When choosing the right video interface for your industrial systems or custom cable harness solutions, it’s important to understand the core differences between HDMI and VGA. These two technologies serve the same basic purpose—transmitting video signals—but they differ significantly in performance, compatibility, and application. This article explores both interfaces in detail to help you make a well-informed decision for your project.
What Is HDMI? A Modern Digital Video and Audio Interface
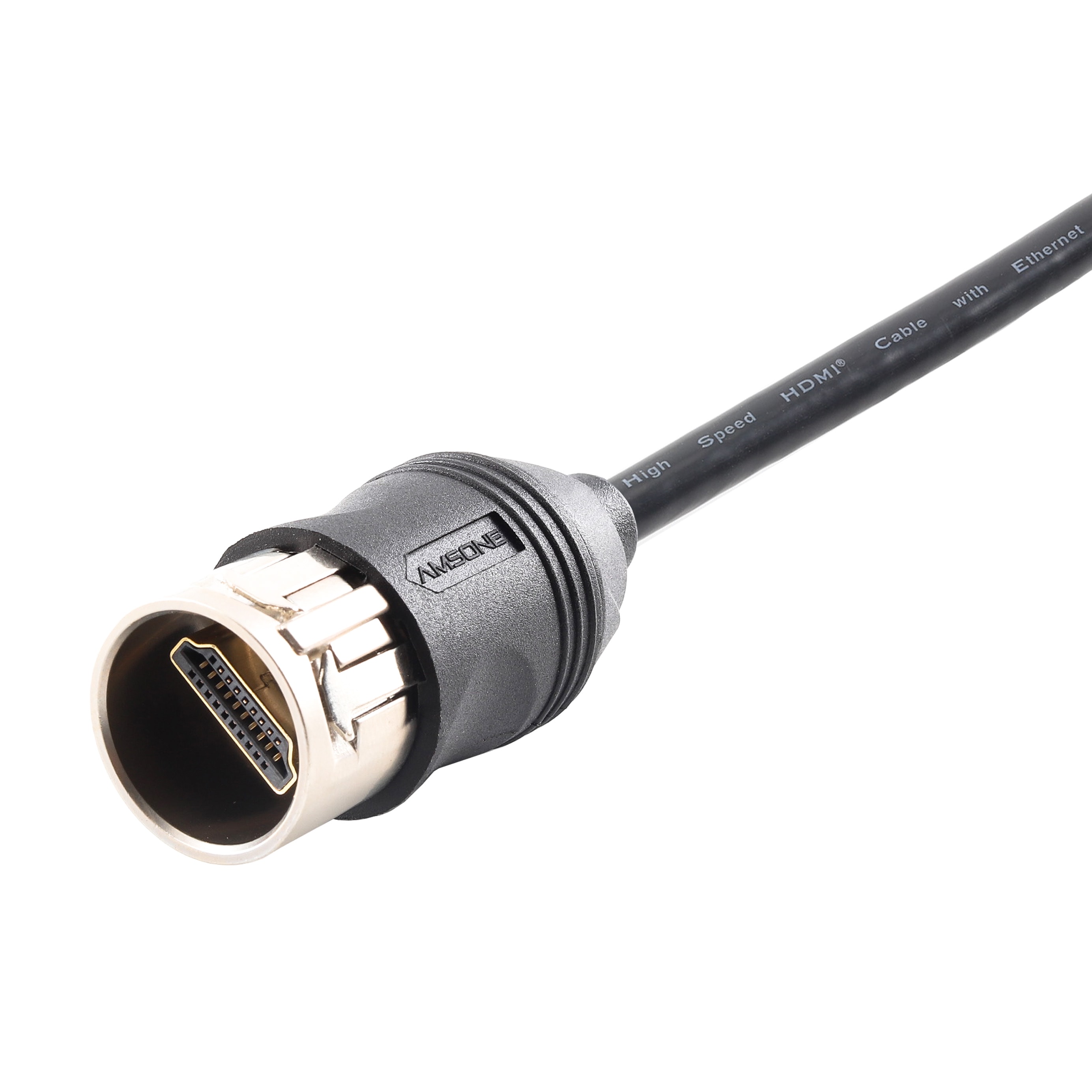
Let’s begin with HDMI, which stands for High-Definition Multimedia Interface. It’s a widely adopted standard used to transmit both high-quality video and audio through a single cable. HDMI is commonly found in TVs, monitors, laptops, set-top boxes, and industrial display systems.
Unlike older interfaces, HDMI supports digital signals, enabling it to deliver high-resolution content such as 1080p and 4K. Many modern devices rely on HDMI for its simplicity and superior performance.
Advantages and Limitations of HDMI
HDMI cable offers several advantages for both commercial and industrial applications:
High Video Quality: With digital signal transmission, HDMI maintains image clarity and supports higher resolutions.
Audio and Video in One: HDMI can carry both video and audio signals, reducing the need for multiple cables.
Compatibility with Modern Devices: HDMI interfaces are standard on modern display equipment and embedded systems.
Advanced Features: HDMI supports HDCP (High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection), CEC (Consumer Electronics Control), and other features to enhance user experience.
However, HDMI does have limitations. Signal quality may degrade over long cable distances without amplification. Also, connecting HDMI to legacy equipment may require adapters, which could add complexity to your setup.
For those seeking a reliable HDMI cable harness for digital video interface integration, working with an experienced manufacturer is essential to ensure signal integrity and system compatibility.

What Is VGA? A Legacy Analog Video Standard
VGA, or Video Graphics Array, is one of the oldest video transmission technologies still in use. Originally developed by IBM in 1987, it transmits analog video signals using a 15-pin connector. VGA cables were once the standard for computer monitors and projectors.
While VGA has become less common in modern systems, it remains relevant in certain industrial applications that still rely on older hardware or analog video outputs.
Advantages and Limitations of VGA
VGA remains in use due to several practical benefits:
Widespread Compatibility with Older Equipment: Many legacy monitors and industrial systems still depend on VGA ports.
Cost-Effective: VGA cables and connectors are generally less expensive than HDMI alternatives.
Simplicity for Analog Displays: In older analog systems, VGA can be a straightforward choice.
On the downside, VGA’s analog signal results in lower image quality and limited resolution support. It cannot transmit audio, which means a separate cable is required for sound. Over long distances, VGA is also more prone to signal degradation.
If you're integrating a custom VGA connector into an industrial control system or machine, make sure the cable assembly is properly shielded to minimize interference.
HDMI vs VGA: Side-by-Side Technical Comparison
Understanding the technical differences can clarify when to choose one interface over the other:
| Feature | HDMI | VGA |
|---|
| Signal Type | Digital | Analog |
| Audio Support | Yes | No |
| Max Resolution | Up to 4K | Limited (~1600x1200) |
| Cable Complexity | Single cable for audio/video | Separate audio required |
| Device Compatibility | Modern systems | Legacy systems |
| Interference Resistance | High | Low |
| Advanced Functions | HDCP, CEC, ARC | Not supported |
For custom cable assembly providers like Amissiontech, designing and producing reliable industrial cable harnesses depends on accurately matching the interface type with the application environment.
Choosing the Right Interface for Industrial Cable Assemblies
The selection between HDMI and VGA should depend on the system requirements and usage environment:
Choose HDMI if your system demands high-definition output, integrated audio, and compatibility with modern digital displays.
Select VGA if you are working with older equipment that only supports analog signals or needs basic video output.
Whether your project involves embedded systems, control cabinets, machine vision setups, or industrial displays, the right custom video interface will impact performance, stability, and integration.

Real-World Applications of HDMI and VGA in Industrial Settings
In actual industrial applications, HDMI and VGA are not only used for office or home audio-visual equipment, but also commonly used in various industrial systems. Depending on the type of equipment and system architecture, choosing the right interface is important for image transmission stability, cost control, and long-term maintenance.
Typical HDMI applications in industry:
Human-machine interface (HMI) and touchscreen displays: Modern factories use high-definition large screens as operation control centers. HDMI interfaces ensure clear image details and fast response times, making them suitable for SCADA systems or PLC control platforms.
Connecting Industrial PCs (IPCs) to Display Devices : HDMI is widely used for connecting embedded computers, industrial servers, and high-definition displays, particularly in systems requiring high-definition video capture, image analysis, or data visualization.
Visual Inspection and Machine Vision Systems: In visual systems requiring high-resolution image feedback, HDMI is the preferred interface, supporting high-definition image transmission to aid in identifying minor defects or markings.
Control terminals for smart production lines: Modern production lines extensively use touchscreen terminals or embedded tablets with HDMI interfaces for real-time data display and command input.
Typical industrial applications of VGA:
Compatible display connections for legacy equipment: Many factories still operate machinery over ten years old, such as legacy CNC machines or industrial testing equipment, which natively only support VGA displays.
Traditional monitoring terminals and data acquisition systems: In certain non-HD video scenarios, using VGA interfaces remains cost-effective, particularly in large-scale deployments with non-HD requirements.
Backup interfaces in meeting rooms/training systems: In some factory training classrooms or meeting areas, VGA interfaces are retained for emergency use or to accommodate visitor devices.
By understanding these practical application scenarios, enterprises can make more targeted decisions when upgrading or selecting systems, choosing between HDMI or VGA. They can also combine Amissiontech's custom cable assembly services to design high-reliability connection solutions that better align with device interface requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
To help you quickly understand the usage differences and practical issues between HDMI and VGA, here are some common questions and answers:
Q1: Which is more suitable for industrial automation systems, HDMI or VGA?
A: If the device supports it, we recommend prioritizing HDMI. It can simultaneously transmit audio and video, offering higher image quality, especially suitable for modern industrial control terminals and monitoring systems. VGA is more suitable for older devices or cost-sensitive projects.
Q2: Can VGA be converted to HDMI for use?
A: Yes, but an active converter with a chip is required. Since VGA is an analog signal and HDMI is a digital signal, a simple cable cannot directly convert between them; an additional power-supply converter is needed to process the signal.
Q3: What is the maximum transmission distance for an HDMI cable?
A: Generally, the optimal distance is no more than 10 meters. For distances exceeding this, a signal amplifier or fiber optic HDMI solution is required. Amissiontech offers custom cable solutions supporting long-distance HDMI transmission.
Q4: Can VGA still be used in new projects?
A: It can still be used in projects with limited budgets or where compatibility with older equipment is required. However, if higher image quality is required, we recommend using newer technologies such as HDMI or DisplayPort.
Q5: Can VGA and HDMI be used simultaneously on the same device?
A: This depends on whether the device supports dual display output. Some industrial computers support simultaneous output of HDMI and VGA signals for different displays. This should be determined based on the specific hardware specifications.
Amissiontech: Your Partner for Custom HDMI and VGA Solutions
At Amissiontech, we specialize in both standard and custom cable assemblies, offering tailored solutions for a wide range of industries. Our in-house team handles every stage from concept to production—including cable preparation, overmolding, assembly, and testing.
Whether you need a custom HDMI cable harness, a tailor-made VGA connector, or a hybrid interface assembly, we’re ready to support your design and manufacturing needs with precision and reliability.
Conclusion: Compatibility and Performance Matter
Both HDMI and VGA serve valuable roles depending on the context. HDMI delivers superior video and audio performance for modern systems, while VGA continues to support legacy hardware effectively. Understanding their differences helps engineers and system integrators select the best-fit interface for their applications.
Looking for a reliable manufacturer for custom cable harnesses and connectors? Contact Amissiontech today to discuss your project needs.

 EN
EN DE
DE JP
JP ES
ES SE
SE FR
FR IT
IT CN
CN 한국어
한국어 ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย بالعربية
بالعربية Nederlands
Nederlands Türkçe
Türkçe Język polski
Język polski Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Zulu
Zulu Bahasa Malay
Bahasa Malay


