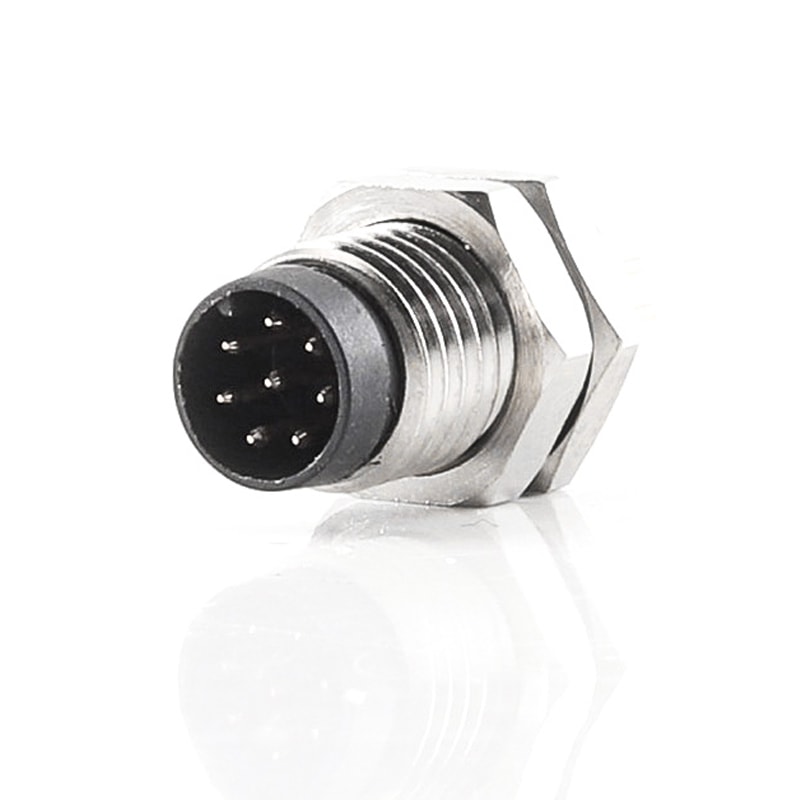

P/N: AM08M0622A001
M8 Device Connector Panel Rear Mount M8 6P Male ReceptacleView All -
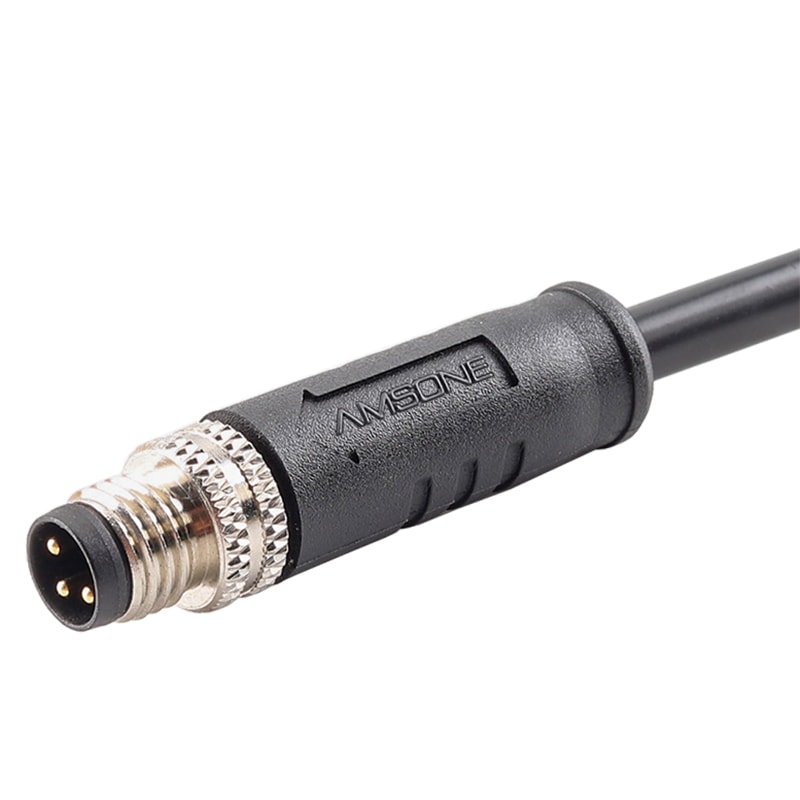

P/N: AM08M0811AXX1-XXX
M8 8Pin Pre-molded Cable Male Straight M8 ConnectorView All -
P/N: AM08M0822A003
M8 Device Connector Male 8Pin PCB Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Right Angled ShieldedView All -
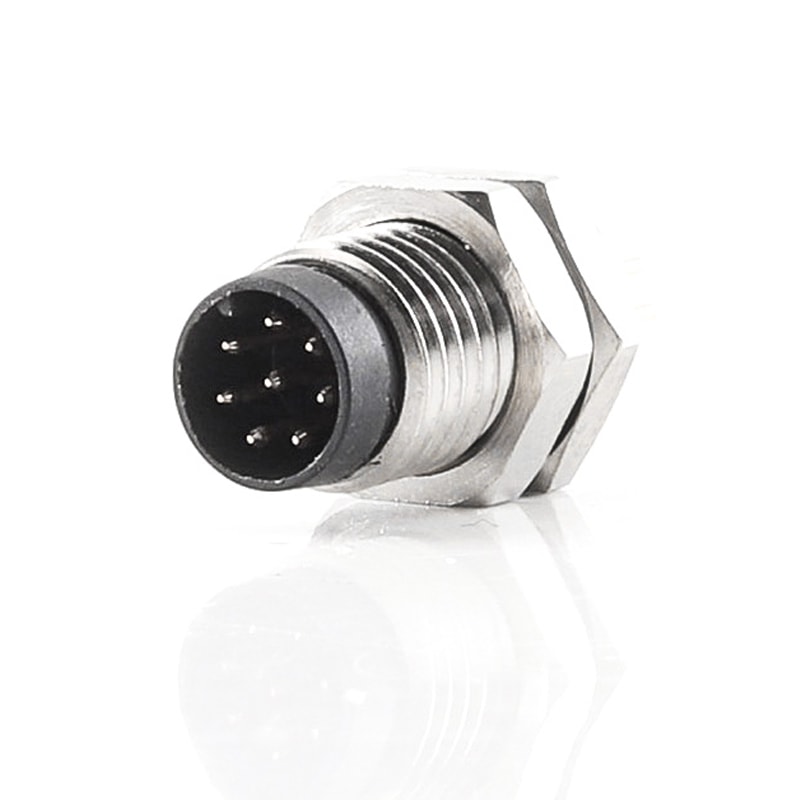

P/N: AM08M0822A001
M8 Device Connector Panel Rear Mount M8 8P Male ReceptacleView All -
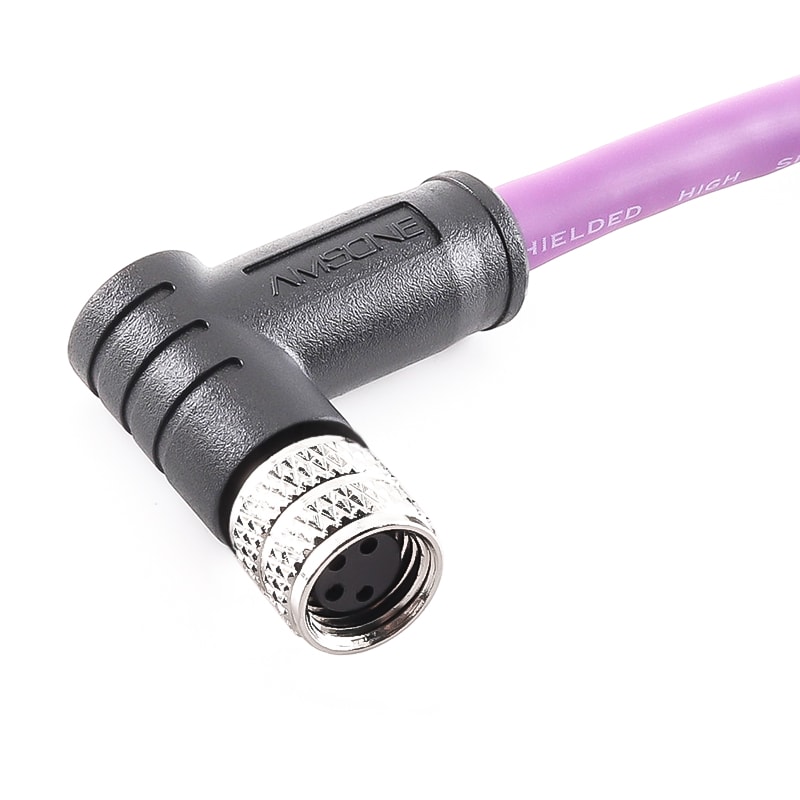

P/N: AM08F0811AXX3-XXX
M8 8P Female Shield Connector Pre-molded Cable Right Angled IP67View All -
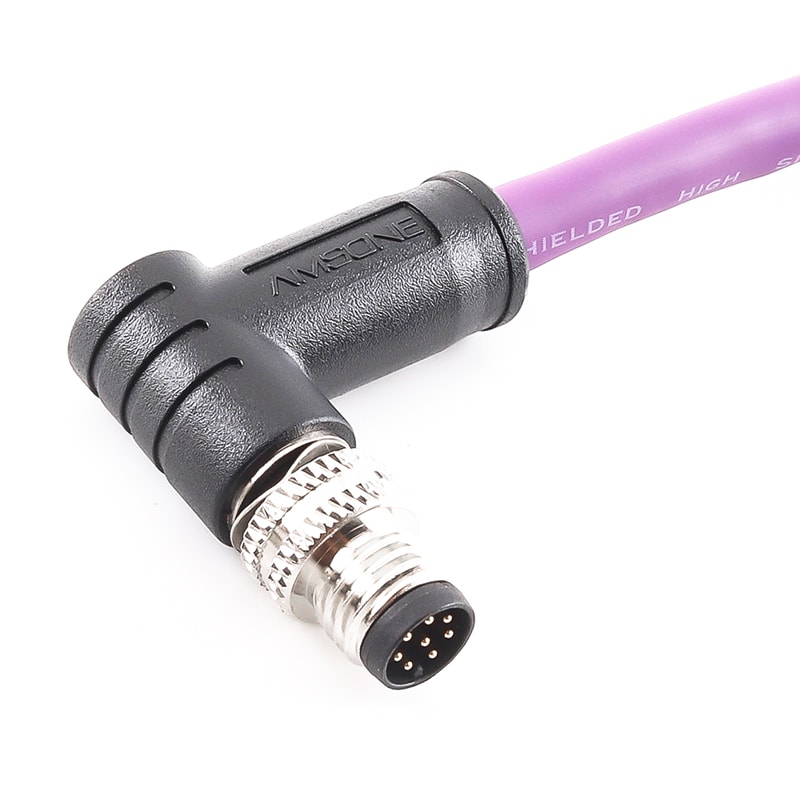

P/N: AM08M0811AXX3-XXX
M8 Connector 8P Male Shield Pre-molded Cable Right Angled IP67View All
-
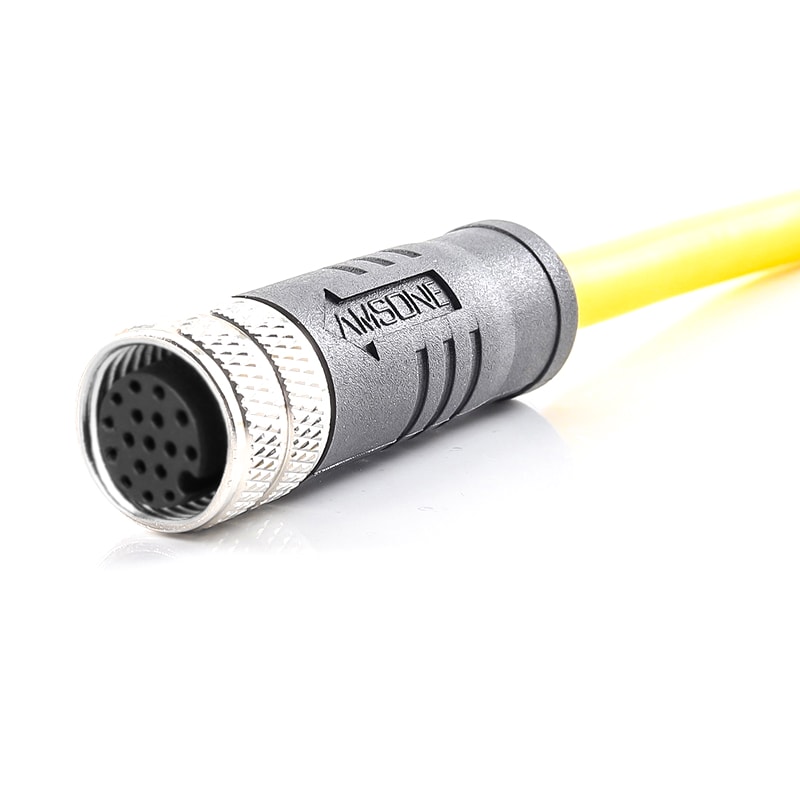

P/N: AM12F1211AXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts: 12,solder connection, A code, straight, IP67View All -
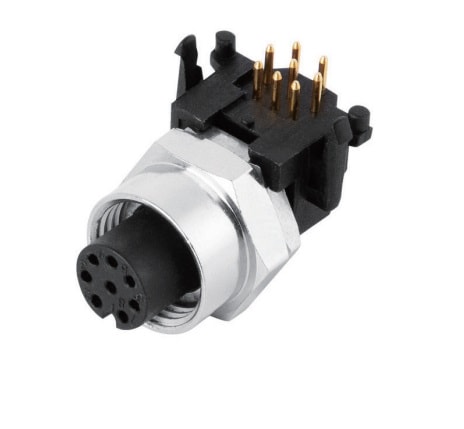

P/N: AM12F0822A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts: 8, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
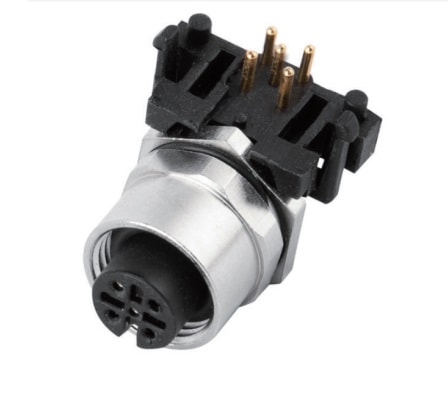

P/N: AM12F0522A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts: 5, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
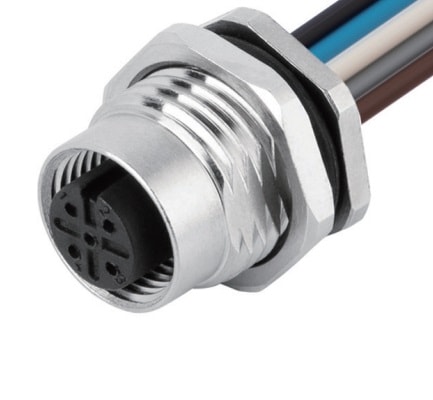

P/N: AM12F0512AXX1-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts: 5, solder connection for wires, A code, straight, IP67View All -
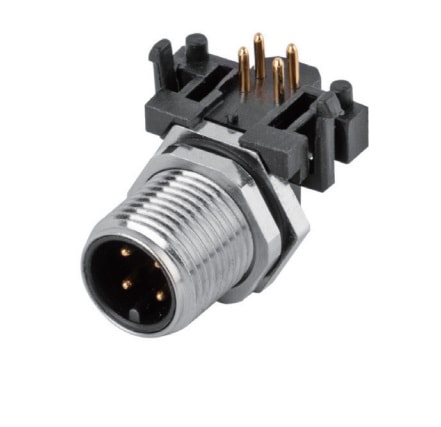

P/N: AM12M0422A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts: 4, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
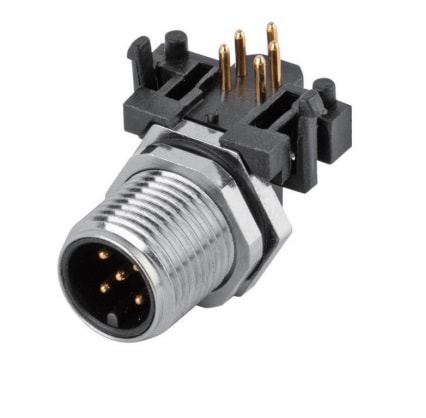

P/N: AM12M0522A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts: 5, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
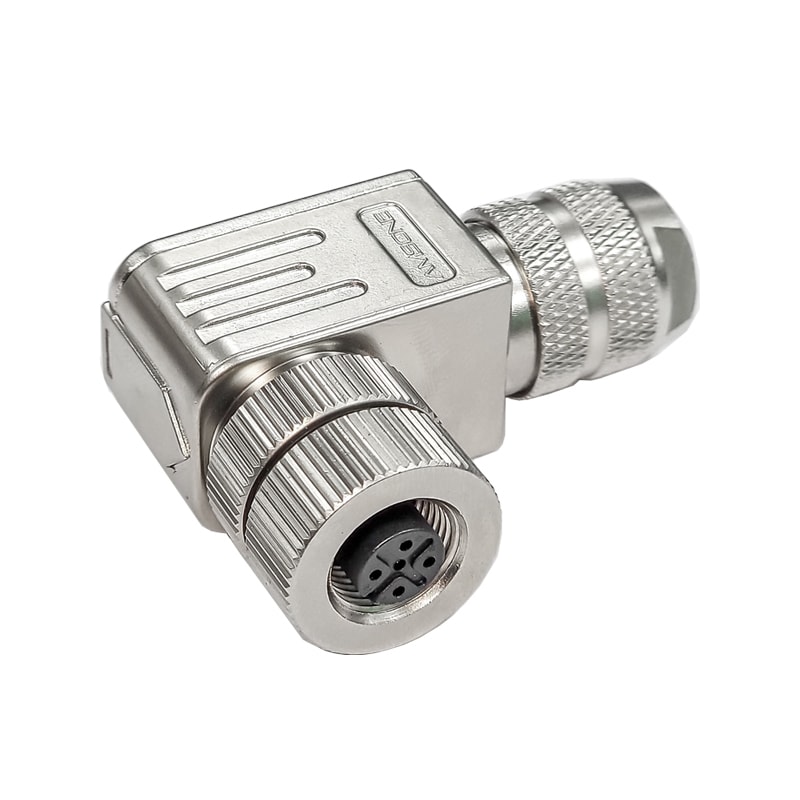

P/N: AM12F0534A007
M12 cable connector, female, contacts:5, field assembly type, screw connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
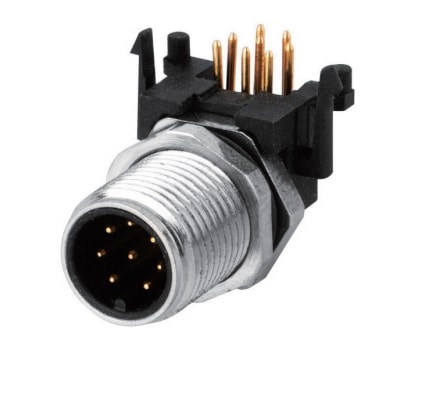

P/N: AM12M0822A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts: 8, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All
-
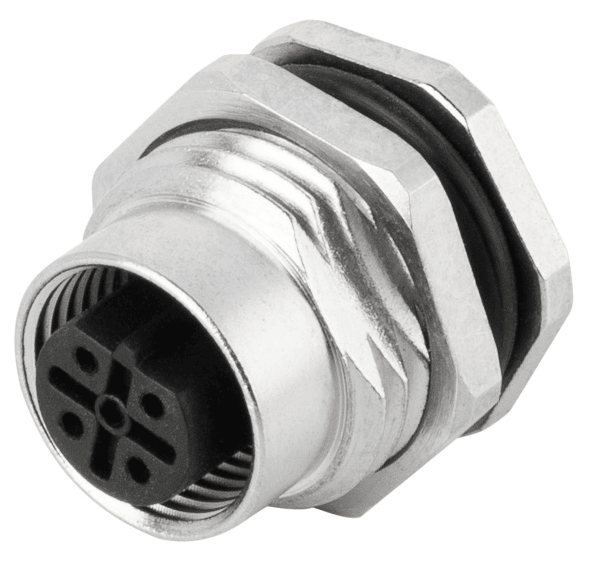

P/N: AM12F0522B001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:5, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -
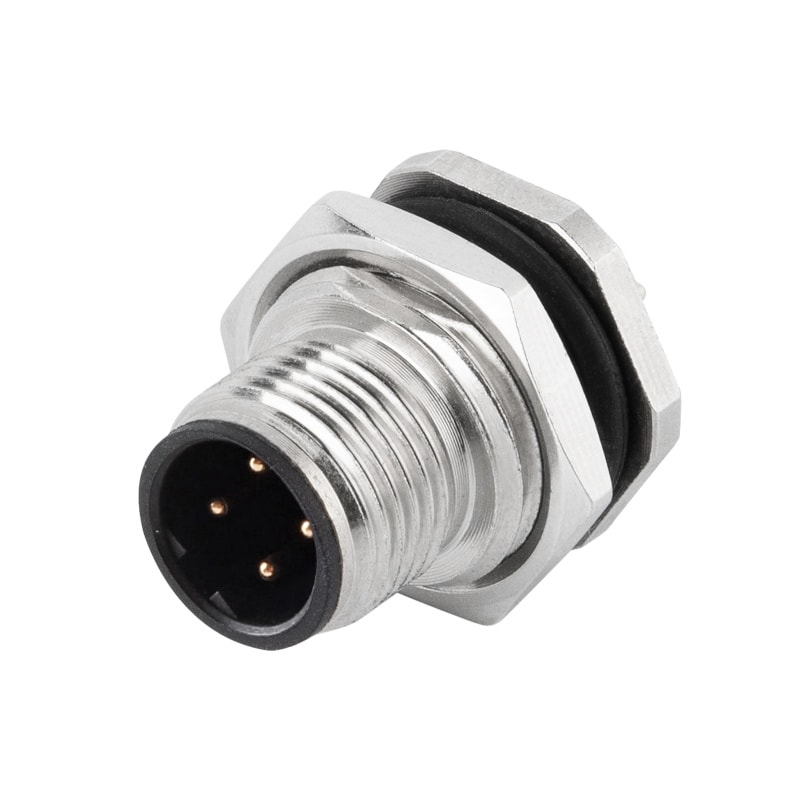

P/N: AM12M0522B001
M12 B Code Male Panel Rear Mount Receptacle PCB Connector PG9View All -
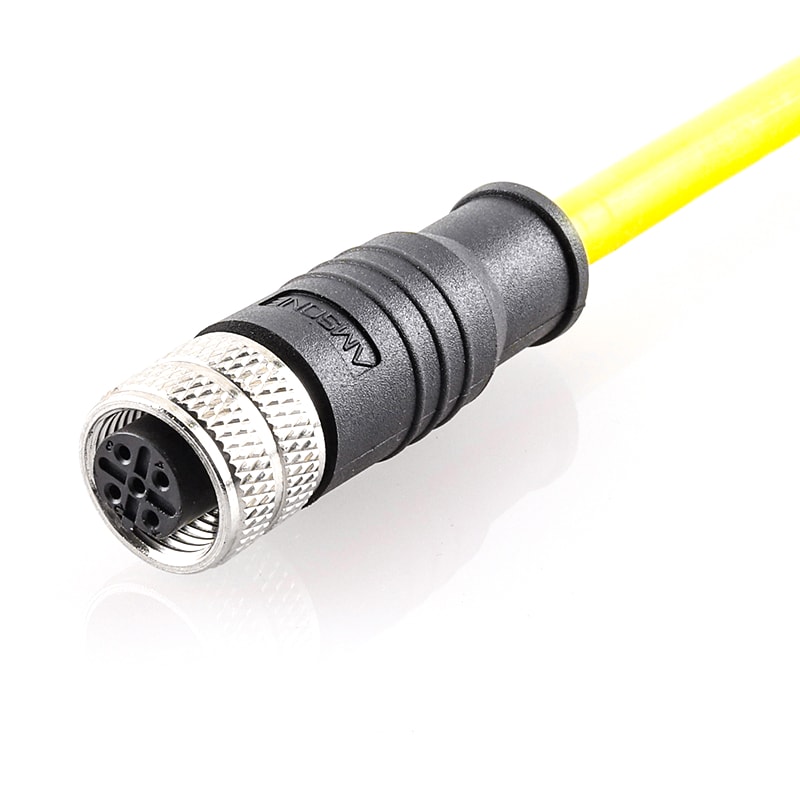

P/N: AM12F0511BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:5, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -
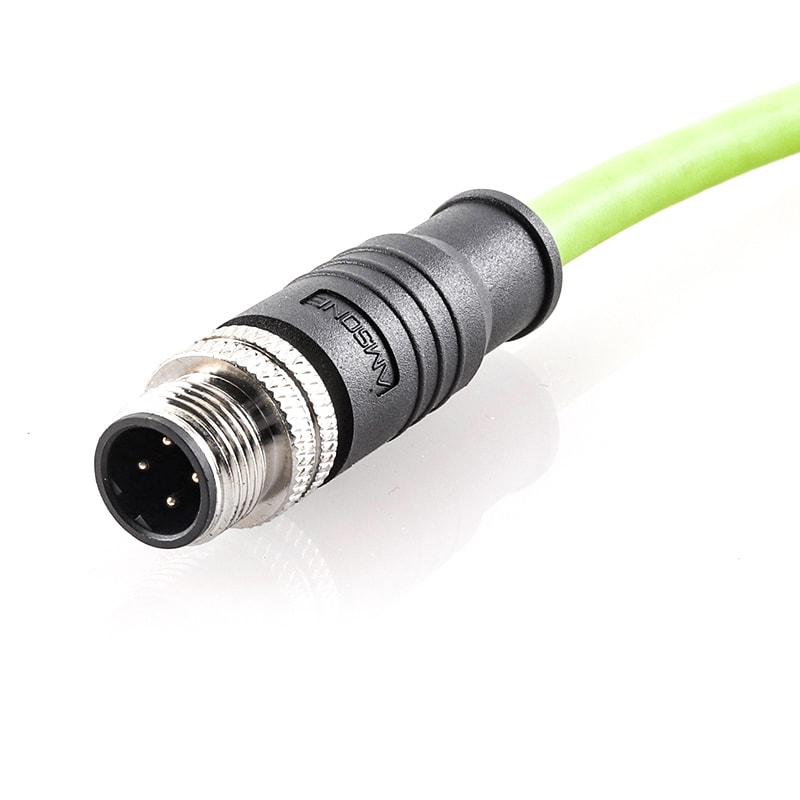

P/N: AM12M0511BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:5, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -
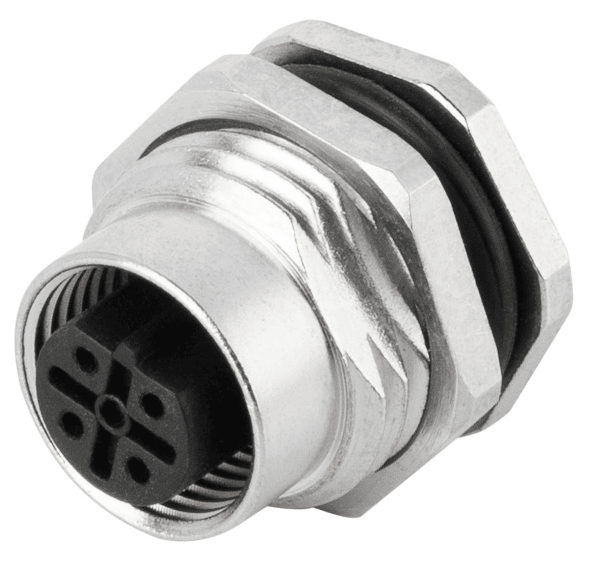

P/N: AM12F0422B001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -
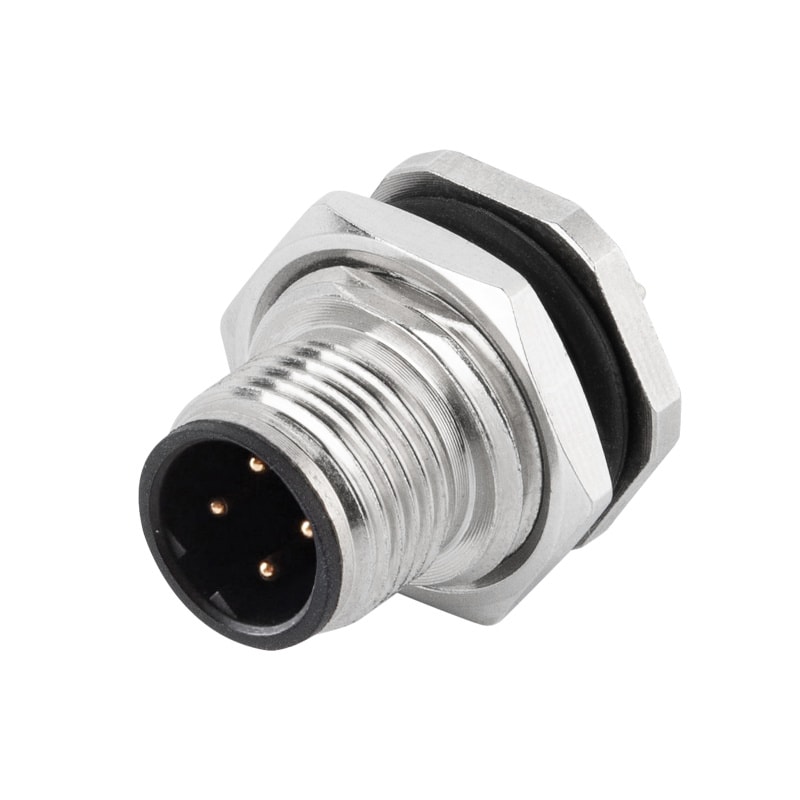

P/N: AM12M0422B001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -
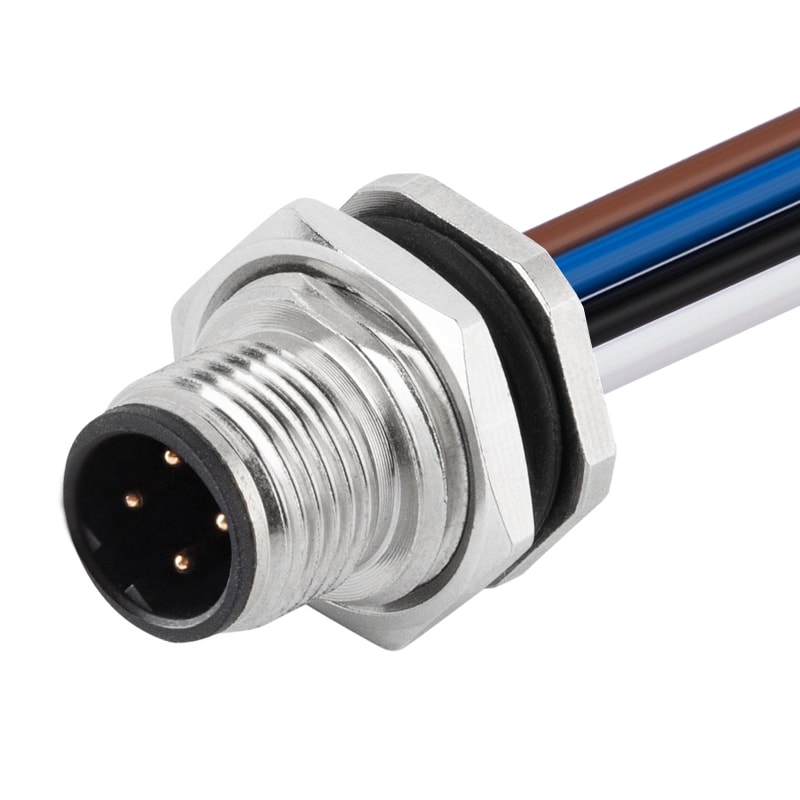

P/N: AM12M0512B002
M12 5P Male B Code Panel Rear Mount Receptacle Wires Solder Connector M16*1.5View All -

P/N: AM12M0512B001
M12 5P Male B Code Panel Rear Mount Receptacle Wires Solder Connector PG9View All
-
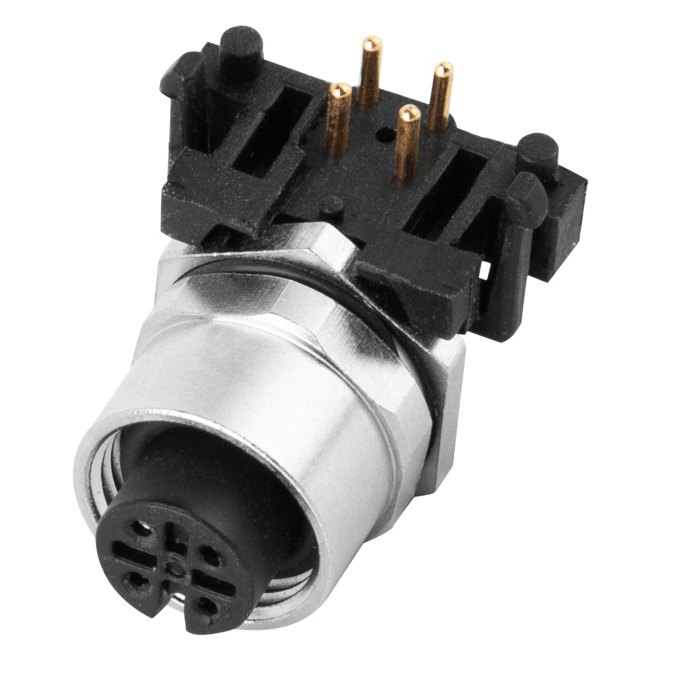
P/N: AM12F0422D006
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, D code, right angled, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0412D001
M12 D Code Male Panel Rear Mount Receptacle For Wires Solder Connector PG9View All -

P/N: AM12F0413D001
M12 panel receptacle, front mount, female, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, D code, straight, IP67View All -
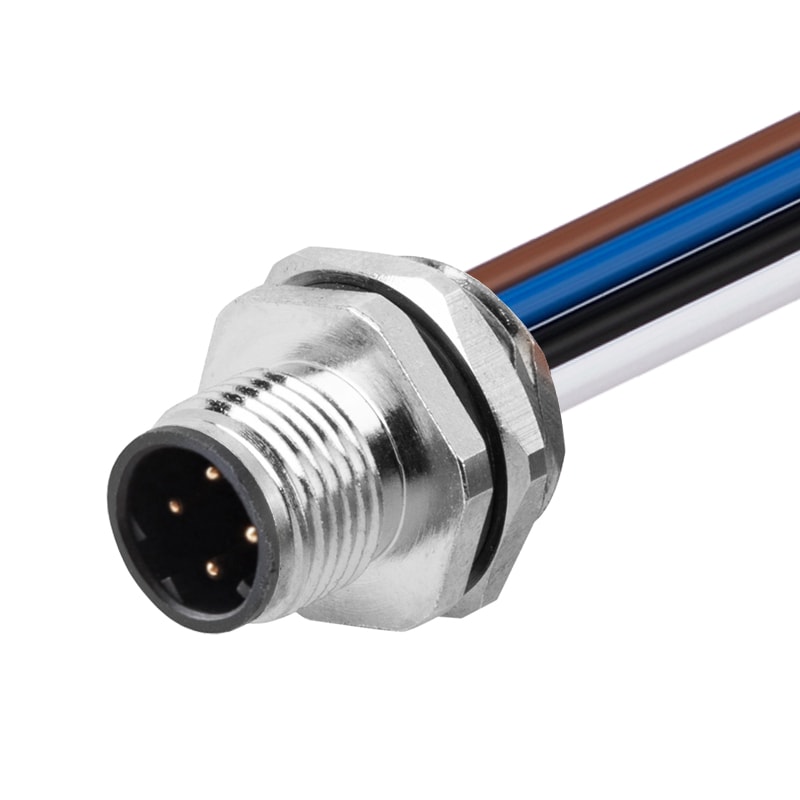

P/N: AM12M0413D351-005
M12 Panel Receptacle Front Mount Male 4Pin Solder Connection For Wires D Code Straight IP67View All -
P/N: AM12F0422D001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, D code, straight, IP67View All -
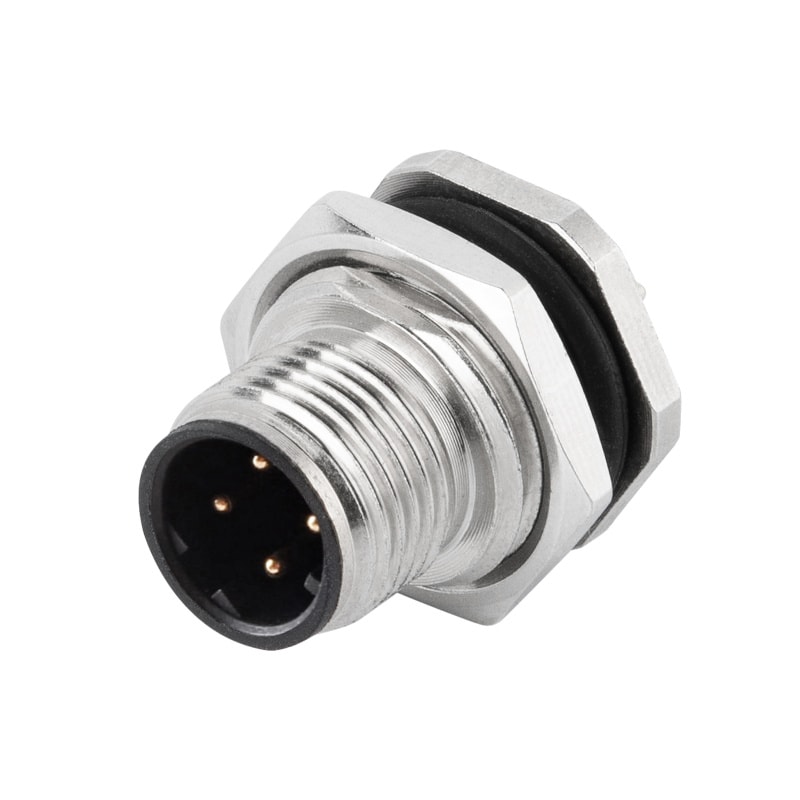

P/N: AM12M0422D001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, D code, straight, IP67View All -
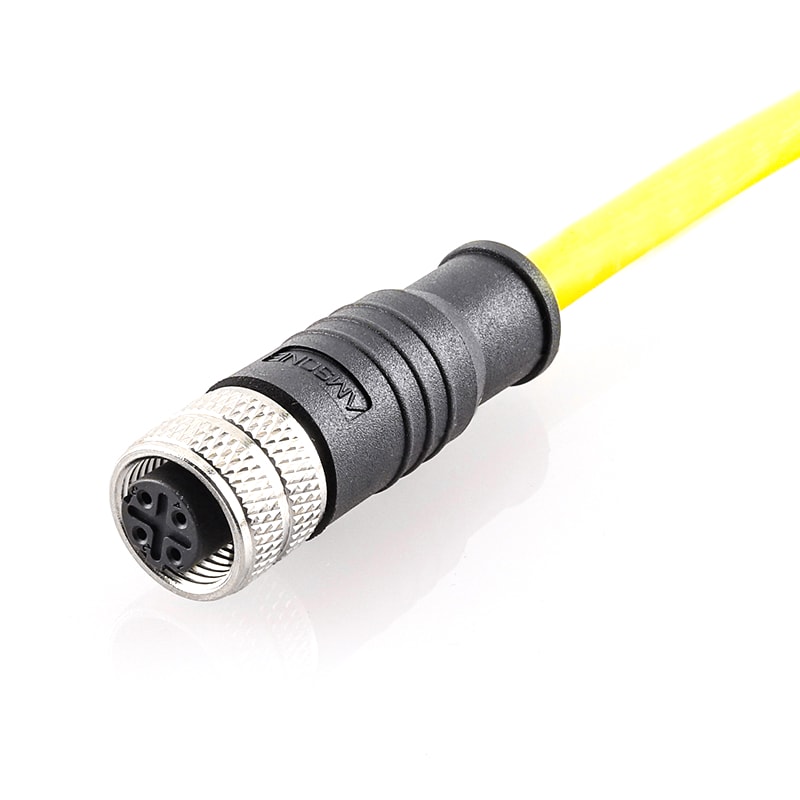

P/N: AM12F0411D241-010
M12 4P D Code Pre-molded Cable Connector Female Straight IP67View All -
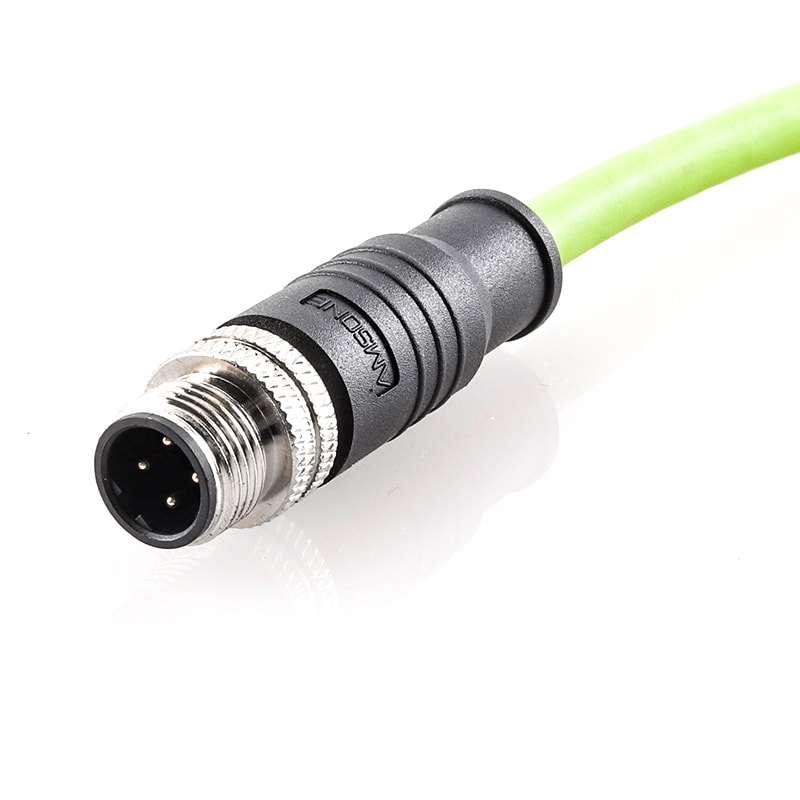

P/N: AM12M0411D241-010
M12 pre-molded cable connector male solder connection D code straight IP67View All
-
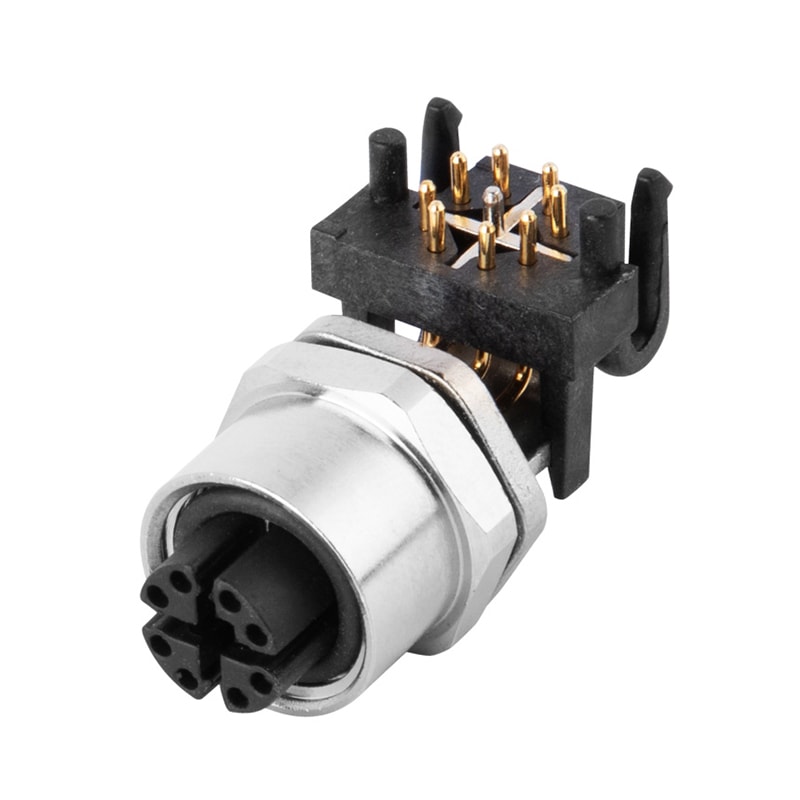

P/N: AM12F0822X008
M12 X Code 8Pole Panel Receptacle Rear Mount Female PCB Dip-solder Connection Right Angled IP67View All -
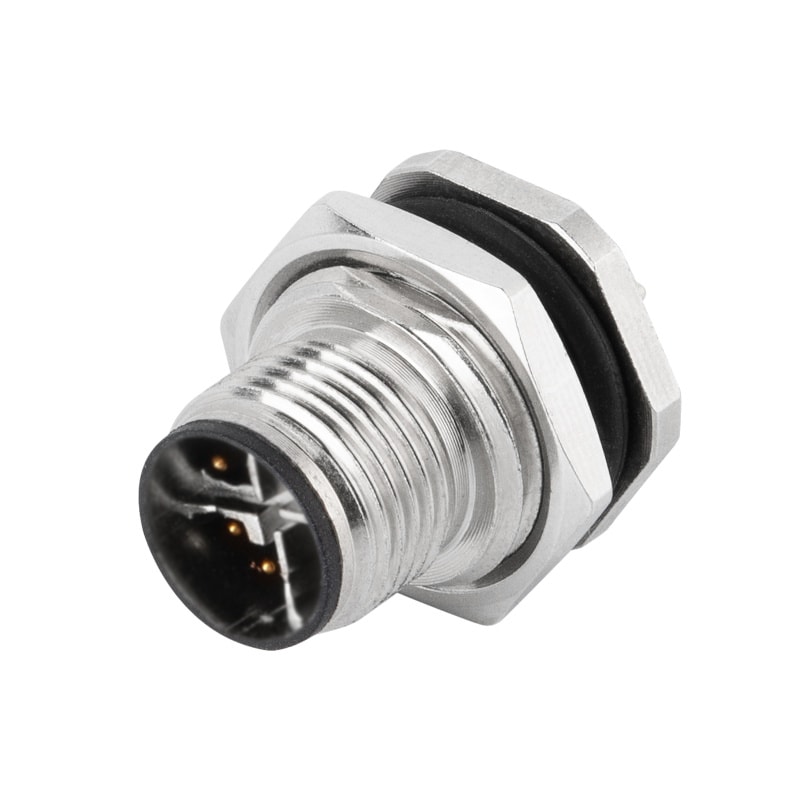

P/N: AM12M0822X001
M12 Panel Receptacle Rear Mount Male PCB DIP Solder X Code StraightView All -
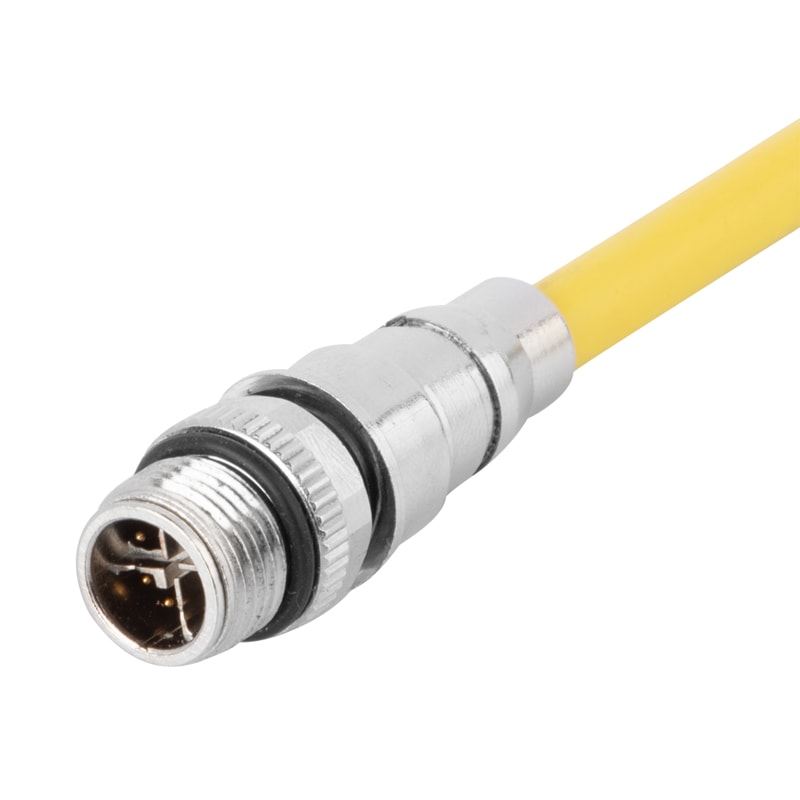

P/N: AM12M0811X003
M12 data cable connector, contact: 8P, male, for pre-molding , X code, straight, 360 EMC shielding, solder connection, 0.5A/60VView All -
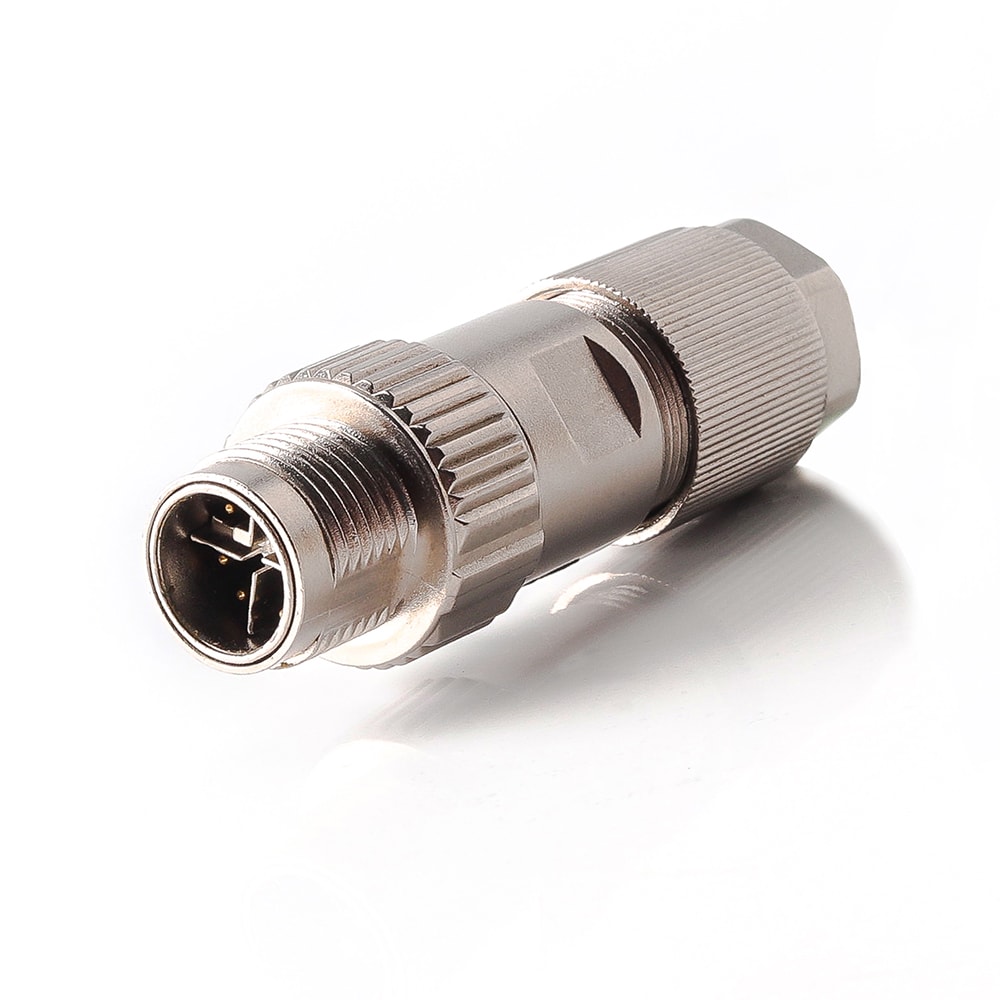

P/N: AM12M0844X003
M12 X Code Field Assembly Connector Male EMC Shielded Straight IP67 Crimp ContactsView All -
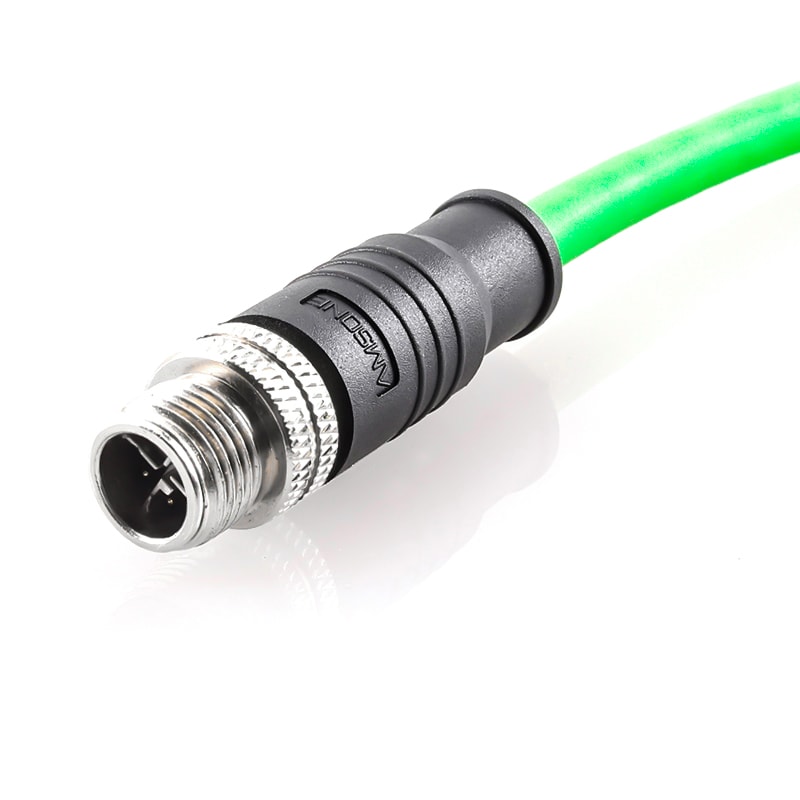

P/N: AM12M0811X233-100
M12 Pre-molded Cable Connector 8Pole Male X Code EMC Profinet/Ethernet Cable StraightView All -
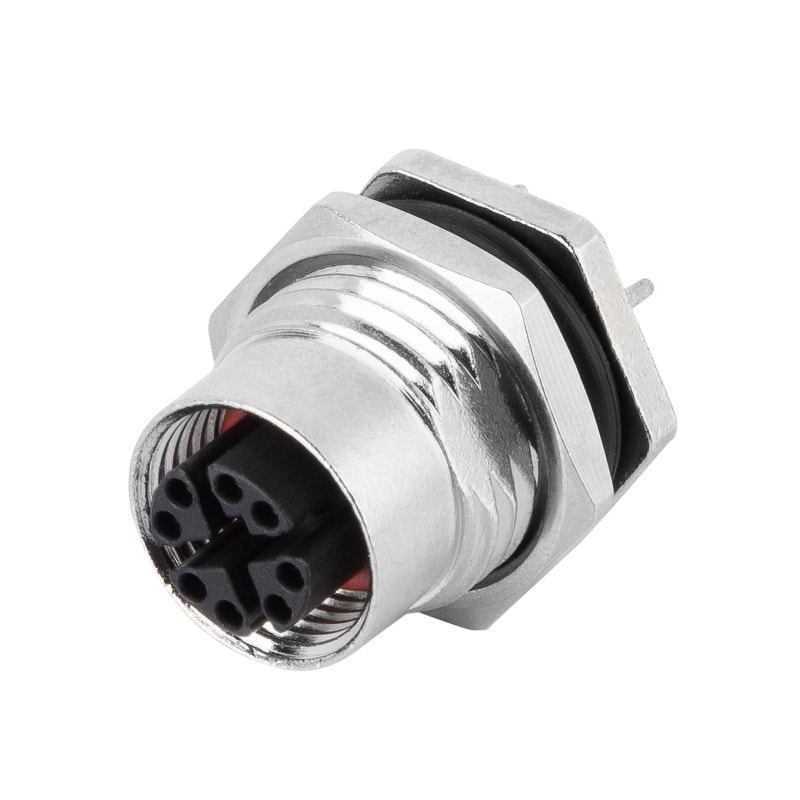

P/N: AM12F0822X002
M12 X Code Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female PCB DIP Connection M16*1.5View All -
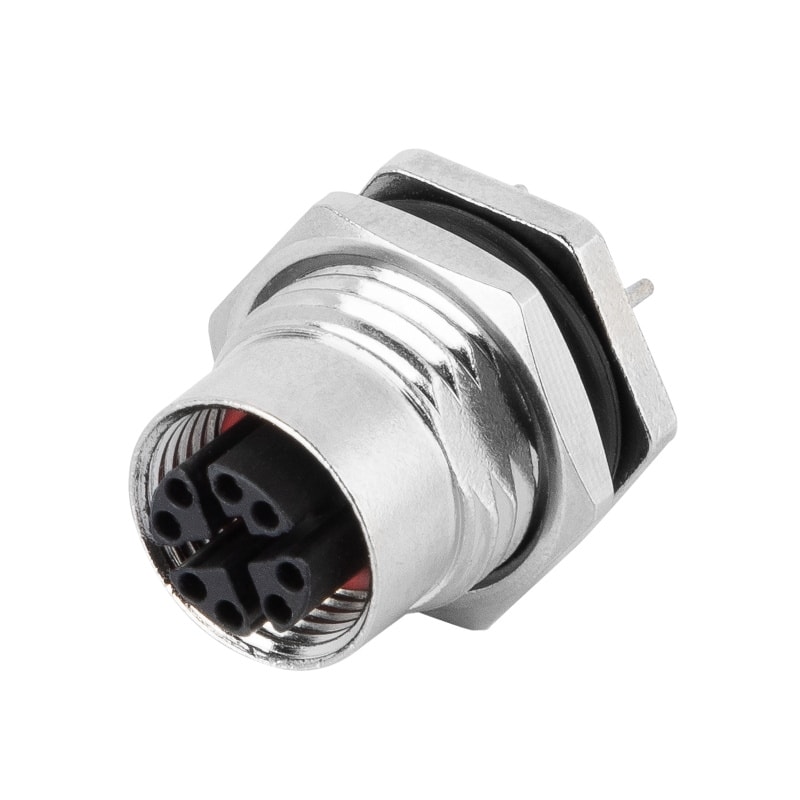

P/N: AM12F0822X001
M12 X Code Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female PCB DIP Connection PG9View All -
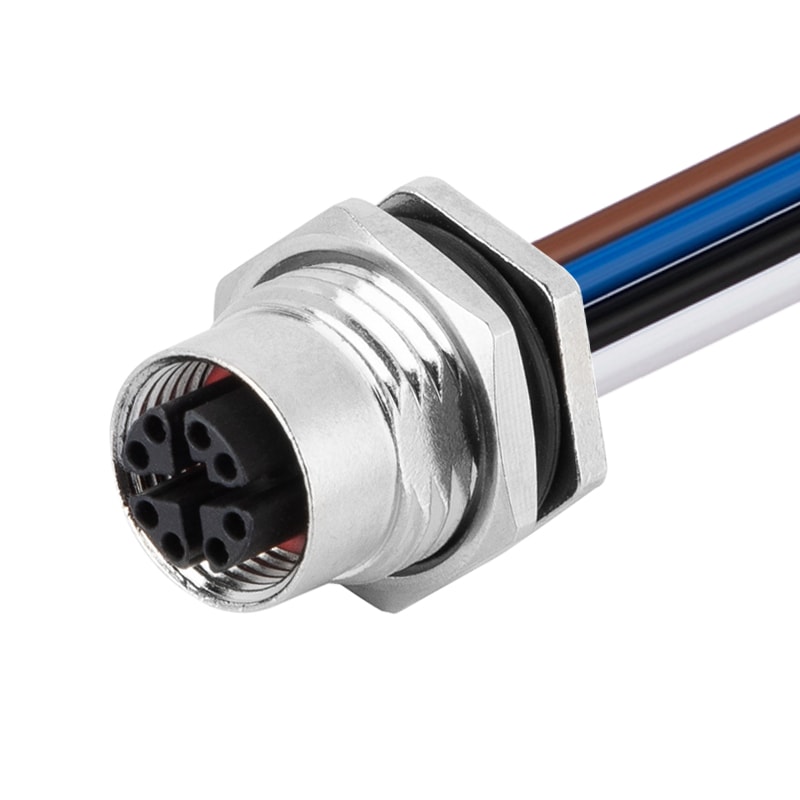

P/N: AM12F0812X001
M12 X Code Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female For Solder Wires ConnectionView All
-
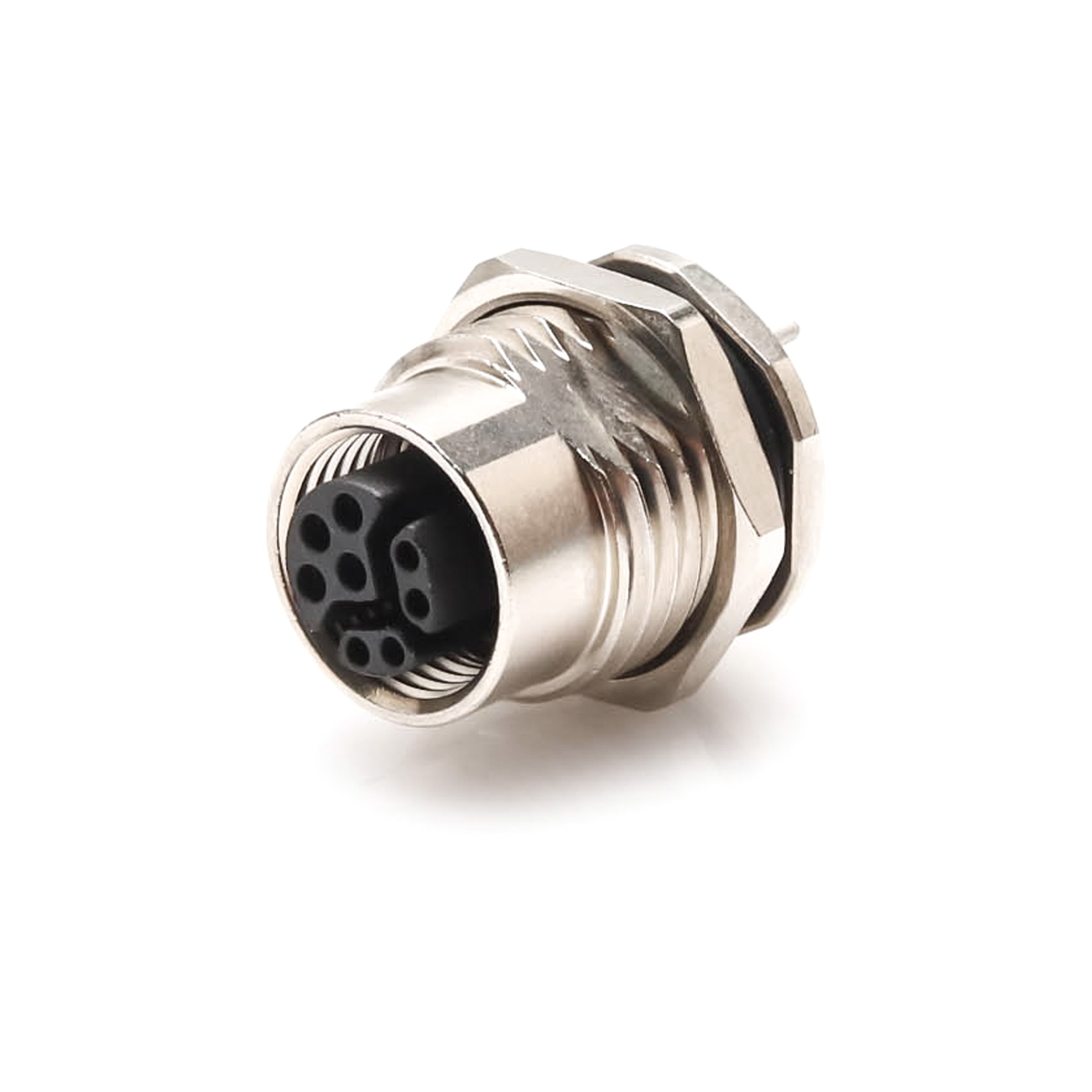

P/N: AM12F0822Y002
M12 Hybrid Connector,Y Code,Female,Panel Mount Receptacle,M12 Device ConnectorView All -
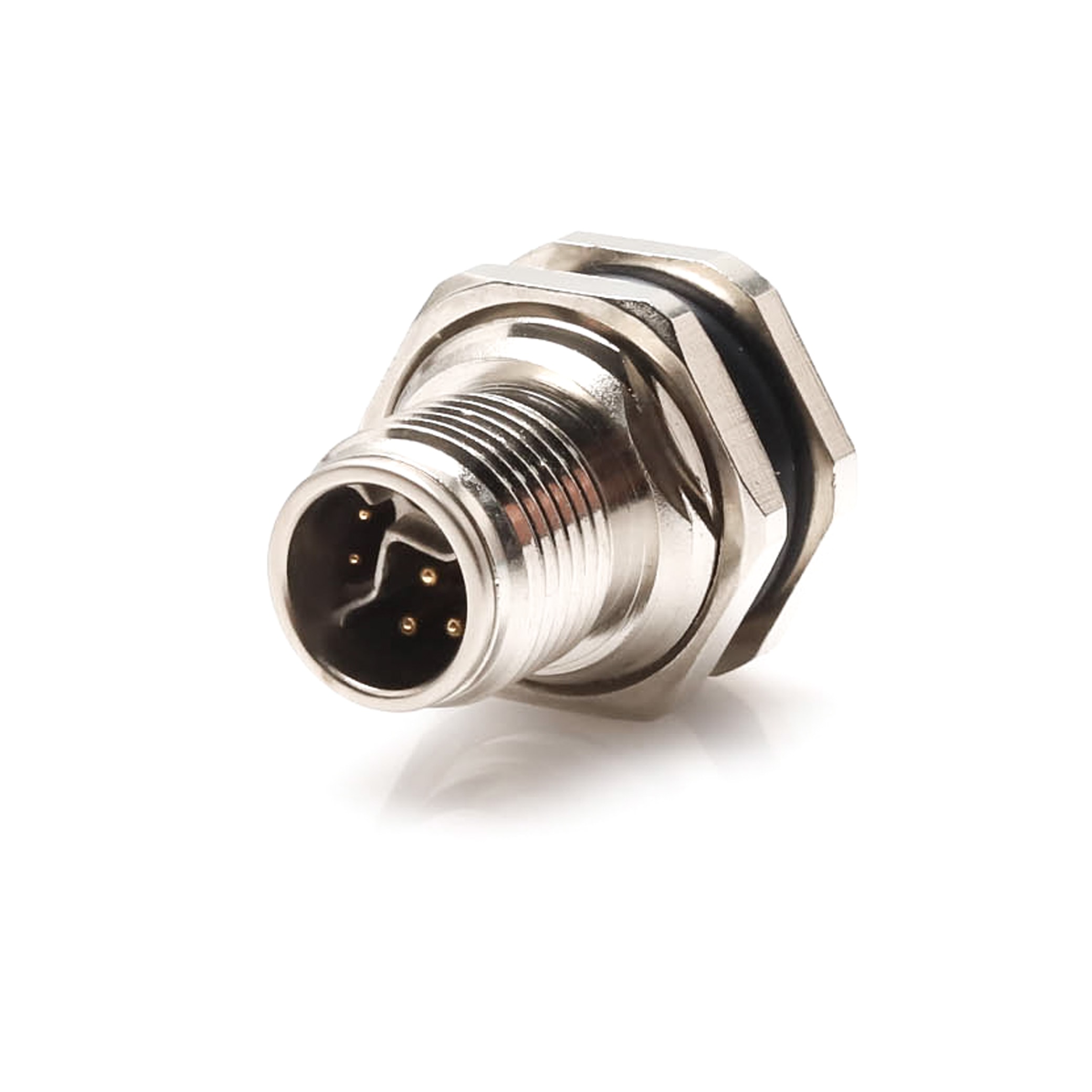

P/N: AM12M0822Y002
M12 Hybrid Connector,Y Code,Male,Panel Mount Receptacle,M12 Device ConnectorView All -
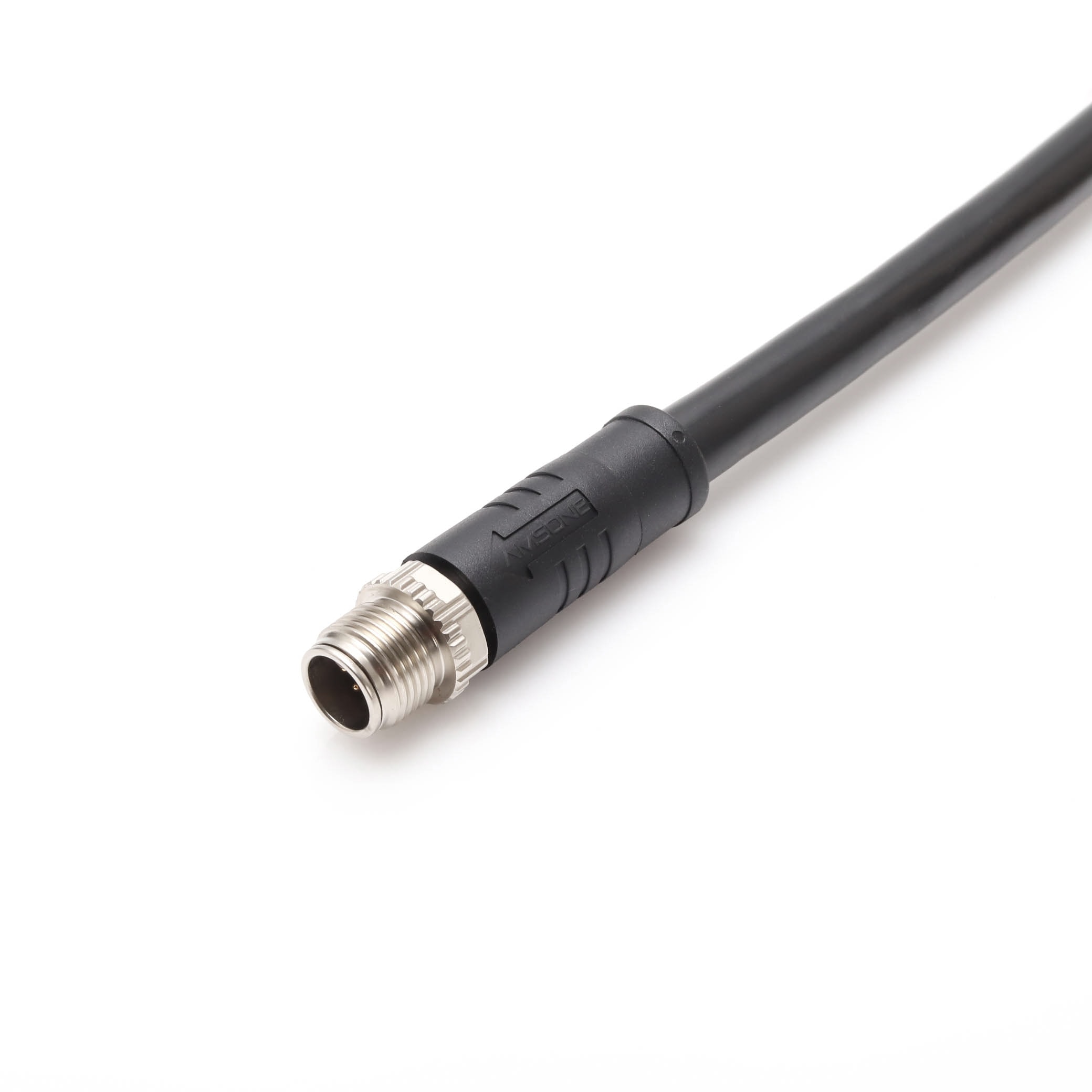

P/N: AM12M0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Male,M12 Y-Coded Power Signal Ethernet CableView All -
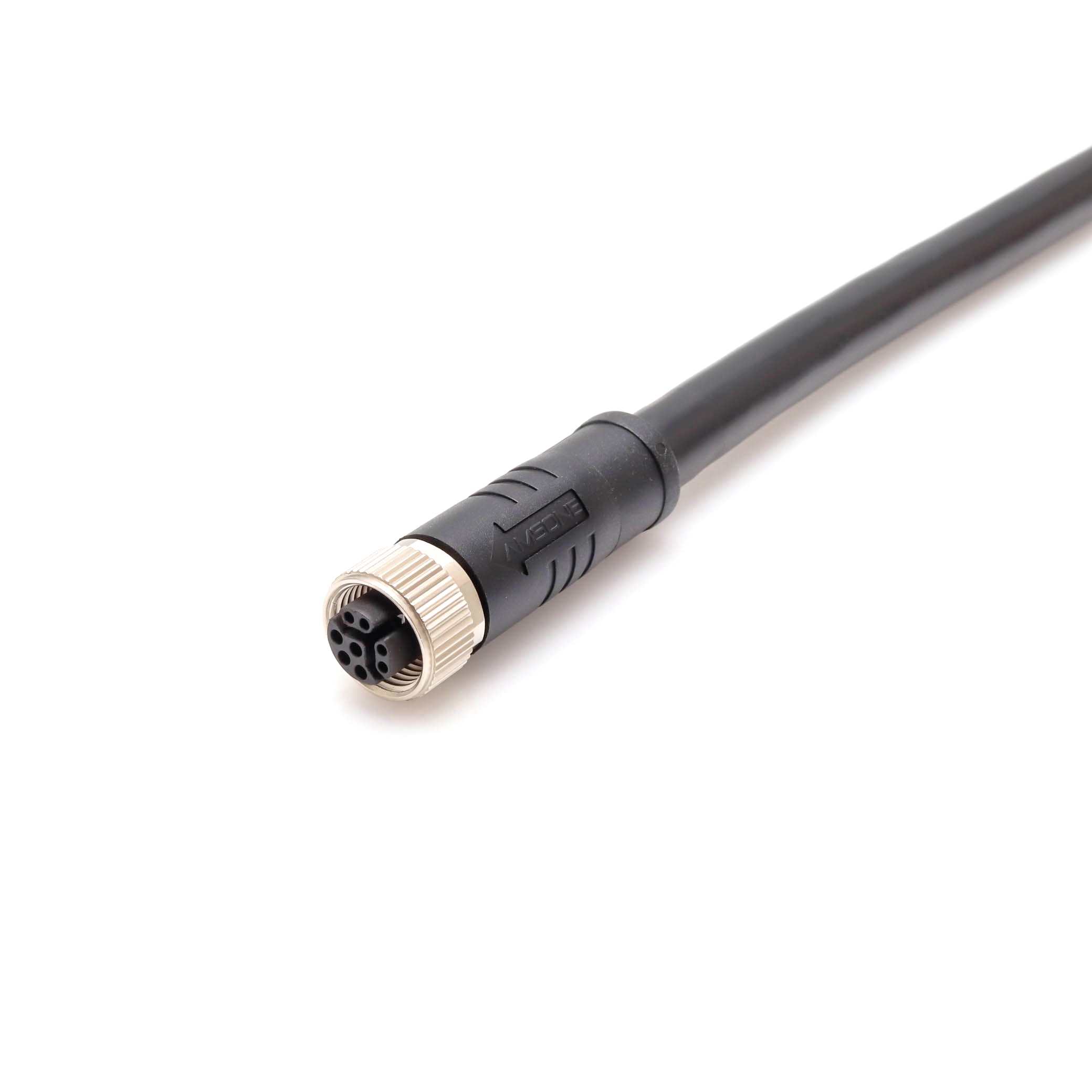

P/N: AM12F0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Power Signal,M12 Y-Coded CablesView All -
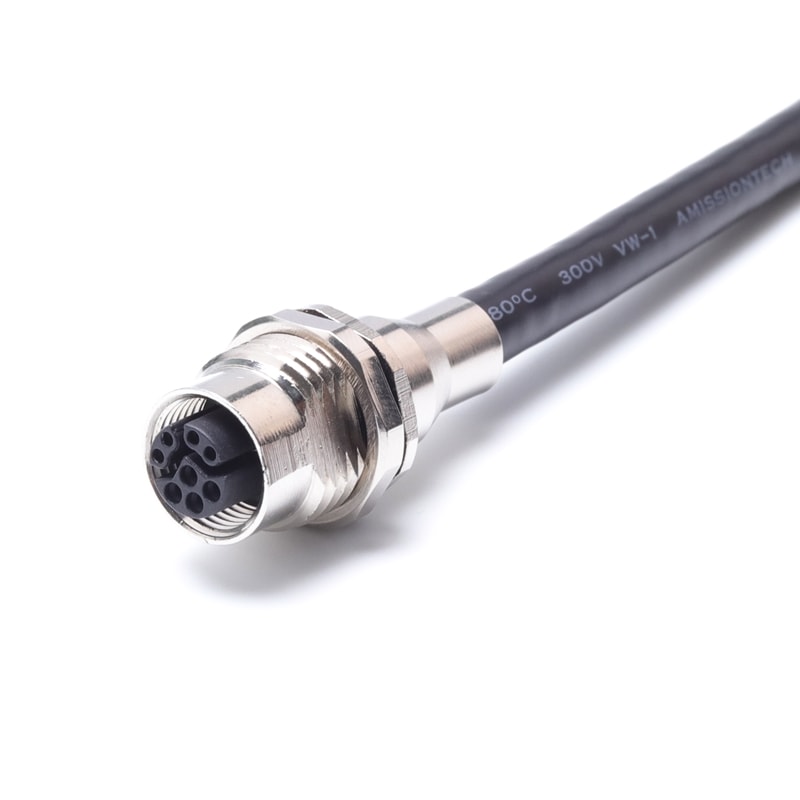

P/N: AM12F0812Y003
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Panel Mount Shielded,M12 Y-CodedView All
-
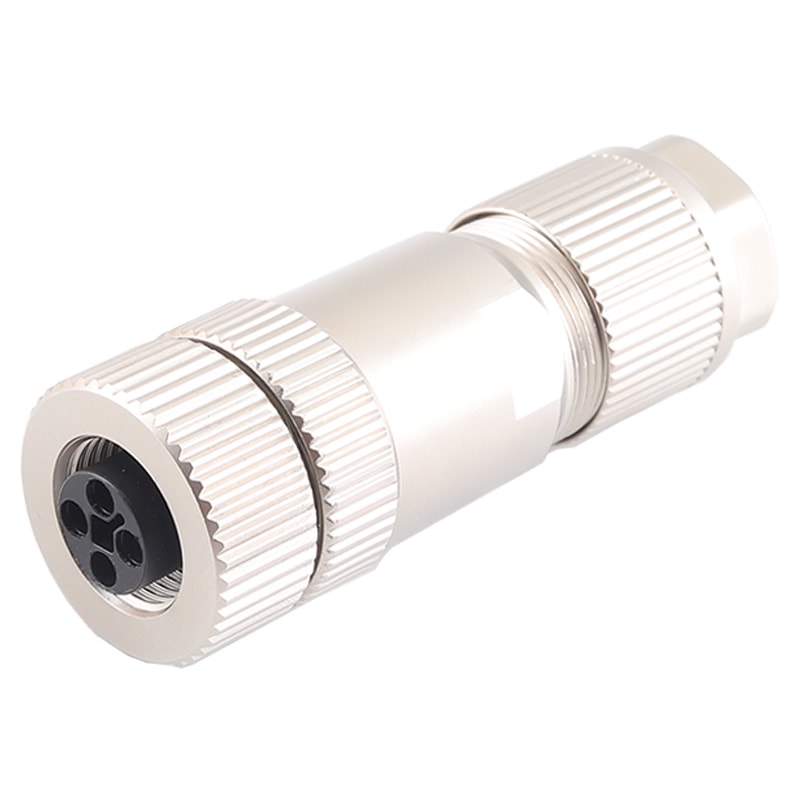

P/N: AM12F0434T001
M12 cable connector, female, contacts: 4, field assembly type, screw connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -
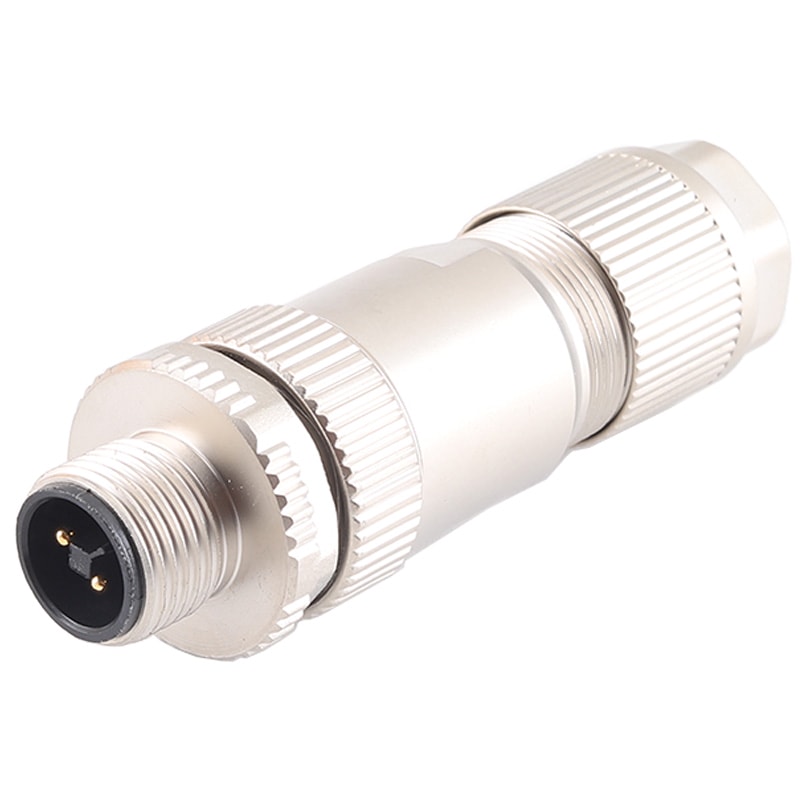

P/N: AM12M0434T001
M12 cable connector, male, contacts: ,4, field assembly type, screw connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -
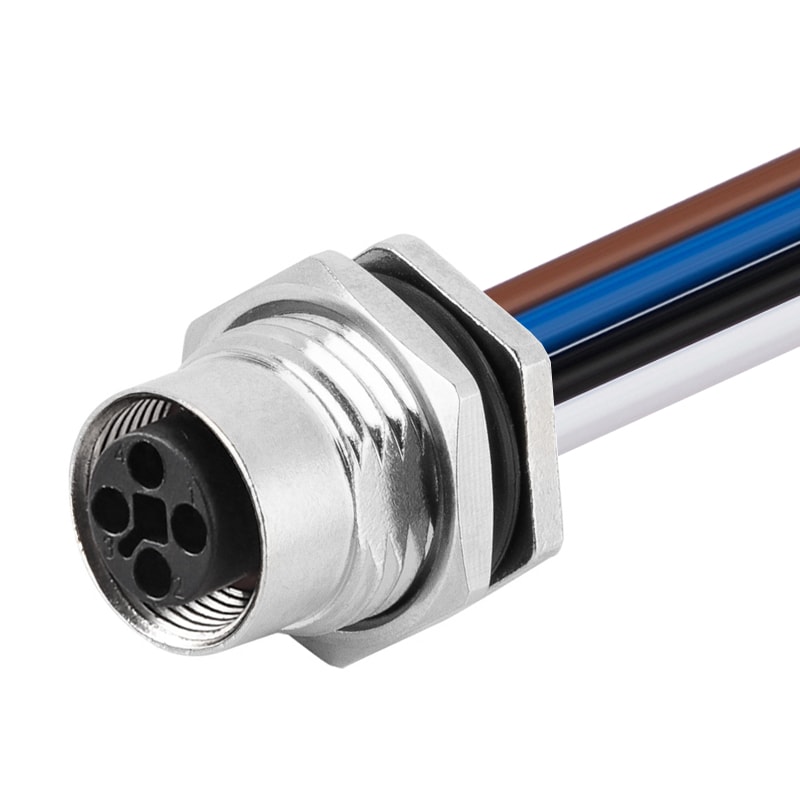

P/N: AM12F0412T171 -XXX
M12 panel receptacle, female, contacts: 4, solder connection for wires, T code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0412T171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, male, contacts: 4, solder connection for wires, T code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0322T001
M12 panel receptacle, female, contacts: 3,PCB dip-solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0322T001
M12 panel receptacle, male, contacts: 3,PCB dip-solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0311TXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts: 3,solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -
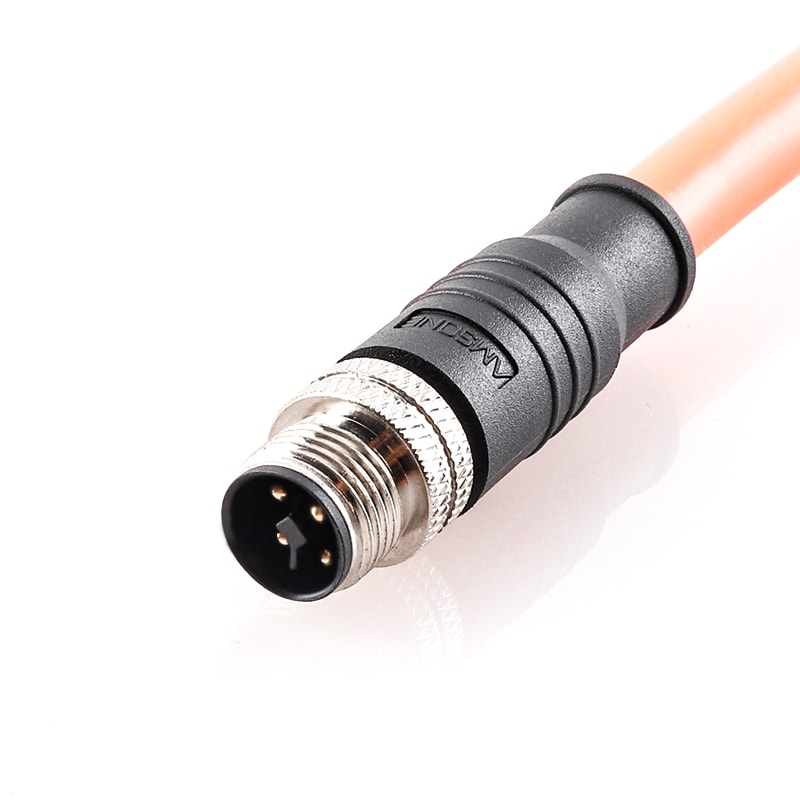

P/N: AM12M0311TXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:3, solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All
-
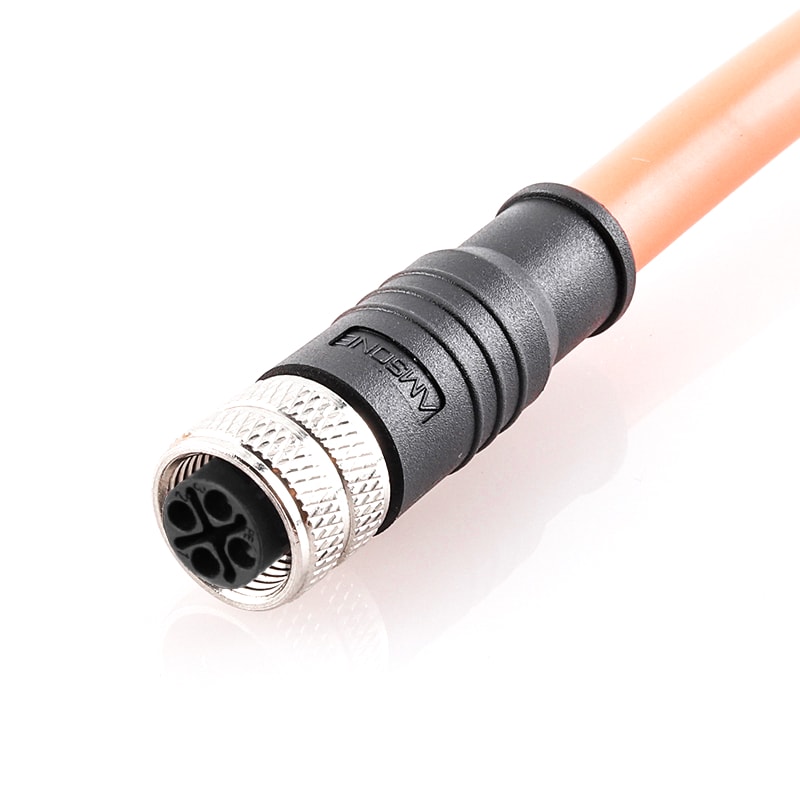

P/N: AM12F0411SXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4(3+PE), solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -
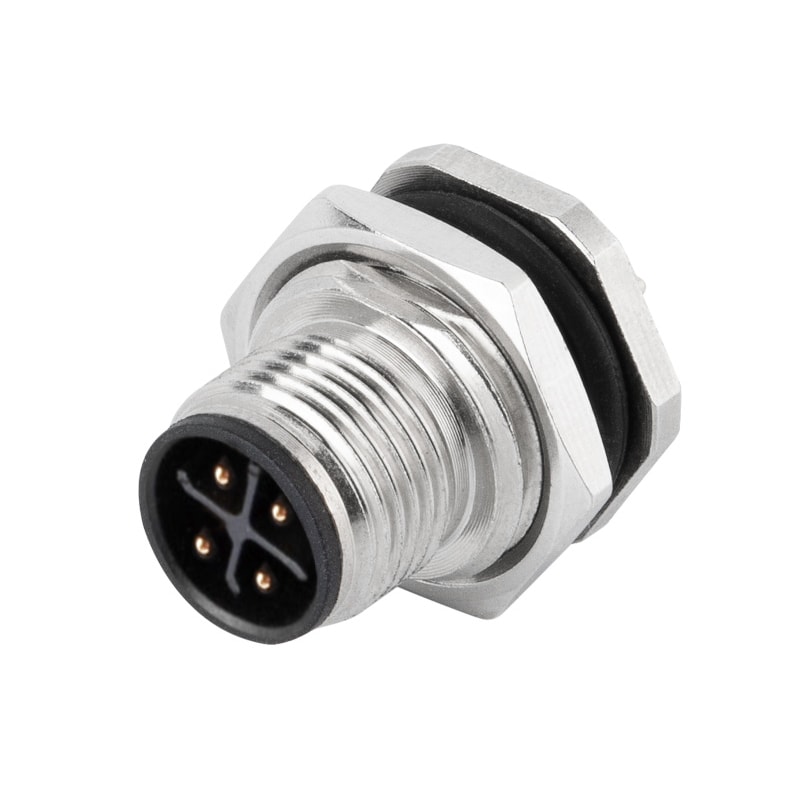

P/N: AM12M0322S001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:3(2+PE),PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0412S171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, S code, straight, IP67View All -
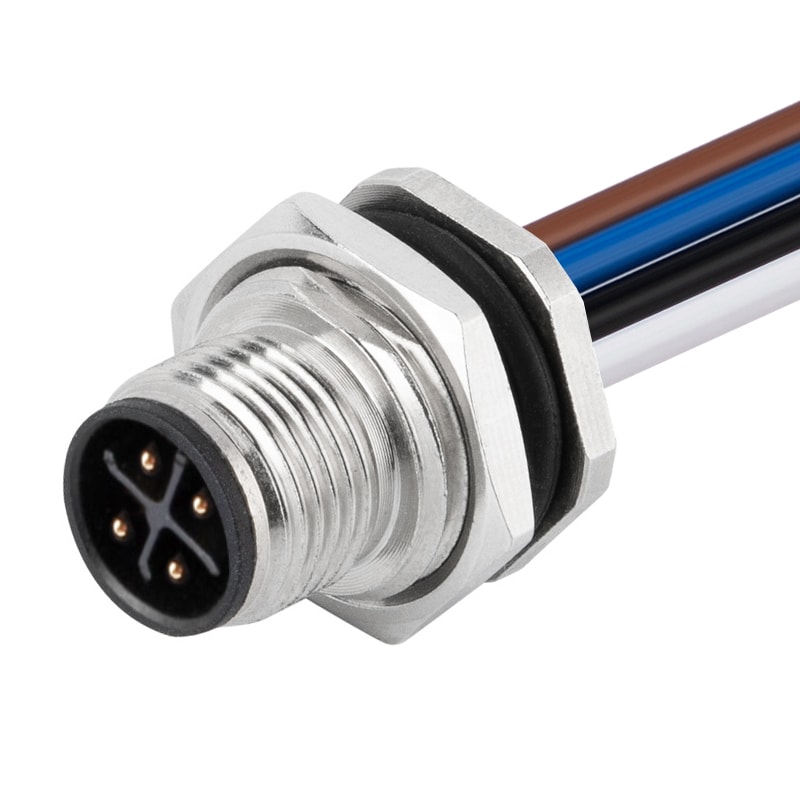

P/N: AM12M0412S171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, S code, straight, IP67View All -
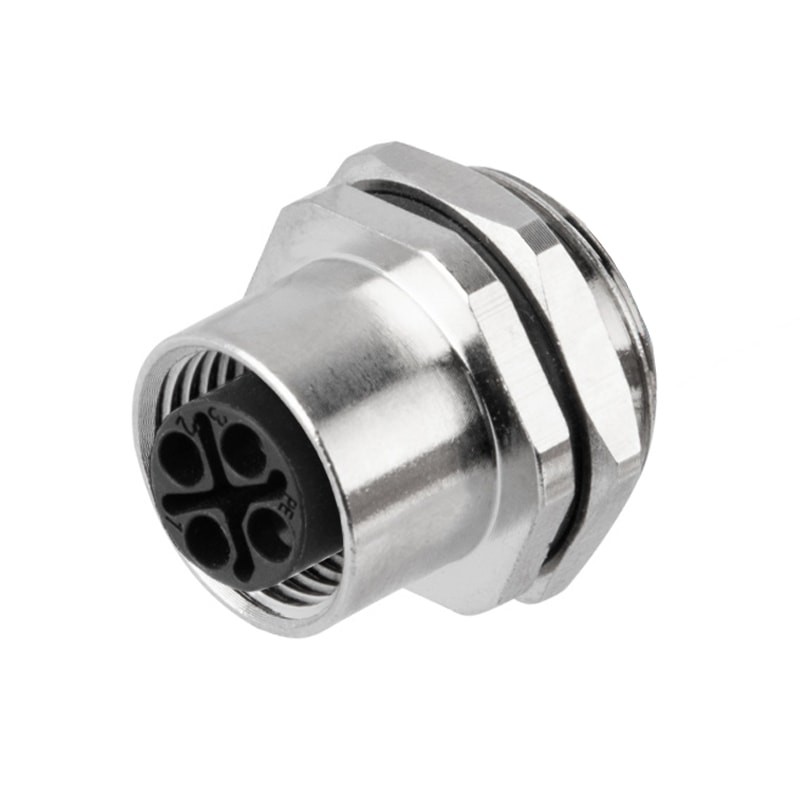

P/N: AM12F0322S001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:3(2+PE),PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -
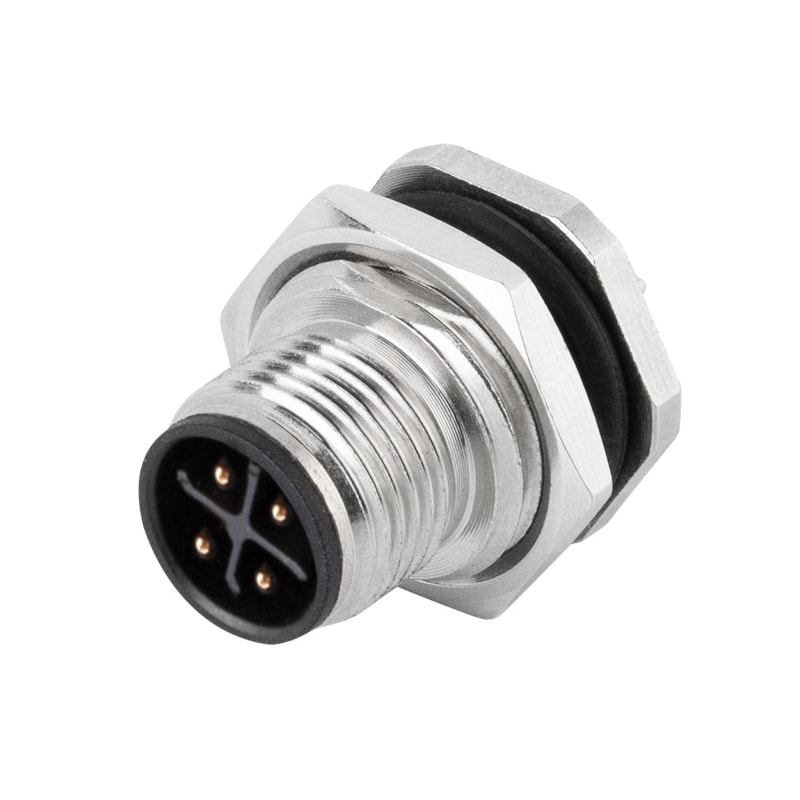

P/N: AM12M0422S001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:,4(3+PE), PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -
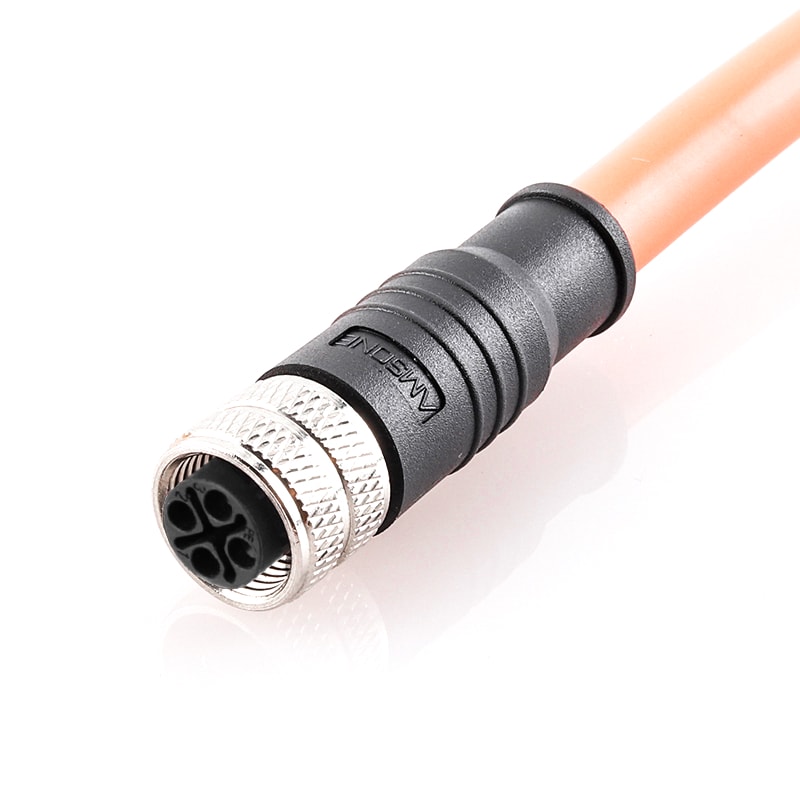

P/N: AM12F0311SXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:3(2+PE), solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -
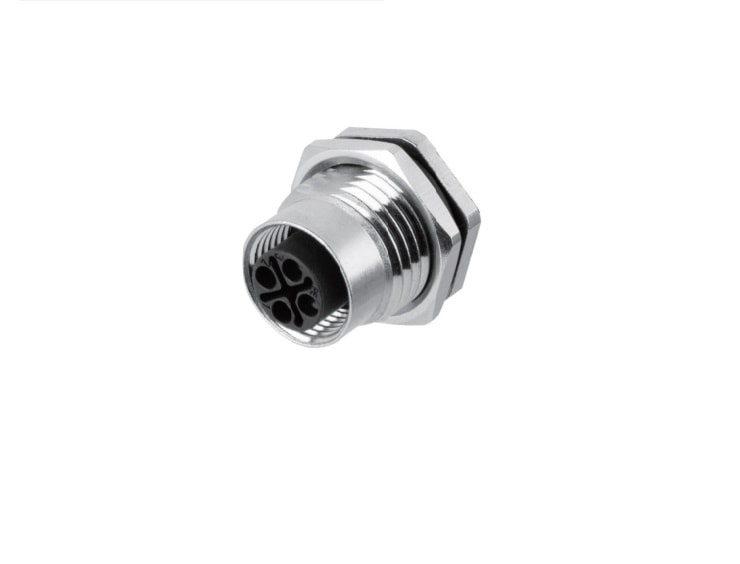

P/N: AM12F0322S002
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:3(2+PE), PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All
-

P/N: AM12M0511Lxx1-xxx
M12 L Coded Power 5P Connector Male Drag Chain Pre-Molded CableView All -

P/N: AM12M0412L171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0522L001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:5, PCB dip-solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0411LXX2-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0411LXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:4, solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0322L001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:3, PCB dip-solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0422L001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4,PCB dip-solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0311LXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:3, solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All
-

P/N: AM12M0312K171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:3,solder connection for wires, K code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0522K001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:5, PCB dip-solder connection, K code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0522K001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:5,PCB dip-solderconnection, K code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0311KXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:3, solder connection, K code, straight, IP67View All -
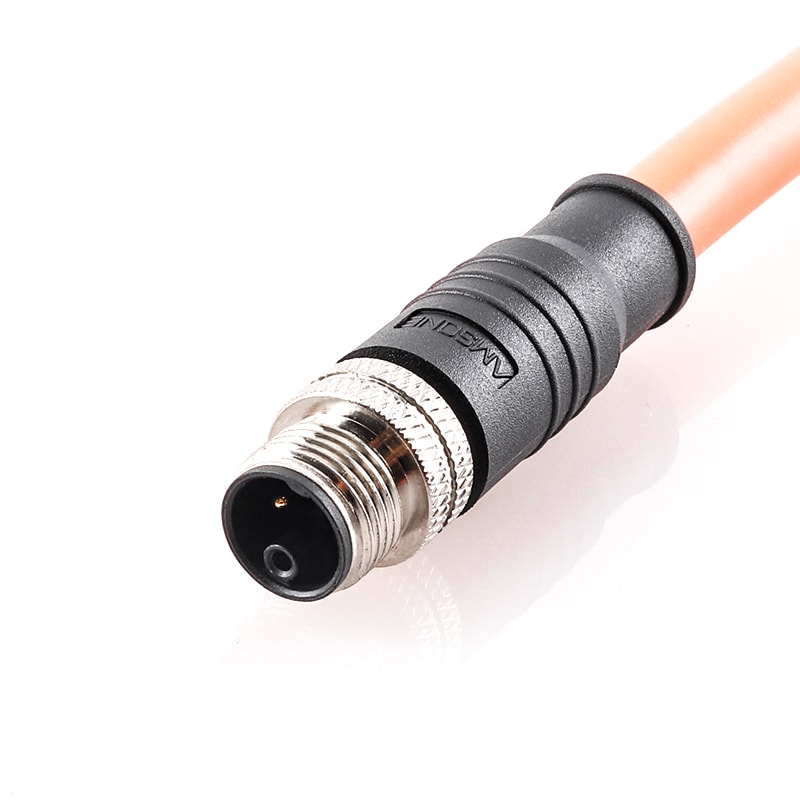

P/N: AM12M0311KXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:3, solder connection, K code, straight, IP67View All -
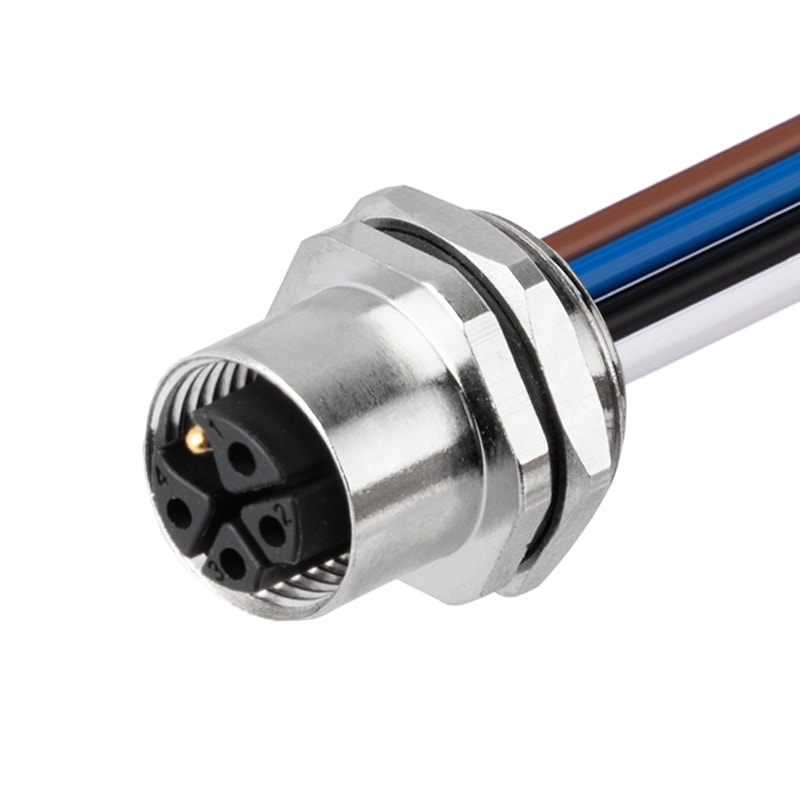

P/N: AM12F0513K371-005
M12 K Code 5P(4+PE) Female Panel Front Mount Receptacle ConnectorView All -
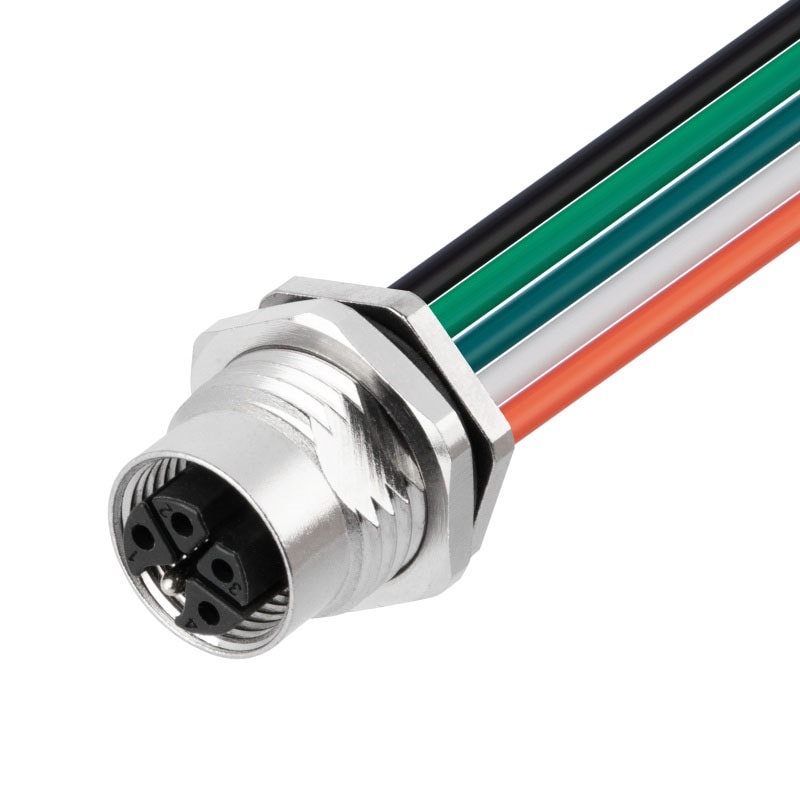

P/N: AM12F0312K171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:3, solder connection for wires, K code, straight, IP67View All
-
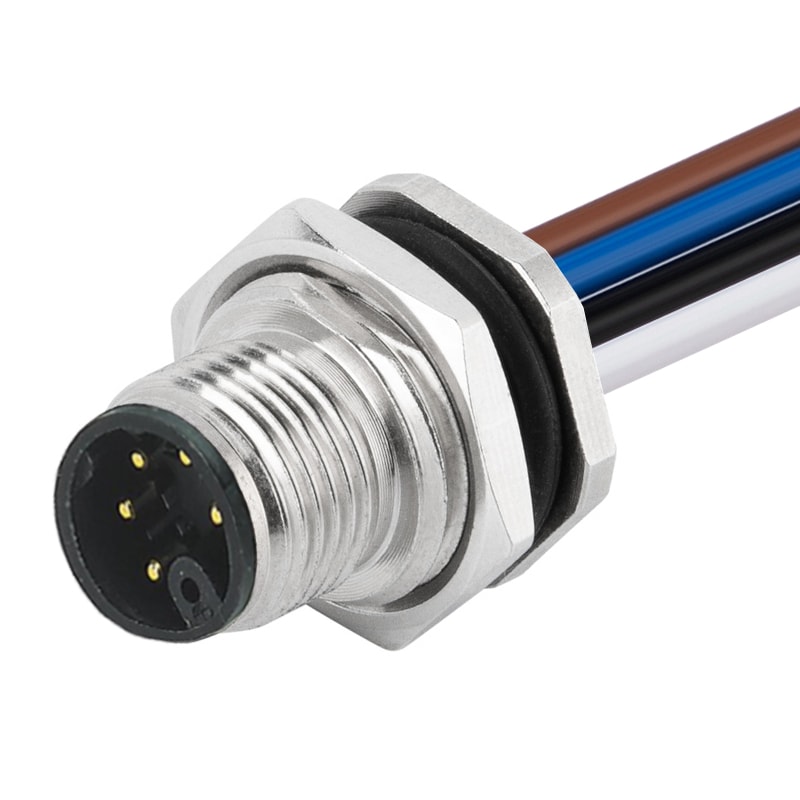

P/N: AM12M0512M371-XXX
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Male 5Pin Connector For WiresView All -

P/N: AM12F0322M001
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Female 3Pin PCB ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM12F0612M171-XXX
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Female 6Pin Connector For WiresView All -

P/N: AM12M0612M371-XXX
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Male 6Pin Connector For WiresView All -

P/N: AM12M0522M001
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Male 5Pin PCB ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM12F0611MXX1-XXX
M12 M Code 5+PE Pre-molded Cable 6Pin Female Straight ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM12M0611MXX1-XXX
M12 M Code 5+PE Pre-molded Cable 6Pin Male Straight ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM12F0522M001
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Female 5Pin PCB ConnectorView All
-

P/N: AM09F0522A001
M9 Connector Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female 5Pole PCB Dip-solderView All -

P/N: AM09F0411A001
M9 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM09F0311A001
M9 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts: 3, solder connection, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM09F0822A001
M9 Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle 8Pin PCB Waterproof ConnectorView All -
P/N: AM09F0422A001
M9 4P Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle PCB Waterproof ConnectorView All -
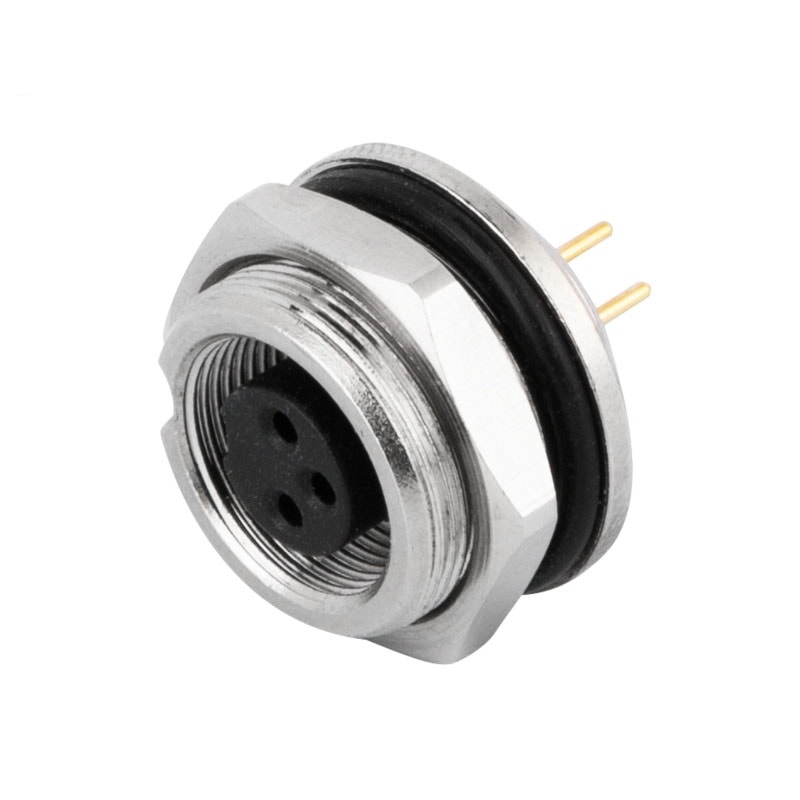

P/N: AM09F0322A001
M9 3Pole Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle PCB Waterproof ConnectorView All -
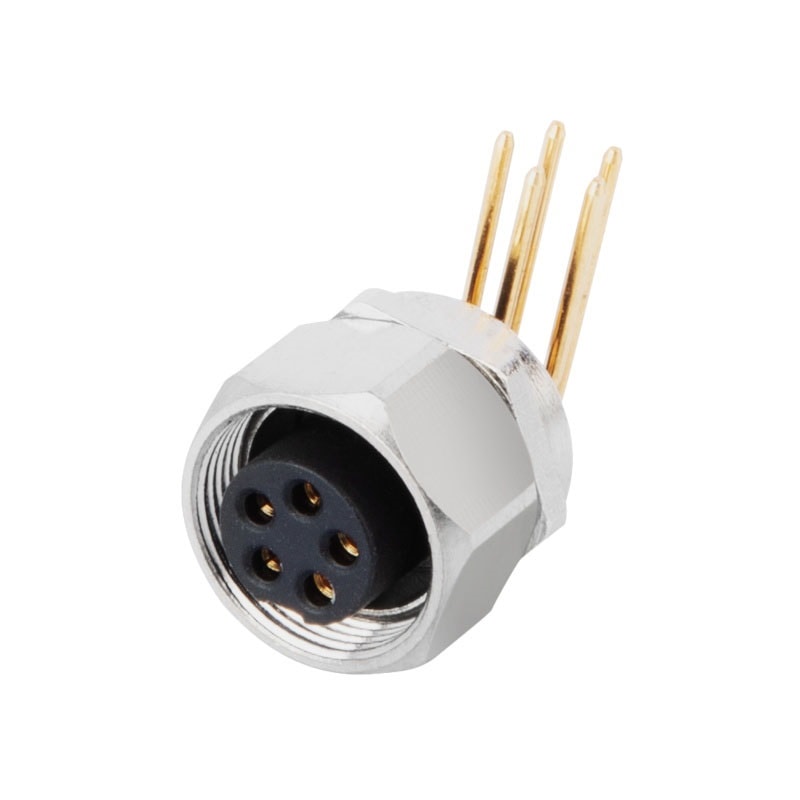

P/N: AM09F0522A201
M9 Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle 5Pin PCB Connector Right AngledView All
-
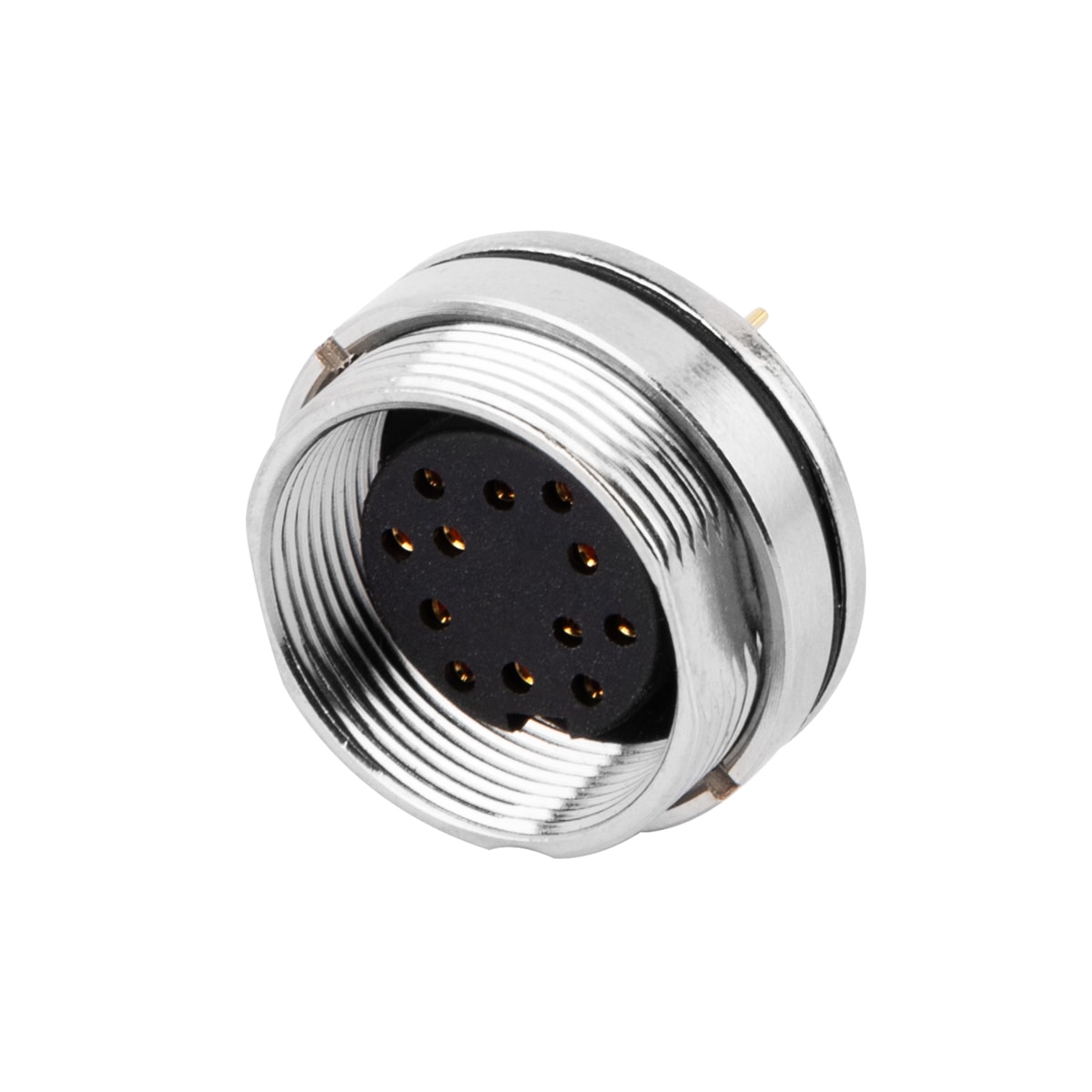

P/N: AM16F2422A001
M16 panel receptacle,rear mount,Female, contacts:24, PCB dip- solder connection,straight,IP67,UL certifiedView All -
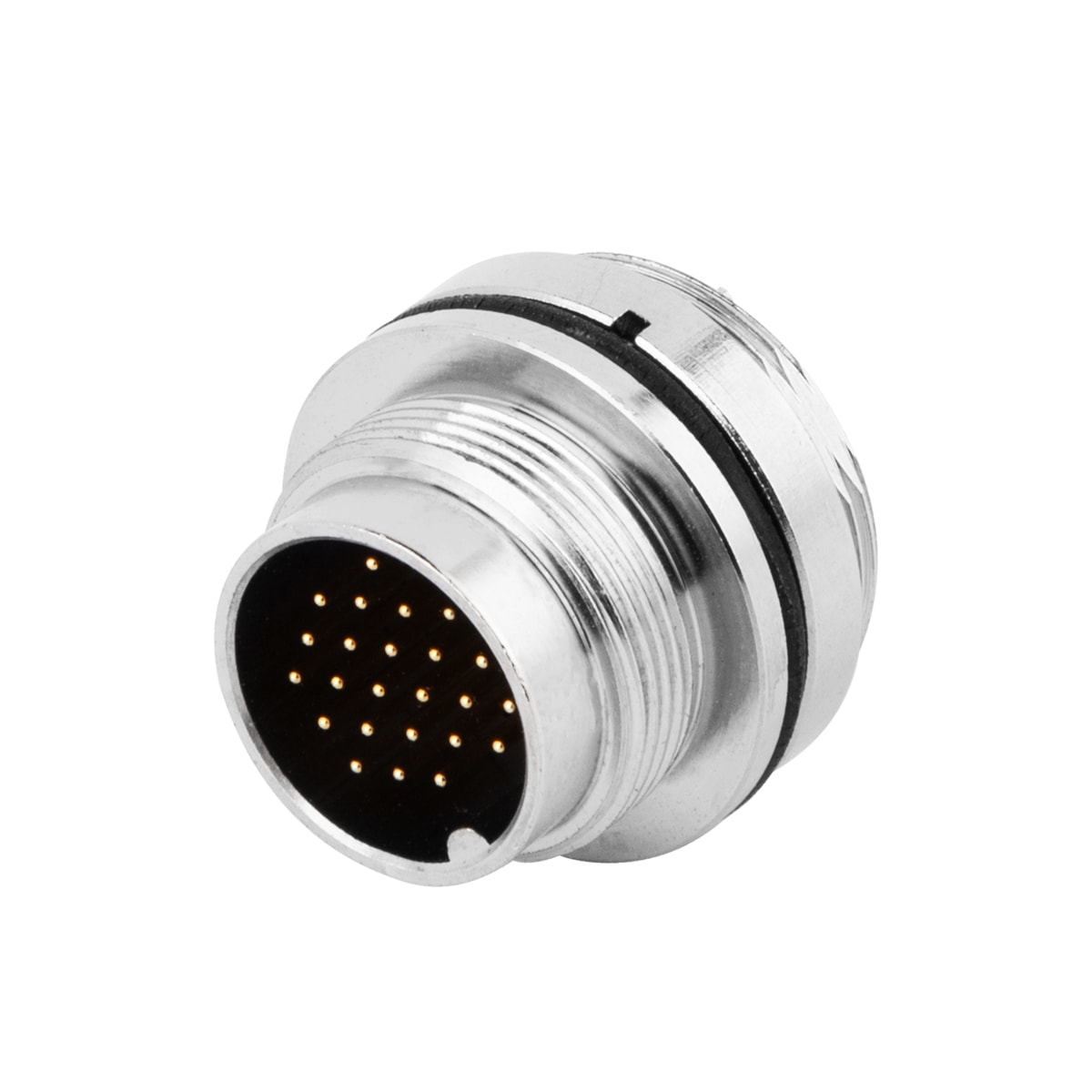

P/N: AM16M2422A001
M16 panel receptacle,rear mount,male, contacts:24, PCB dip- solder connection,straight,IP67,UL certifiedView All -
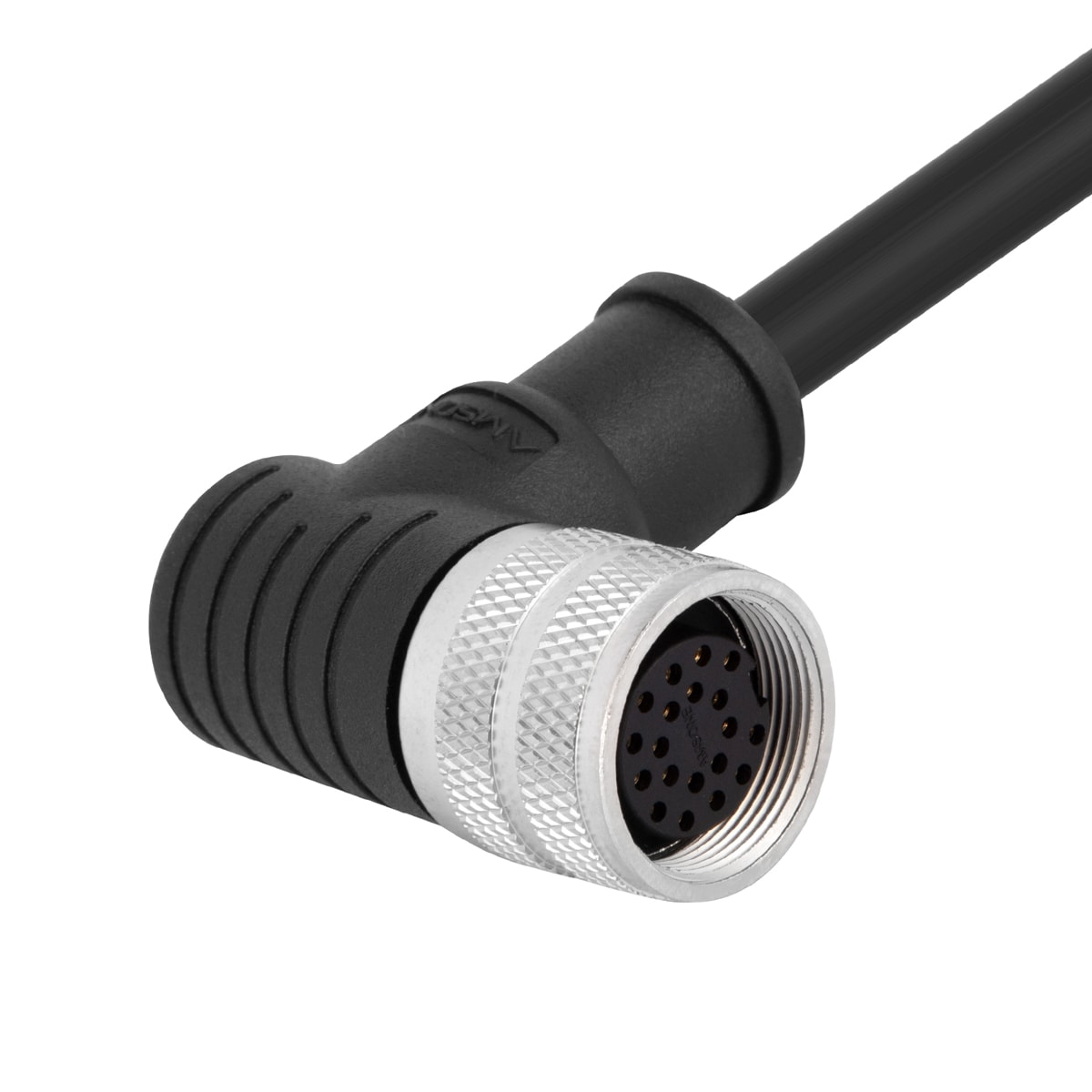

P/N: AM16F2411AXX2-XXX
M16 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:24, solder connection, right angled, IP67, shieldable, UL certifiedView All -
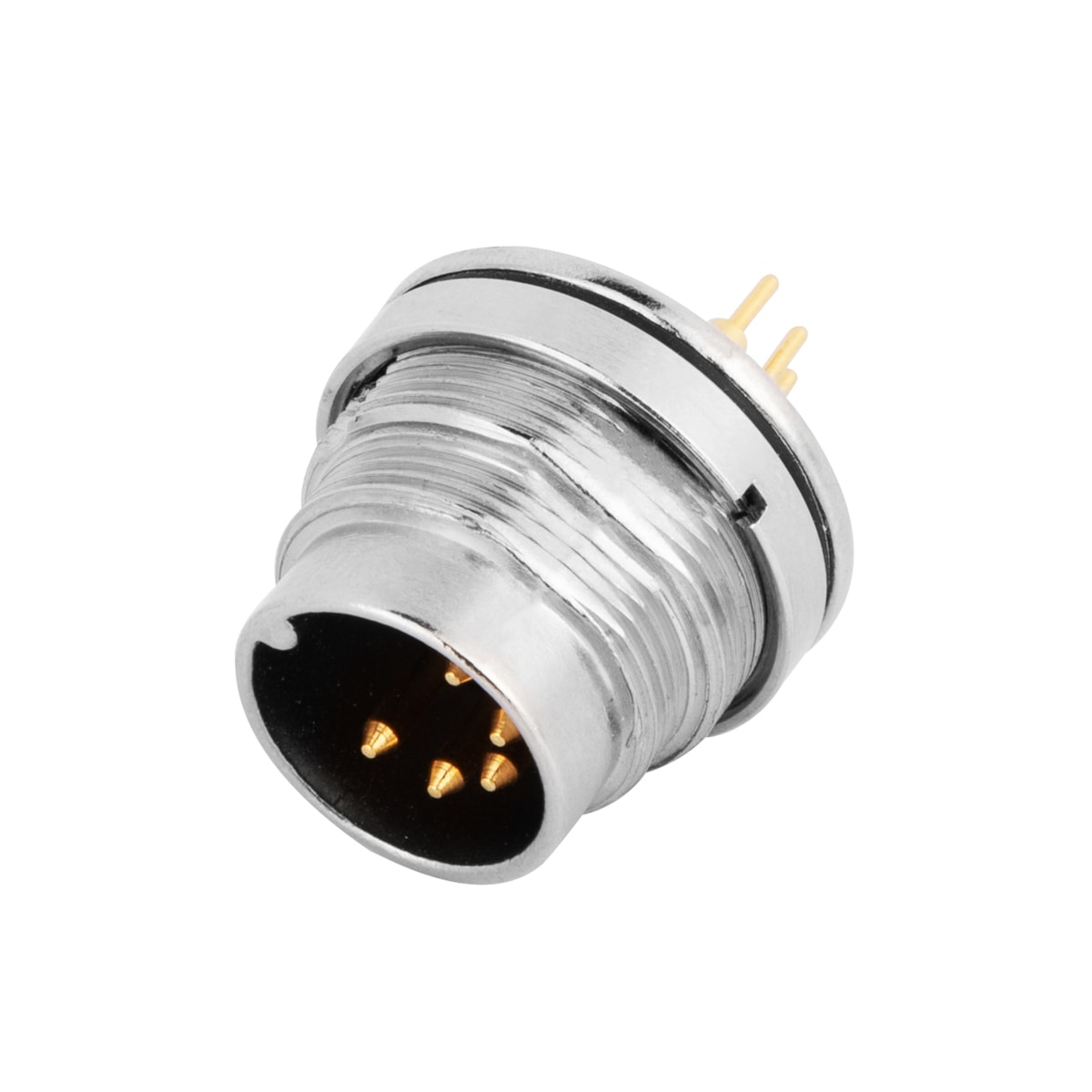

P/N: AM16M0522B001
M1M16 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:5, PCB dip-solderconnection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All -
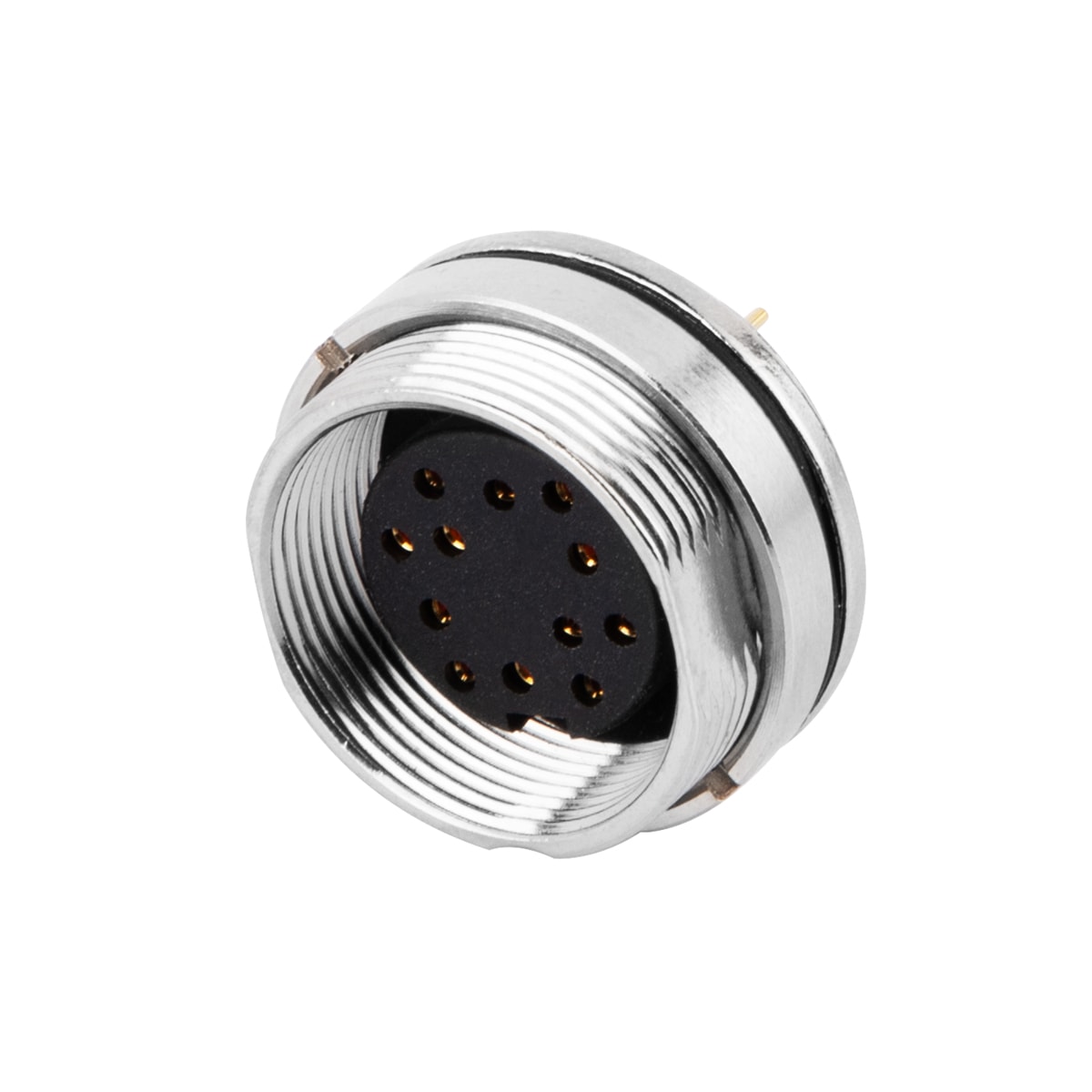

P/N: AM16F1222A001
M16 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:12,PCB connection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All -
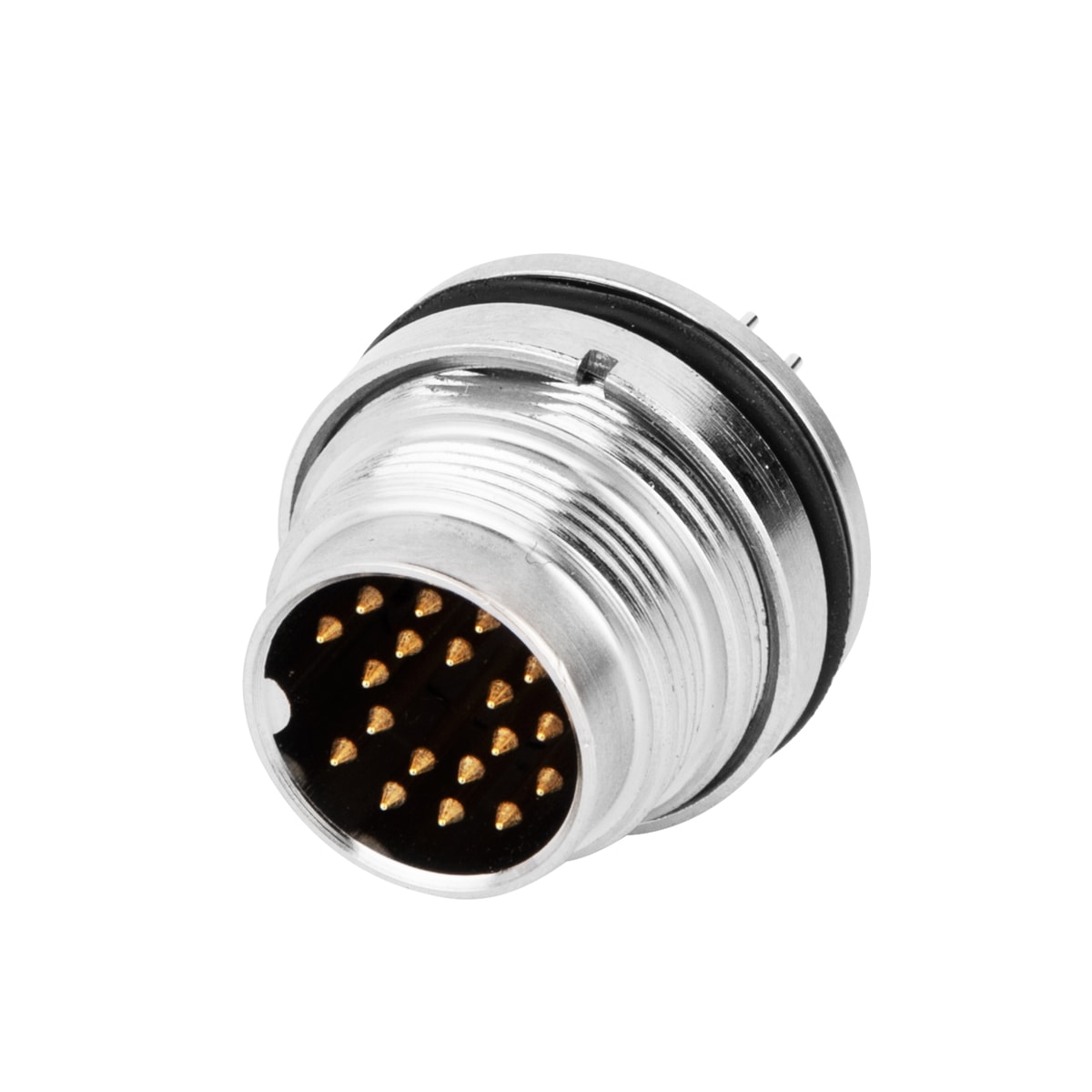

P/N: AM16M1222A001
M16 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:12,PCB dip-solder connection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All -

P/N: AM16M2411AXX1-XXX
M16 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:24, solder connection, straight, IP67, shieldableView All -

P/N: AM16M1214A001
M16 cable connector, male, contacts:12,field assembly type, solder connection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All
-
P/N: AM78F0511A162-010
MINI-Change 7/8View All -
P/N: AM78M0522A001
MINI-Change 7/8-16UNF Panel Rear Mount Receptacle Male 5Pin PCB ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM78F0412A371-050
7/8View All -

P/N: AM78M0412A371-050
7/8View All -

P/N: AM78F0512A371-050
7/8View All -
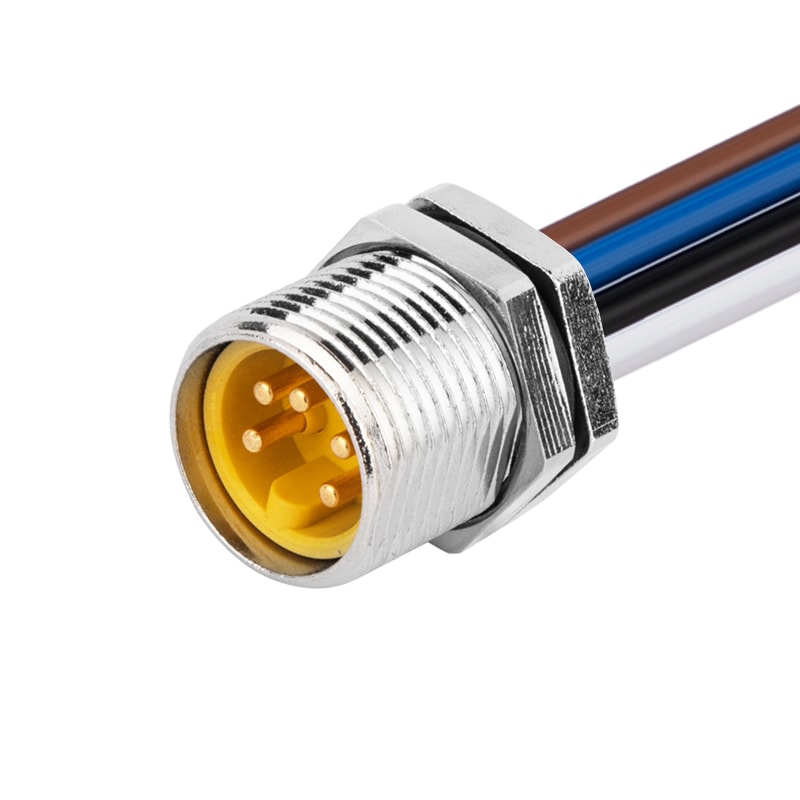

P/N: AM78M0512A371-050
7/8View All -
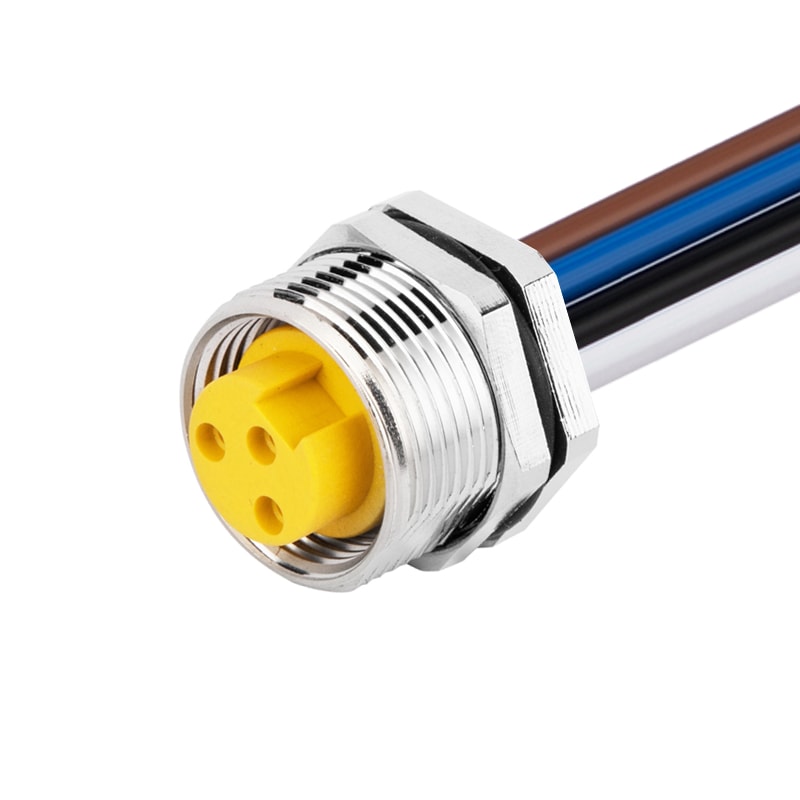

P/N: AM78F0312A371-050
7/8View All -
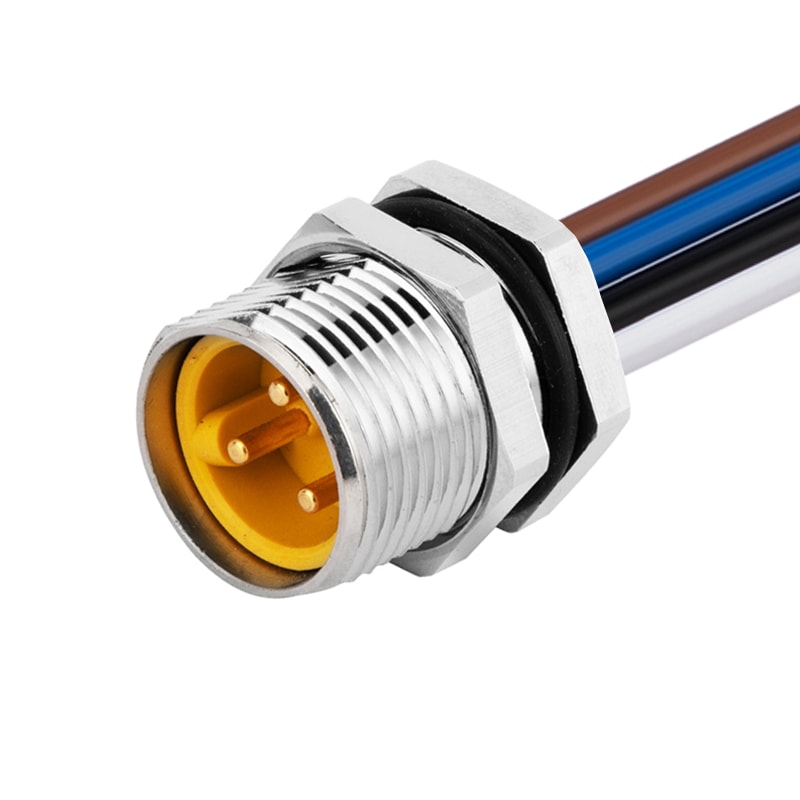

P/N: AM78M0312A371-050
7/8View All
-
P/N: AM23M1912A002
M23 Panel Receptacle Rear Mount Male 19P(16+3) Solder Connection For Wires Straight IP67View All -
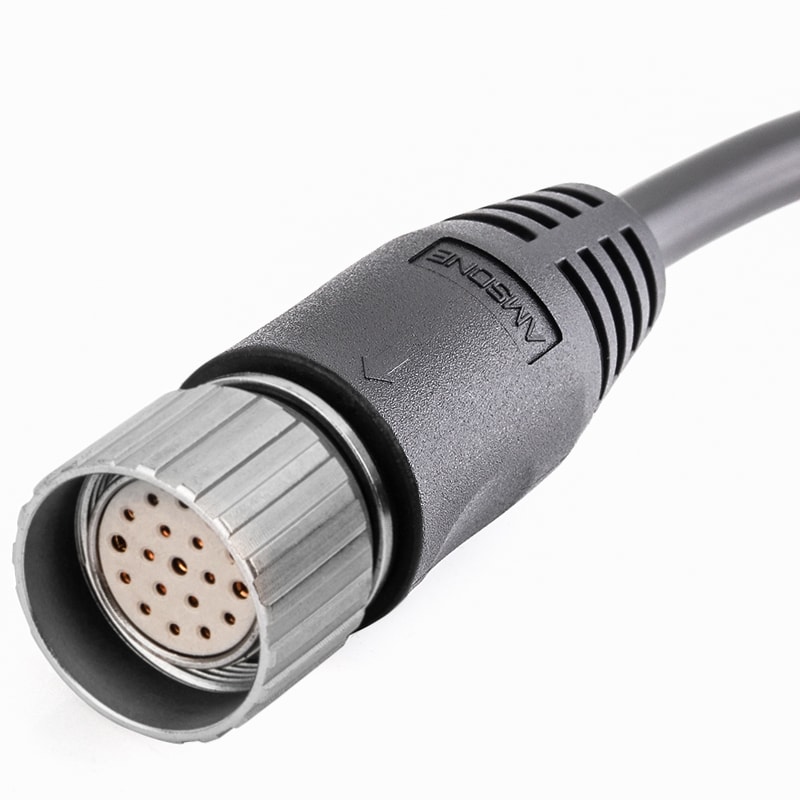

P/N: AM23F1911AXX1-XXX
M23 Pre-molded Cable Connector Female 19P(16+3) Solder Connection Straight IP67View All -
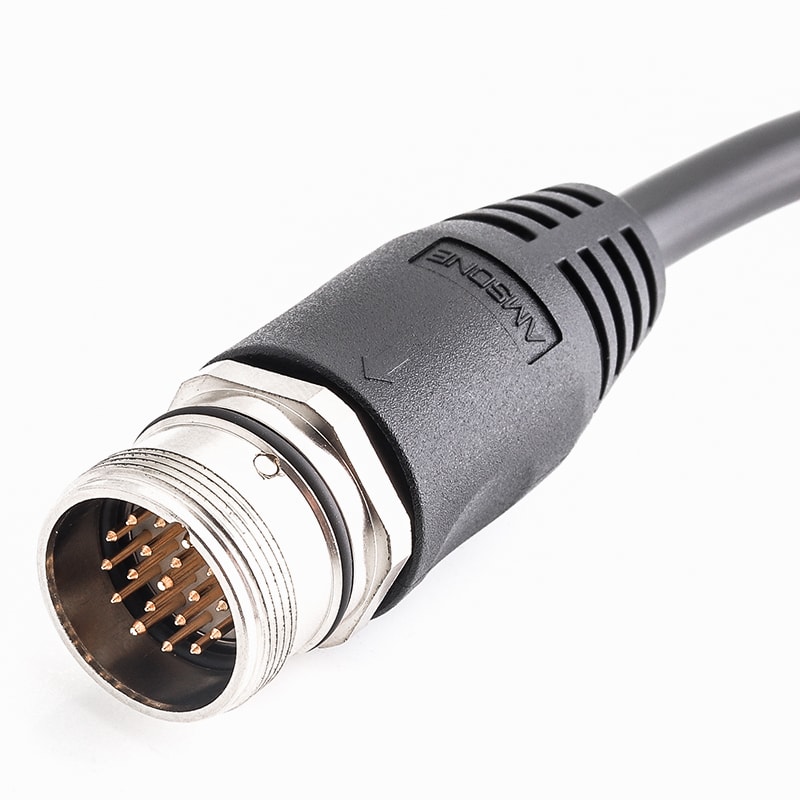

P/N: AM23M1911AXX1-XXX
M23 Pre-molded Cable Connector Male 19P(16+3) Solder Connection Straight IP67View All
-
P/N: BM24F0212A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 2P Receptacle Panel Mount Solder ConnectView All -
P/N: BM24M0214A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 2P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24M0314A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 3P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24F0312A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 3P Receptacle Panel Mount Solder ConnectView All -
P/N: BM24M0414A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 4P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24F0412A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 4P Receptacle Panel Mount Solder ConnectView All -
P/N: BM24M1214A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 12P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24F1222A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 12P Receptacle Panel Mount PCB ConnectView All
Industrial Cable Harnesses
-

P/N: AM12F0411D241-010
M12 4P D Code Pre-molded Cable Connector Female Straight IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0411D241-010
M12 pre-molded cable connector male solder connection D code straight IP67View All -
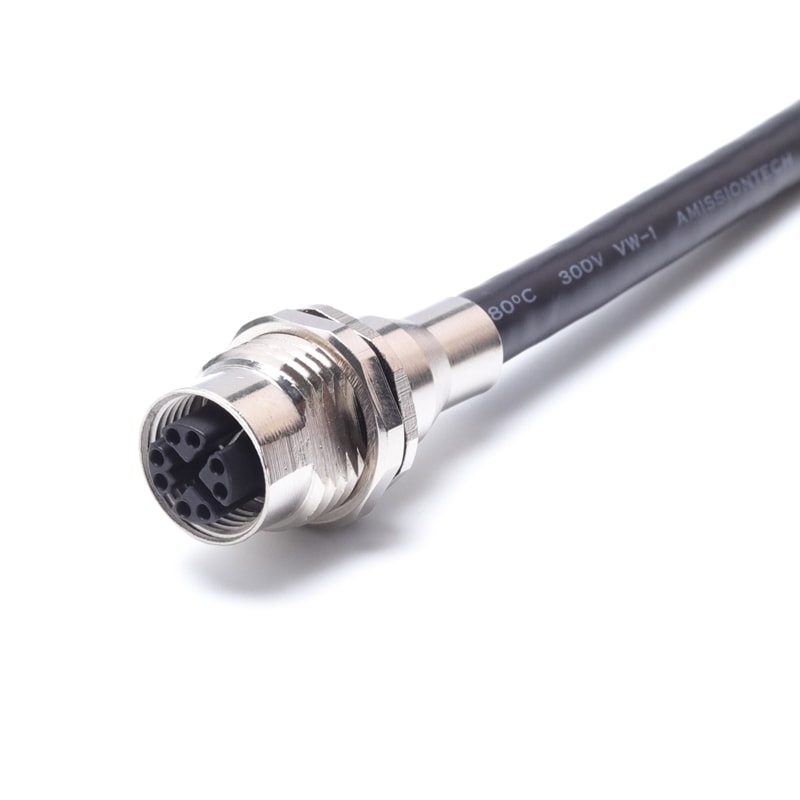

P/N: AM12F0812X003
M12 Device Connector X Code Female EMC Shielded Panel Rear Mount ReceptacleView All -
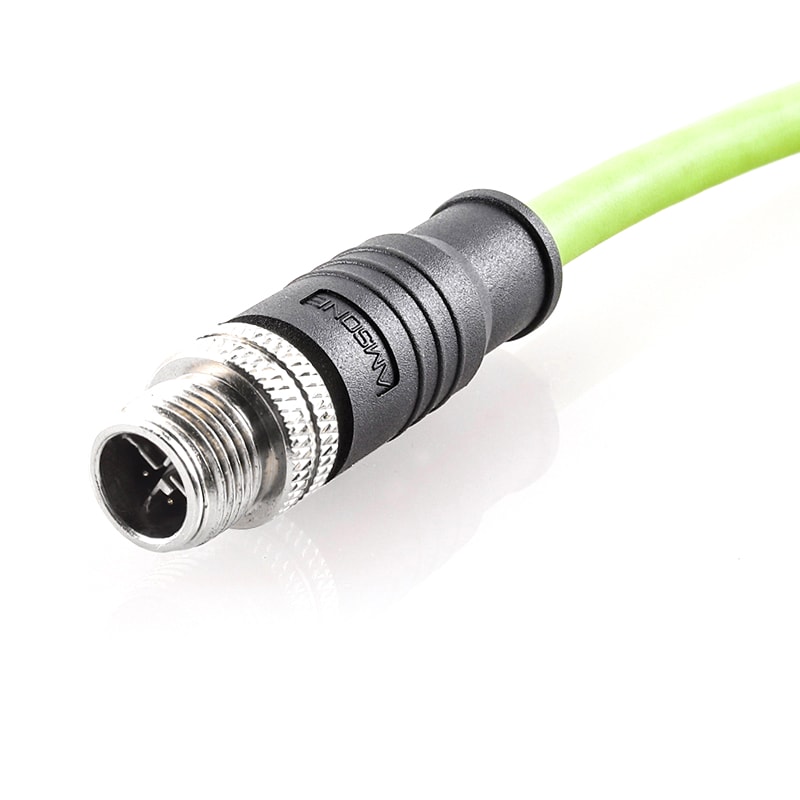

P/N: AM12M0811X231-030
M12 Pre-molded Cable Connector 8Pole Male X Code Cable StraightView All -
P/N: AM12F0411BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -
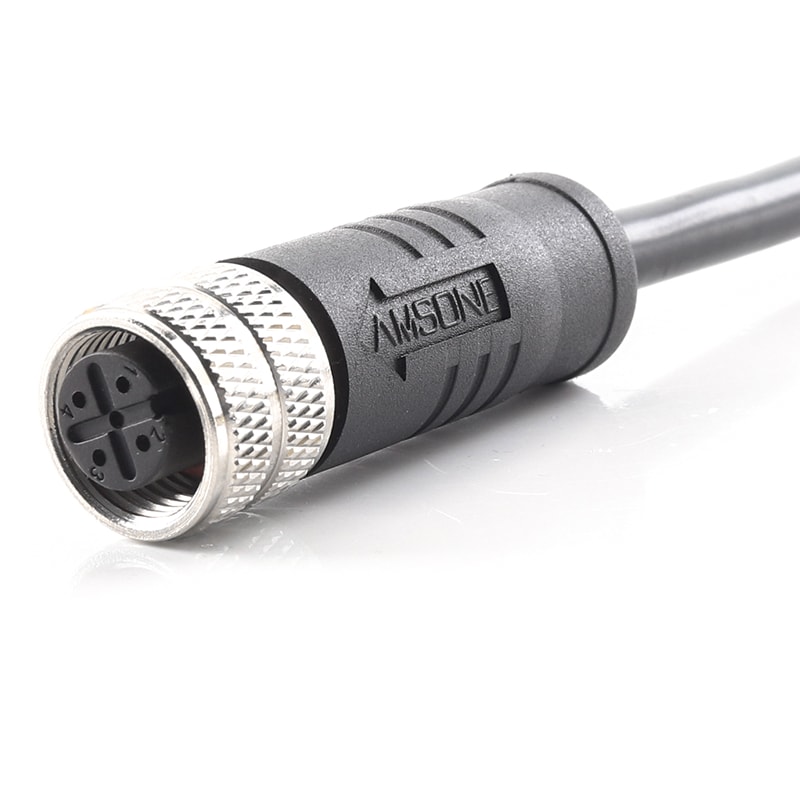

P/N: AM12F0511A241-010
M12 FieldBUS Cable Industrial Automation DeviceNet CanOpen CableView All -
P/N: EhterNet Cable
EhterNet Cable CAT5/CAT6/CAT7 PROFIBUS Industrial Network cableView All -

P/N: AM12M0814X221-010
M12 X Code Male ProfiNET/EtherNET Cable M12 Connector X CodedView All
-

P/N: AM12F0411D241-010
M12 4P D Code Pre-molded Cable Connector Female Straight IP67View All -

P/N: AM78M0411A272-050
DeviceNET 7/8View All -
P/N: AM12F0411BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0511A241-010
M12 FieldBUS Cable Industrial Automation DeviceNet CanOpen CableView All -

P/N: AM78M0511A172-030
MINI-Change 7/8View All
-

P/N: AM12M0411D241-010
M12 pre-molded cable connector male solder connection D code straight IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0812X003
M12 Device Connector X Code Female EMC Shielded Panel Rear Mount ReceptacleView All -

P/N: AM12M0811X231-030
M12 Pre-molded Cable Connector 8Pole Male X Code Cable StraightView All -
P/N: EhterNet Cable
EhterNet Cable CAT5/CAT6/CAT7 PROFIBUS Industrial Network cableView All -

P/N: AM12M0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Male,M12 Y-Coded Power Signal Ethernet CableView All -

P/N: AM12F0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Power Signal,M12 Y-Coded CablesView All -

P/N: AM12F0812Y003
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Panel Mount Shielded,M12 Y-CodedView All
-

P/N: AM78H0511A433-XXX
Electrical Automation Power Supply Connector Cable 7/8-16UNF Pre-molded H-SplitterView All -

P/N: AM12H0811AXX1-XXX
M12 A Code 8P/4P Connector Y-Splitter Industrial Automation Sensor CableView All -

P/N: AM08Y0411A001-000
M8 Y-Splitter Electrical Automation Sensor Connector AdapterView All
Underwater Connectors and Cables
-

P/N: RMK5F
RMK5F 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 And 8 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: MCDLS-F
MCDLS-F 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 8 contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: MCBH5MTI
MCBH5MTI 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 And 8 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: HPBH9M
HPBH9M 9 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: HF75 50CXBH6F
HF75 50CXBH6F 6 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: DMCIL13F M
DMCIL13F M 13 contacts Underwater cable connectorView All -

P/N: AWQ7-42
AWQ7-42 24, 28, 32, 36, 42 contacts Underwater cable connectorView All -

P/N: 1L25F M
1L25F M Circular 12, 16, 25 Contacts Underwater ConnectorView All
company
News
-
 Amissiontech to Showcase Smart Interconnection Solutions at SPS 2025 in NurembergView All
Amissiontech to Showcase Smart Interconnection Solutions at SPS 2025 in NurembergView All -
 2025 Tokyo International Manufacturing Expo: A Perfect ConclusionView All
2025 Tokyo International Manufacturing Expo: A Perfect ConclusionView All -
 Amissiontech to Showcase Advanced Industrial Connectors and I/O Solutions at Manufacturing World Japan 2025View All
Amissiontech to Showcase Advanced Industrial Connectors and I/O Solutions at Manufacturing World Japan 2025View All -
 Amissiontech Reflects on a Successful Participation at ProPak China 2025View All
Amissiontech Reflects on a Successful Participation at ProPak China 2025View All -
 Amissiontech Team-Building Activity at Hailing IslandView All
Amissiontech Team-Building Activity at Hailing IslandView All -
 Dragon Boat Festival Greetings: Celebrating Tradition with AmissiontechView All
Dragon Boat Festival Greetings: Celebrating Tradition with AmissiontechView All -
 Celebrating Women at Amissiontech on International Women’s DayView All
Celebrating Women at Amissiontech on International Women’s DayView All -
 Amissiontech Invites You to HANNOVER MESSE 2025View All
Amissiontech Invites You to HANNOVER MESSE 2025View All
-
 Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All
Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All -
 What is an M12 A coded connector?View All
What is an M12 A coded connector?View All -
 What Do You Know M12 B Coded?View All
What Do You Know M12 B Coded?View All -
 Revolutionizing Field I/O Signal Transmission with Amissiontech's IO-Link HUBView All
Revolutionizing Field I/O Signal Transmission with Amissiontech's IO-Link HUBView All -
 Exploring the Technology Behind Underwater Connectors and CablesView All
Exploring the Technology Behind Underwater Connectors and CablesView All -
 Amissiontech's IO-LINK Modules Shine at HANNOVER MESSE 2024View All
Amissiontech's IO-LINK Modules Shine at HANNOVER MESSE 2024View All -
 Circular ConnectorView All
Circular ConnectorView All -
 IO-Link Module - Connects Future Digital CommunicationsView All
IO-Link Module - Connects Future Digital CommunicationsView All
-
 Understanding Ethernet MHz Speed and Its Impact on Network PerformanceView All
Understanding Ethernet MHz Speed and Its Impact on Network PerformanceView All -
 Top 10 Cable Types and Their UsesView All
Top 10 Cable Types and Their UsesView All -
 HDMI vs VGA: Understanding the Key Differences for Industrial & Custom Cable ApplicationsView All
HDMI vs VGA: Understanding the Key Differences for Industrial & Custom Cable ApplicationsView All -
 Complete Guide to Ethernet Cable CategoriesView All
Complete Guide to Ethernet Cable CategoriesView All -
 Wire Harness Production ExplainedView All
Wire Harness Production ExplainedView All -
 Industrial HDMI Shielded Cable Technology InterpretationView All
Industrial HDMI Shielded Cable Technology InterpretationView All -
 Revolutionize Automation with DeviceNet-Compatible ToolsView All
Revolutionize Automation with DeviceNet-Compatible ToolsView All -
 Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All
Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All
Industries and Solutions
Solutions
Industries
News And Events
Wire Harness Production Explained
1. Introduction
Wire harnesses are essential components in modern electrical and electronic systems, serving as the backbone for power transmission and signal communication. From automotive to aerospace, industrial equipment to consumer electronics, wire harnesses streamline complex wiring into organized, reliable assemblies.
Understanding the full production process of a wire harness — from design to manufacturing and quality control — is crucial for ensuring performance, safety, and compliance with industry standards. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the key processes involved in wire harness production, along with the critical quality requirements at each stage.
2. Overview of Wire Harnesses
Definition and Function
A wire harness is a structured assembly of wires, connectors, terminals, and protective materials bundled together to transmit electrical signals and power efficiently. It simplifies installation, enhances durability, and improves system safety by preventing loose or damaged wiring.
Application Scenarios
Wire harnesses are widely used in:
Automotive (vehicles, EVs, battery systems)
Aerospace (avionics, flight control systems)
Industrial machinery
Medical devices
Consumer electronics
Each application demands specific material choices, structural designs, and performance criteria.

3. Design Phase Considerations
Requirement Analysis
Before beginning the design of a wire harness, engineers must conduct a thorough analysis of both electrical and mechanical requirements. This includes evaluating:
Electrical parameters: Voltage levels, current loads, resistance, and signal integrity
Environmental conditions: Operating temperature range, humidity, exposure to chemicals or UV light, and vibration levels
Mechanical constraints: Available space, mounting points, bending radius limitations, and routing paths
This initial phase ensures that the final harness design will meet all performance expectations and fit seamlessly into the target system.
Component Selection
Selecting high-quality components is critical for long-term reliability and safety. Key components include:
Wires and Cables: Typically made from copper or aluminum, wires are selected based on current-carrying capacity, insulation type (e.g., PVC, Teflon), and flexibility.
Connectors and Terminals: Must be compatible with mating parts, resistant to corrosion, and capable of maintaining secure electrical contact under operational stress.
Insulation and Protective Materials: Used to shield wires from heat, abrasion, moisture, and electromagnetic interference (EMI). Common materials include heat-shrink tubing, braided sleeving, and corrugated conduit.
Fasteners and Clamps: These ensure proper strain relief and prevent movement that could lead to fatigue or damage over time.
Material selection should also consider industry-specific standards and certifications, such as ISO, UL, or automotive OEM specifications.
Schematic and Layout Design
Once requirements and components are defined, engineers proceed with schematic and layout design:
Schematics: Provide a logical representation of electrical connections and signal flow between components. They help in verifying the correctness of the circuit before physical assembly.
Assembly Drawings: Show the physical arrangement of wires, connectors, and protective elements. These drawings guide production teams during assembly and inspection.
Design validation involves comparing prototypes with CAD models and conducting functional tests to ensure compatibility with the end-use application.
4. Manufacturing Preparation
Material Procurement and Inspection
After design approval, the procurement process begins. The Bill of Materials (BOM) serves as the foundation for sourcing all required components.
Incoming materials undergo strict inspection to ensure compliance with specifications:
Wire gauge and insulation thickness
Connector pin alignment and plating quality
Terminal crimp dimensions
Label material durability
Digital systems may be used to record and track inspection data, ensuring traceability throughout the manufacturing process.
Assembly Documentation
To maintain consistency and accuracy during production, comprehensive assembly documentation is created, including:
Step-by-step work instructions
Illustrations and photos showing correct wiring sequences and connector orientations
Test procedures and acceptance criteria
Pegboard layouts for harness assembly
These documents serve as training tools for operators and reference guides for quality inspectors.
Prototype Development
A prototype is built and tested to validate the design before full-scale production begins. The prototype is evaluated for:
Electrical continuity and signal integrity
Mechanical strength and connector engagement
Fit within the target system
Any discrepancies found during testing are addressed through design revisions or process adjustments. Ensuring accuracy at this stage helps avoid costly changes later in production.

Wire Harness Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of a wire harness involves multiple sequential and interdependent steps. Each process must be executed with precision to ensure the final product meets design specifications, performance standards, and safety requirements.
Wire Cutting and Stripping
Process Description:
This is the first physical step in wire harness production. Wires are cut to specified lengths using automatic or semi-automatic wire cutting machines. After cutting, insulation is removed from the ends of the wires through a stripping process that exposes the conductor for crimping or soldering.
Quality Requirements:
Accurate length control (typically ±1 mm)
Clean stripping without nicking or fraying the conductor
Consistent insulation removal to ensure proper contact during termination
Use of magnification tools for visual inspection when necessary
Proper wire preparation is essential to avoid electrical failures or mechanical weaknesses later in the assembly.
Crimping and Soldering
Process Description:
Crimping is the most common method used to attach terminals to stripped wires. A crimping tool compresses the terminal around the conductor to form a secure mechanical and electrical connection. In some cases, especially where high reliability is required, soldering may be used either as an alternative or in combination with crimping.Quality Requirements:
Correct crimp height and force based on terminal specifications
Pull testing to verify mechanical strength (typically ≥ 40N for automotive applications)
Visual and dimensional inspection under magnification
Avoidance of over-crimping (which damages the wire) or under-crimping (which results in loose connections)
Crimped wires are often subjected to micro-section analysis to evaluate the quality of the joint.
Assembly and Routing
Process Description:
Once all wires are prepared and terminated, they are assembled into the full harness according to the design layout. This includes inserting wires into connectors, routing them along the pegboard, and securing them with clamps, brackets, or other fasteners.Quality Requirements:
Correct sequence and orientation of components
Proper labeling and identification of wires and connectors
No crossed or tangled wires
Appropriate bending radius (usually at least six times the wire diameter)
Secure mounting points to prevent movement and stress
Assembly must follow the detailed work instructions and drawings provided during the design phase.
Protective Covering
Process Description:
To enhance durability and protect against environmental factors such as abrasion, heat, and vibration, the assembled harness is wrapped or covered with protective materials. These include:Braided sleeving
Spiral wrap or corrugated tubing
Heat-shrink tubing
PVC conduit or molded boots
Quality Requirements:
Full coverage of exposed wires and sensitive areas
Even wrapping without gaps or overlaps
Secure attachment using adhesive, tape, or tie wraps
Compatibility with environmental conditions (e.g., temperature resistance, UV protection)
Protective covering must not interfere with connector insertion or wire flexibility.
Labeling and Identification
Process Description:
Each wire and connector is labeled to facilitate installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Labels can be applied using various methods, including laser-printed tags, heat-shrink labels, or direct inkjet printing.Quality Requirements:
Clear, legible, and permanent text
Accurate placement per design specifications
Durable under operational conditions (temperature, humidity, chemicals)
Consistent labeling format across the entire harness
Labeling plays a crucial role in ensuring correct installation and simplifying future diagnostics or repairs.
Quality Control and Testing
1. Incoming Material Inspection
All raw materials undergo visual and dimensional checks before use.
2. In-Process Inspection
Operators perform regular checks during assembly, including:
Terminal crimp verification
Connector insertion force
Wire routing correctness
3. Final Testing
Each finished harness is tested for:
Continuity Test: Ensures all circuits are connected properly
Hi-Pot Test: Verifies insulation integrity
Pull Test: Confirms crimp strength
Visual Inspection: Under magnification if necessary
Test results are recorded and stored for traceability.
Common Challenges and Solutions
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Space Constraints | Limited space in compact applications | Use flexible materials and optimize routing with CAD |
| Environmental Exposure | Harsh conditions (heat, moisture, vibration) | Choose resistant materials and add protective layers |
| Complex Routing | Difficult to manage many wires in tight spaces | Use simulation tools and modular design |
| Manual vs. Automated Processes | Some steps still require manual labor | Combine automation with skilled workers for best results |
Future Trends in Wire Harness Manufacturing
1. Automation Integration
Modern manufacturers increasingly adopt automated solutions such as:
Automatic crimping machines
Wire cutting and stripping robots
Intelligent testing systems
Automation increases efficiency, reduces errors, and improves consistency.
2. Digital Transformation
Implementing MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) allows for real-time monitoring, data tracking, and improved process control.
3. Customization and Flexibility
With growing demand for tailored products, manufacturers are investing in modular platforms and agile production lines that support rapid prototyping and customization.
Conclusion
Wire harness production is a multi-step process that requires careful planning, precision execution, and rigorous quality control. From initial design and component selection to final testing and delivery, every stage plays a role in ensuring the reliability and performance of the end product.
By understanding the key manufacturing steps and implementing strict quality requirements, companies can produce wire harnesses that meet diverse industry needs while maintaining high standards of safety, efficiency, and compliance.
Looking for a reliable wire harness manufacturer?
Amissiontech specializes in custom wire harness solutions with full in-house capabilities—from design and prototyping to precision assembly and 100% electrical testing. Whether your application is in automation, medical, transportation, or industrial equipment, we deliver high-quality, cost-effective interconnection solutions tailored to your needs.







































