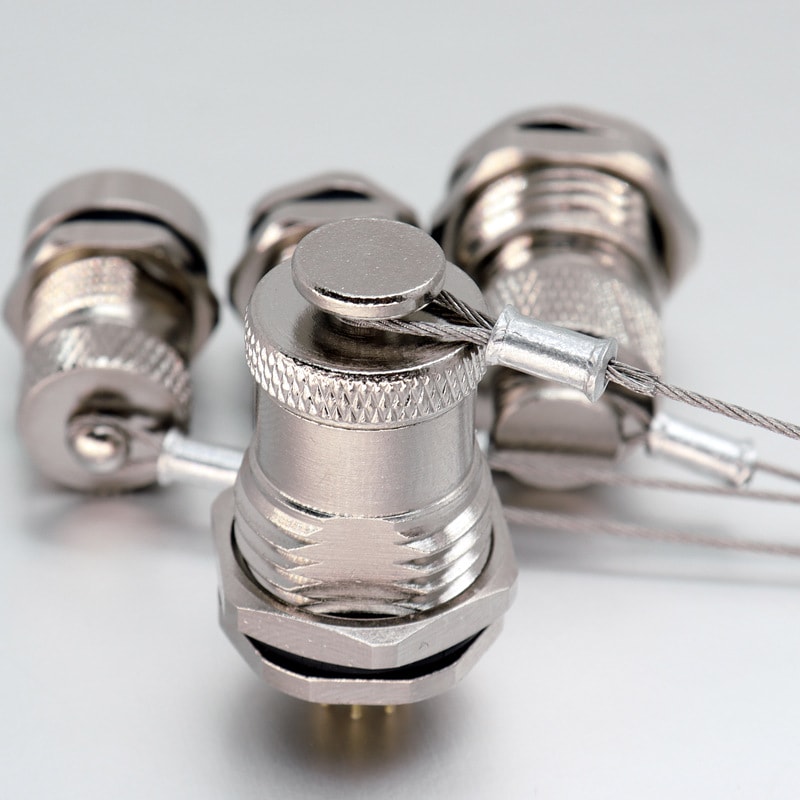
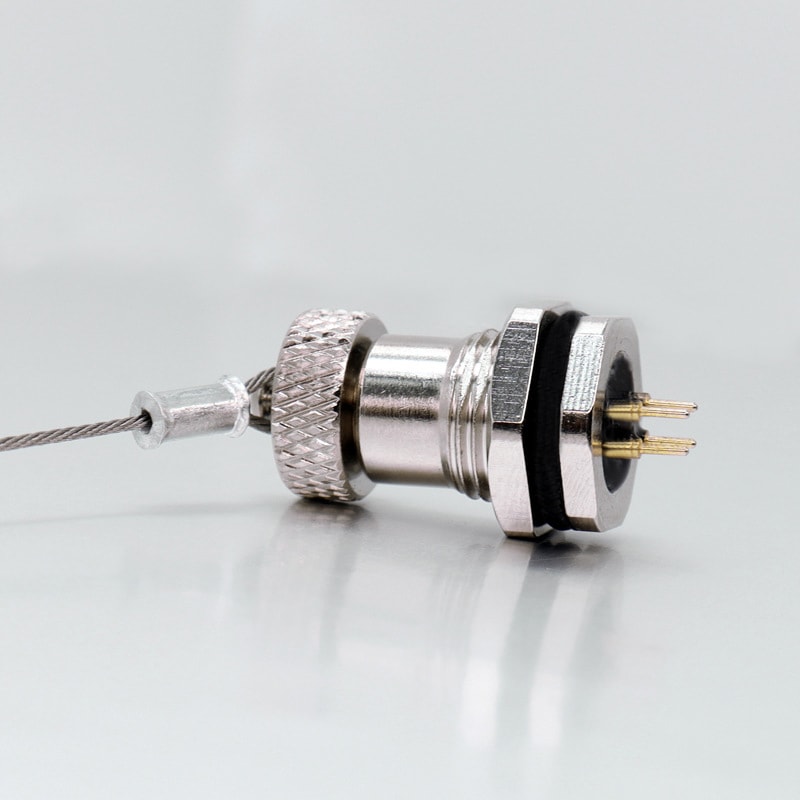
Products
I/O Systems
-
 IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All
IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All -

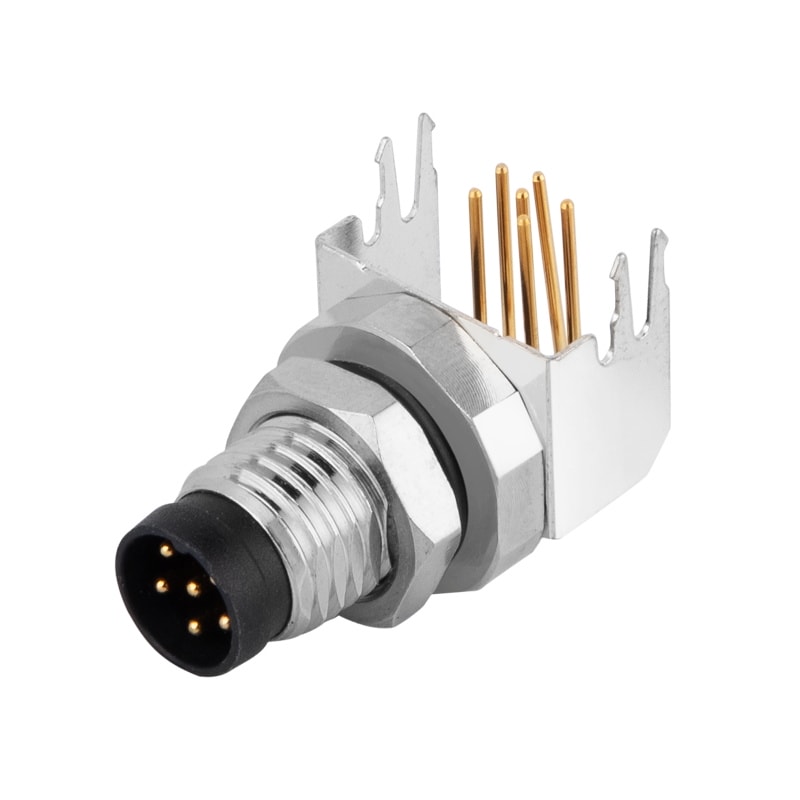
P/N: ALD-HBN1-354XXX
IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Metal Housing Metal Thread / Bayonet LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBN1-310XXX
IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Metal Housing Metal Thread LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP1-372XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 2A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP2-364XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 2A/channel Plastic Housing Metal Thread/Bayonet LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP1-372XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP1-351XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Metal Thread/Bayonet LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP2-330XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 2A/channel Metal Housing Metal Thread LockingView All
-

P/N: ALM-MPA1-051XXX
IO Link Master Multiprotocol Plastic Housing 7/8 Power ConnectorView All -

P/N: ALM-ECA1-010XXX
IO Link Master EtherCAT Single ProtocolView All -

P/N: ALM-MPA1-041XXX
IO Link Master Multiprotocol Plastic Housing M12 L-Codedd Power ConnectorView All -

P/N: ALM-MPA1-030XXX
IO Link Master Multiprotocol Metal Housing M12 L-Codedd Power ConnectorView All -

P/N: ALM-PNA1-010XXX
IO Link Master Profitnet Single ProtocolView All
Circular Connectors
-
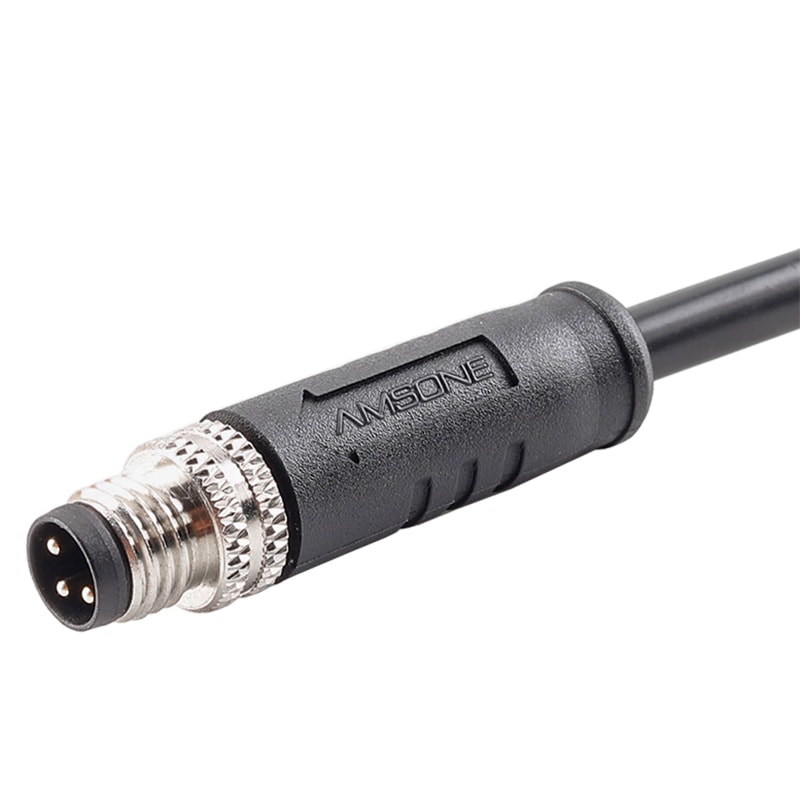

P/N: AM08M0411AXX1-XXX
M8 4Pin Pre-molded Cable Male Straight M8 ConnectorView All -
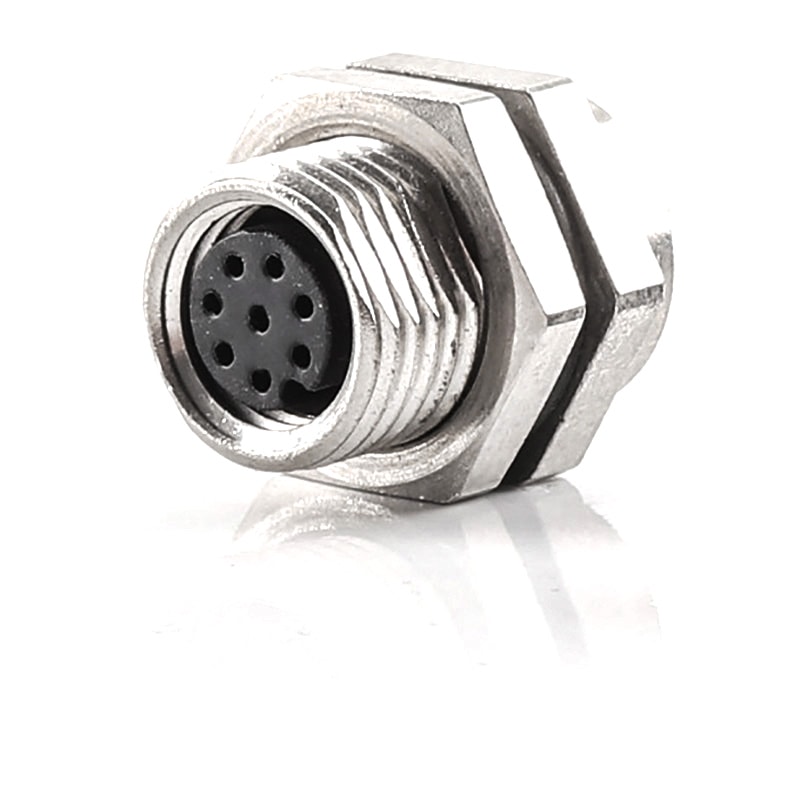

P/N: AM08F0822A001
M8 Device Connector Panel Rear Mount M8 8P Female ReceptacleView All -
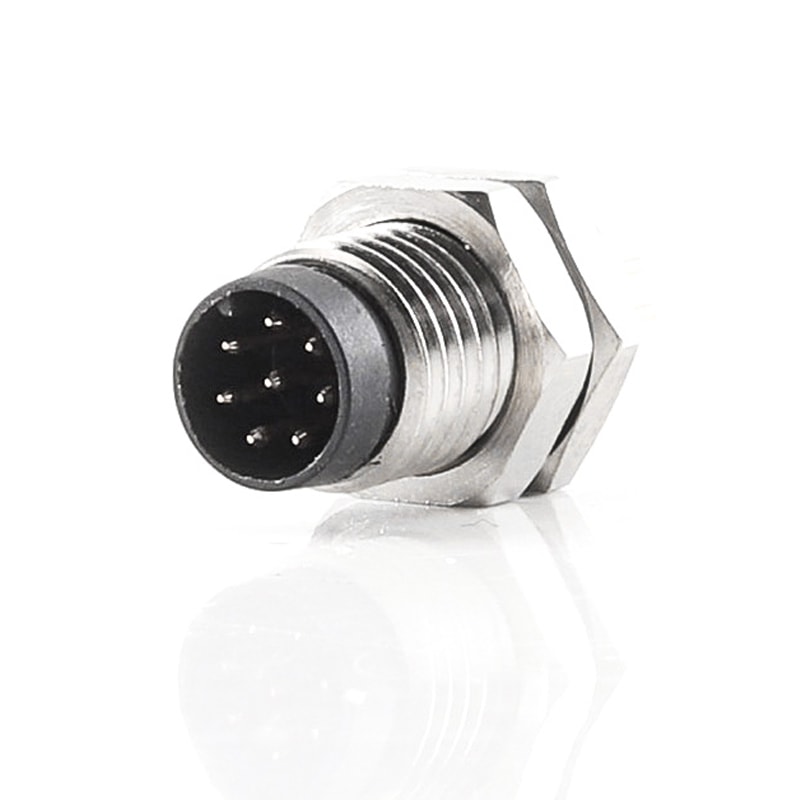

P/N: AM08M0622A001
M8 Device Connector Panel Rear Mount M8 6P Male ReceptacleView All -

P/N: AM08M0811AXX1-XXX
M8 8Pin Pre-molded Cable Male Straight M8 ConnectorView All -
P/N: AM08M0822A003
M8 Device Connector Male 8Pin PCB Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Right Angled ShieldedView All -
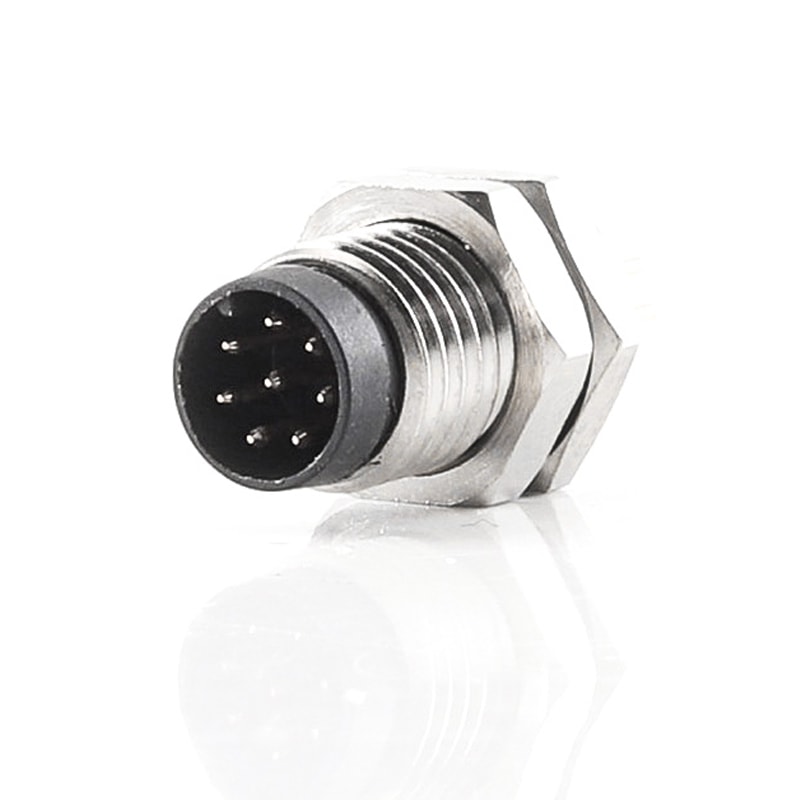

P/N: AM08M0822A001
M8 Device Connector Panel Rear Mount M8 8P Male ReceptacleView All -

P/N: AM08F0811AXX3-XXX
M8 8P Female Shield Connector Pre-molded Cable Right Angled IP67View All -
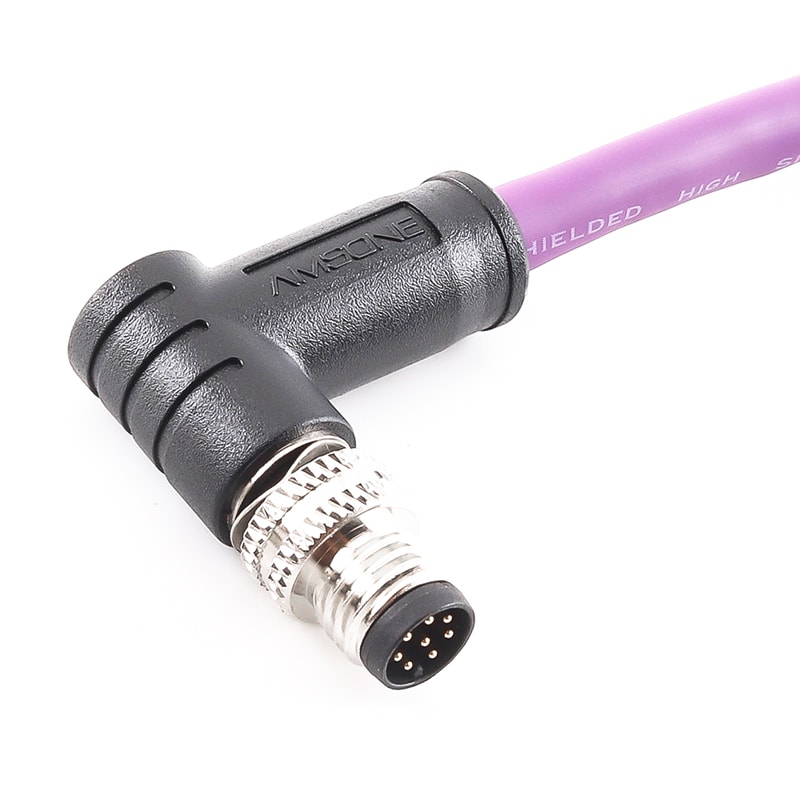

P/N: AM08M0811AXX3-XXX
M8 Connector 8P Male Shield Pre-molded Cable Right Angled IP67View All
-
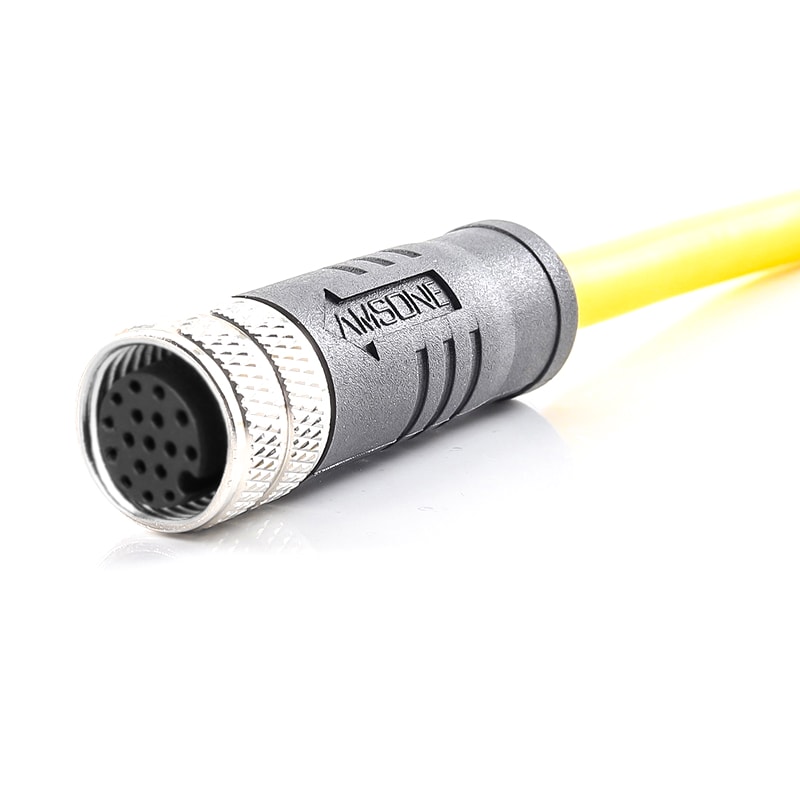

P/N: AM12F1211AXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts: 12,solder connection, A code, straight, IP67View All -
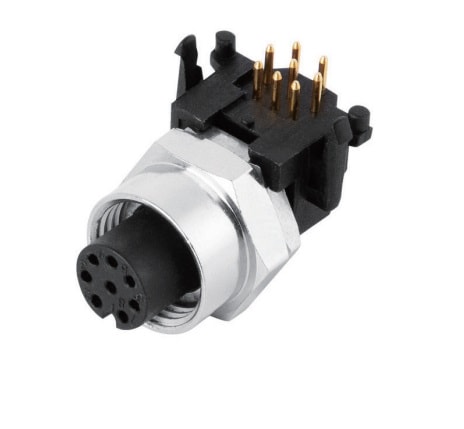

P/N: AM12F0822A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts: 8, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
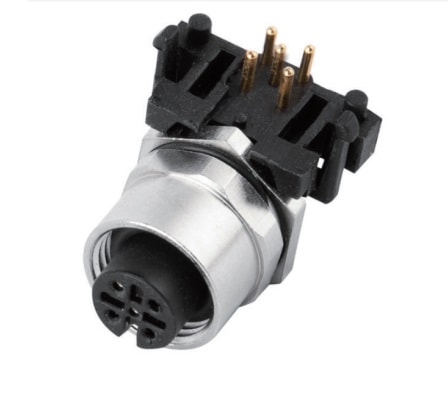

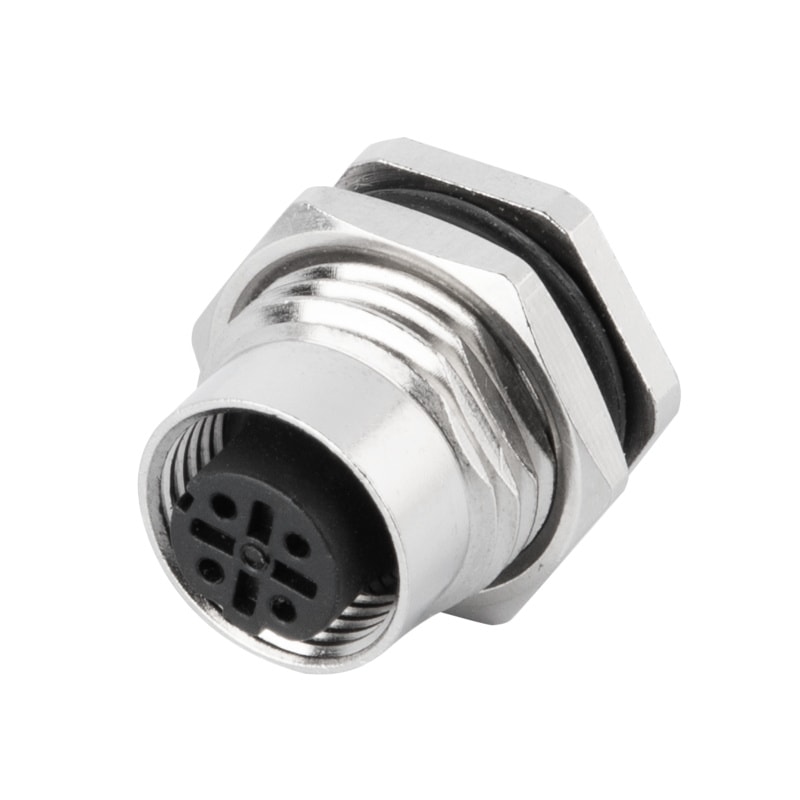
P/N: AM12F0522A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts: 5, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
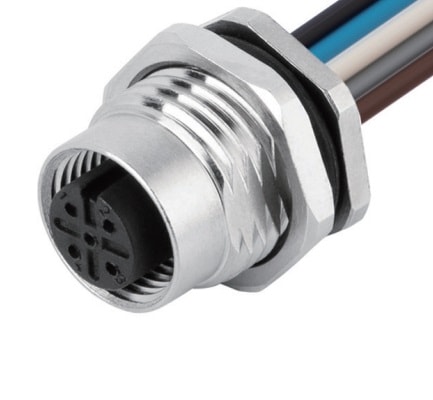

P/N: AM12F0512AXX1-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts: 5, solder connection for wires, A code, straight, IP67View All -
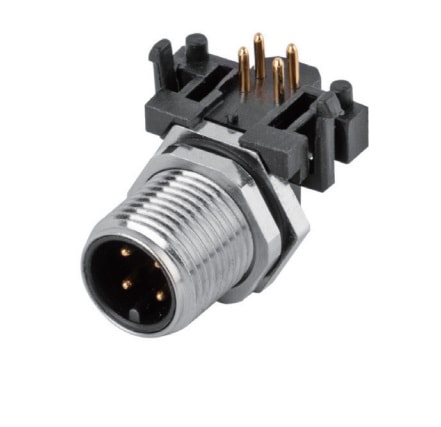

P/N: AM12M0422A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts: 4, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
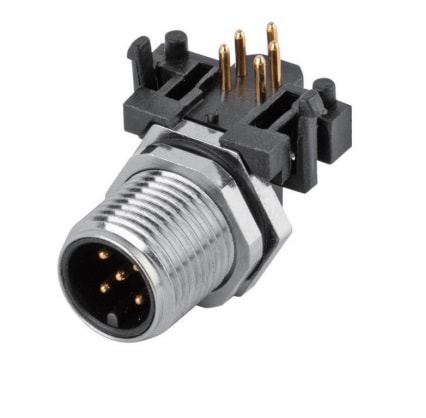

P/N: AM12M0522A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts: 5, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
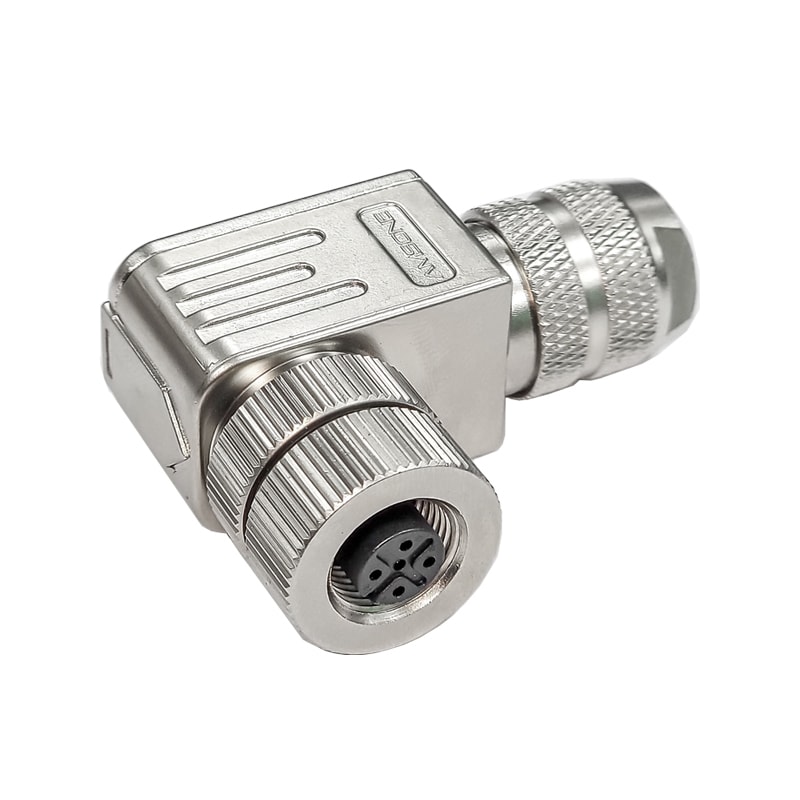

P/N: AM12F0534A007
M12 cable connector, female, contacts:5, field assembly type, screw connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
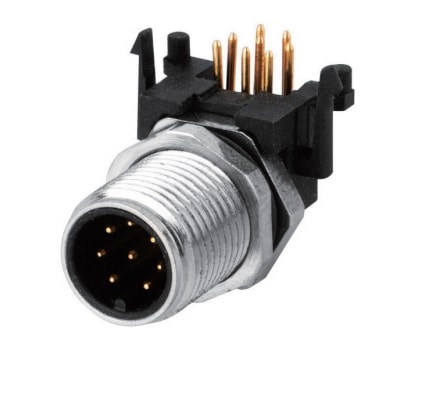

P/N: AM12M0822A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts: 8, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All
-
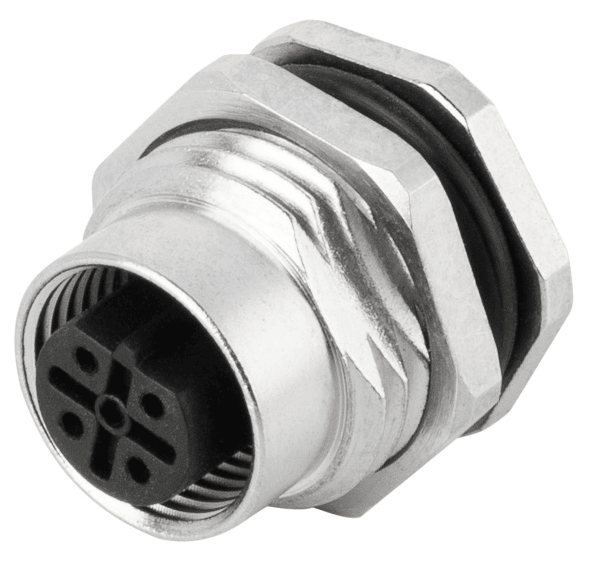

P/N: AM12F0522B001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:5, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -
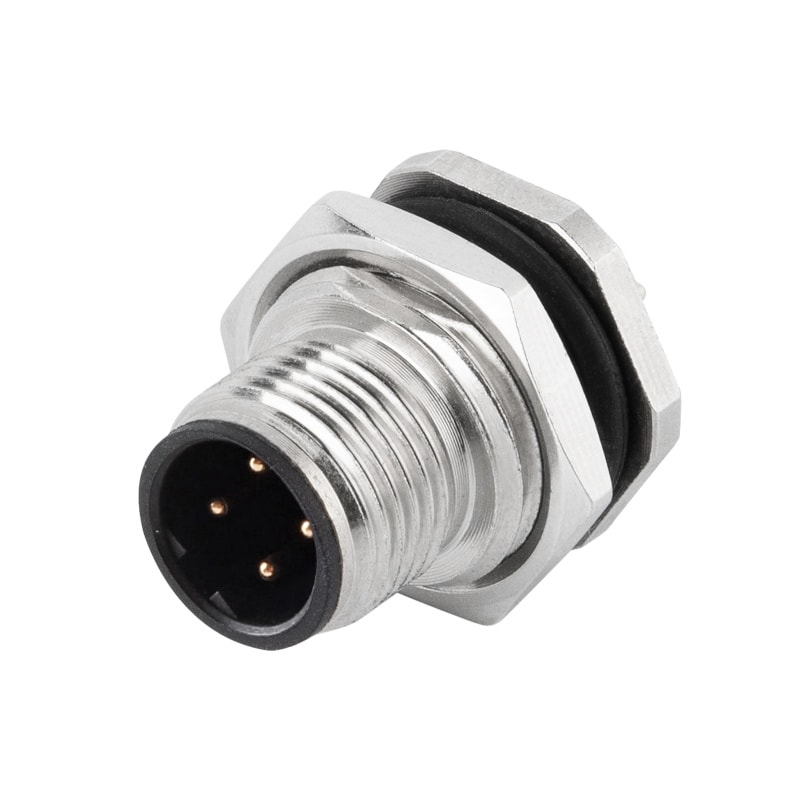

P/N: AM12M0522B001
M12 B Code Male Panel Rear Mount Receptacle PCB Connector PG9View All -
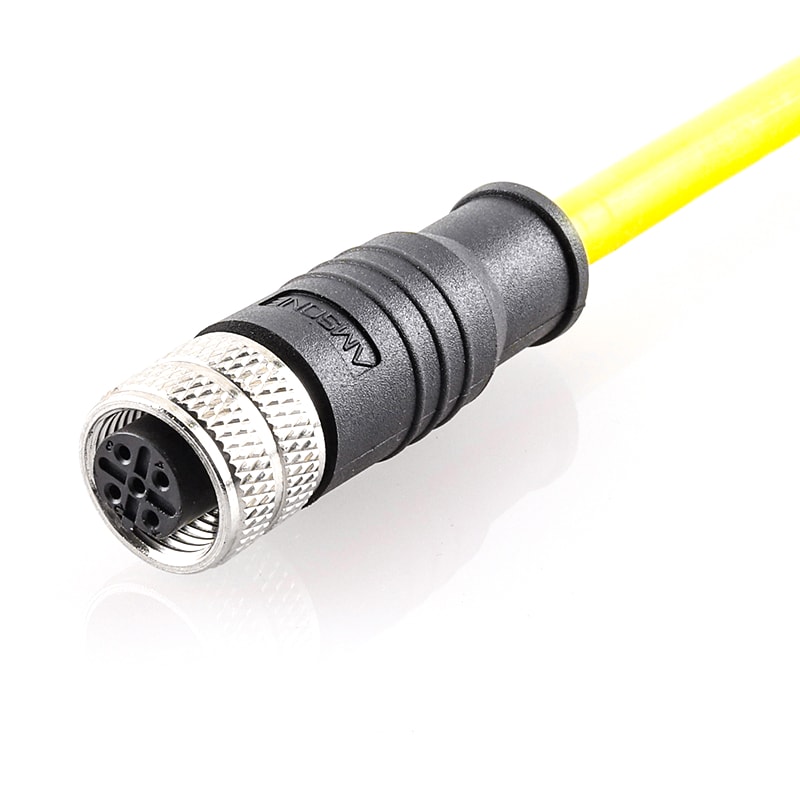

P/N: AM12F0511BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:5, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0511BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:5, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0422B001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0422B001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0512B002
M12 5P Male B Code Panel Rear Mount Receptacle Wires Solder Connector M16*1.5View All -

P/N: AM12M0512B001
M12 5P Male B Code Panel Rear Mount Receptacle Wires Solder Connector PG9View All
-
P/N: AM12F0422D006
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, D code, right angled, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0412D001
M12 D Code Male Panel Rear Mount Receptacle For Wires Solder Connector PG9View All -

P/N: AM12F0413D001
M12 panel receptacle, front mount, female, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, D code, straight, IP67View All -
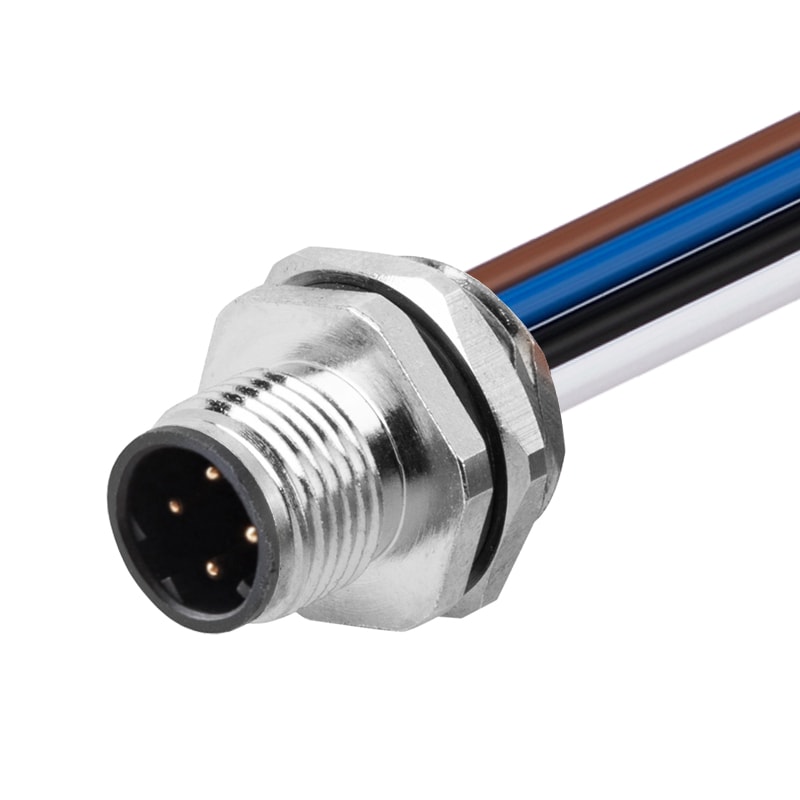

P/N: AM12M0413D351-005
M12 Panel Receptacle Front Mount Male 4Pin Solder Connection For Wires D Code Straight IP67View All -
P/N: AM12F0422D001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, D code, straight, IP67View All -
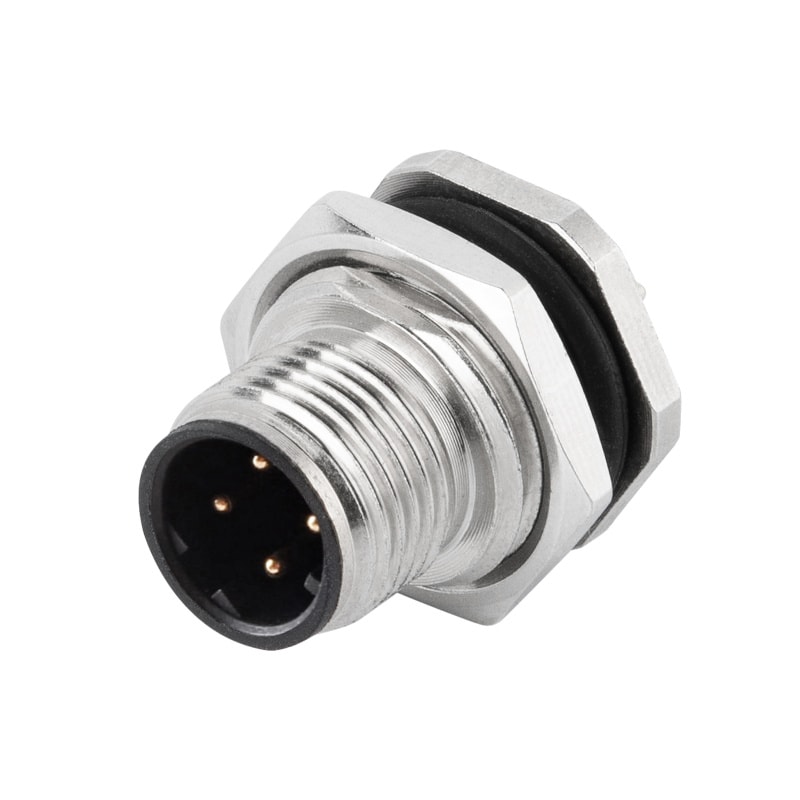

P/N: AM12M0422D001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, D code, straight, IP67View All -
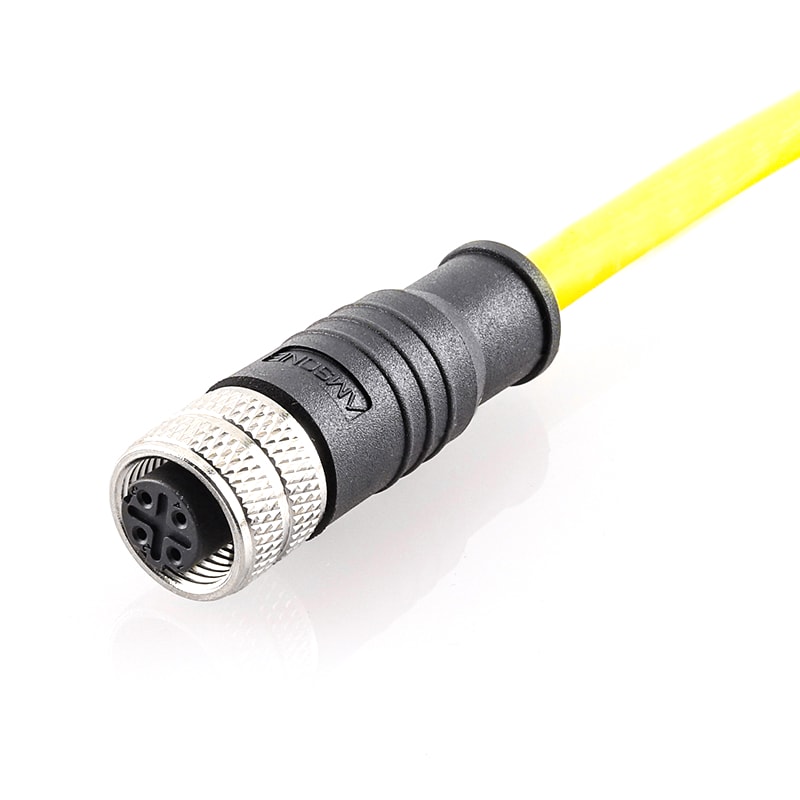

P/N: AM12F0411D241-010
M12 4P D Code Pre-molded Cable Connector Female Straight IP67View All -
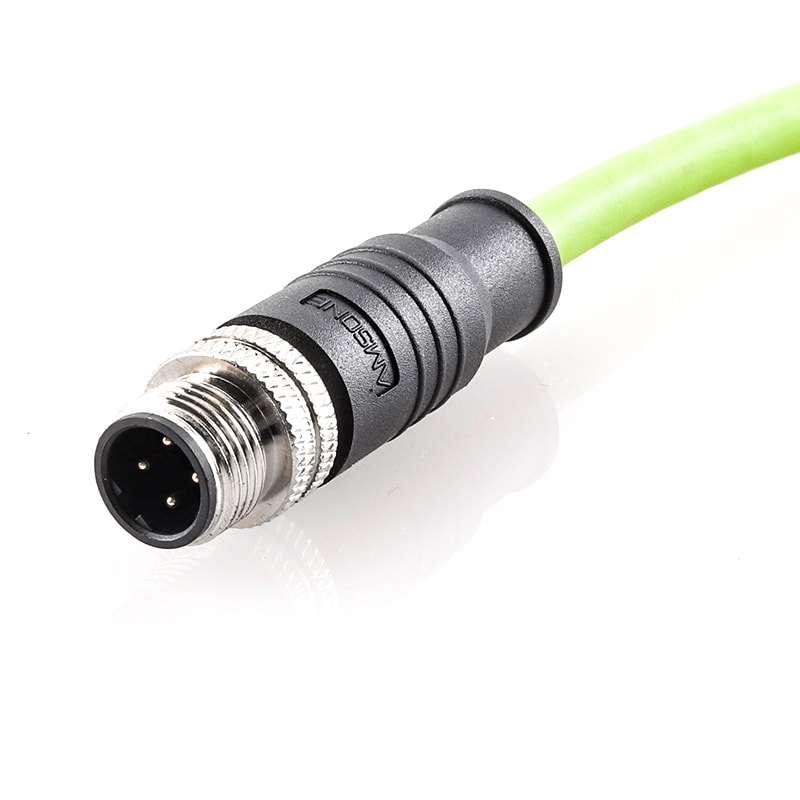

P/N: AM12M0411D241-010
M12 pre-molded cable connector male solder connection D code straight IP67View All
-
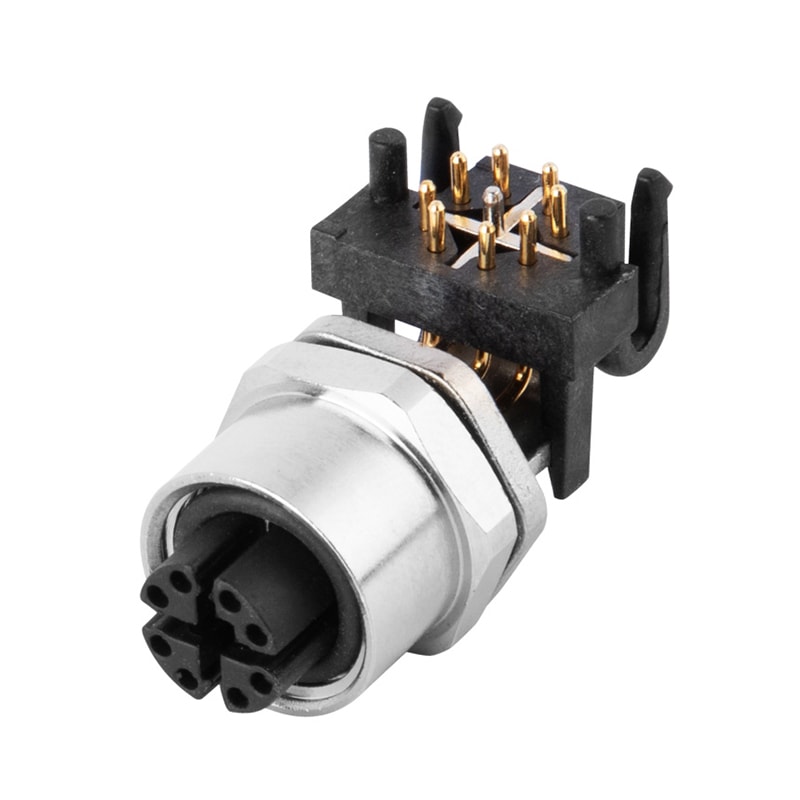

P/N: AM12F0822X008
M12 X Code 8Pole Panel Receptacle Rear Mount Female PCB Dip-solder Connection Right Angled IP67View All -
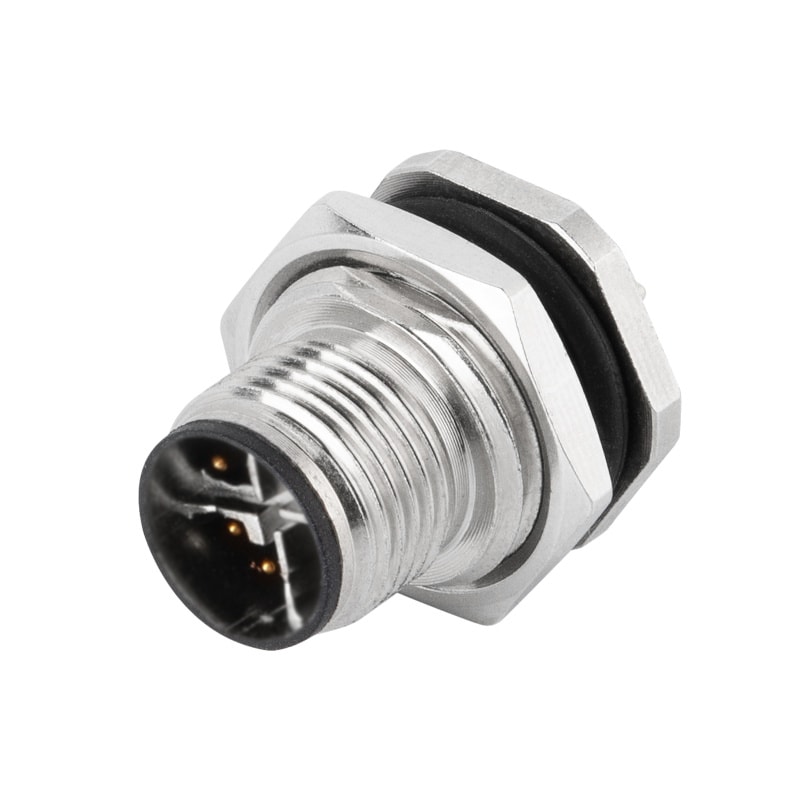

P/N: AM12M0822X001
M12 Panel Receptacle Rear Mount Male PCB DIP Solder X Code StraightView All -
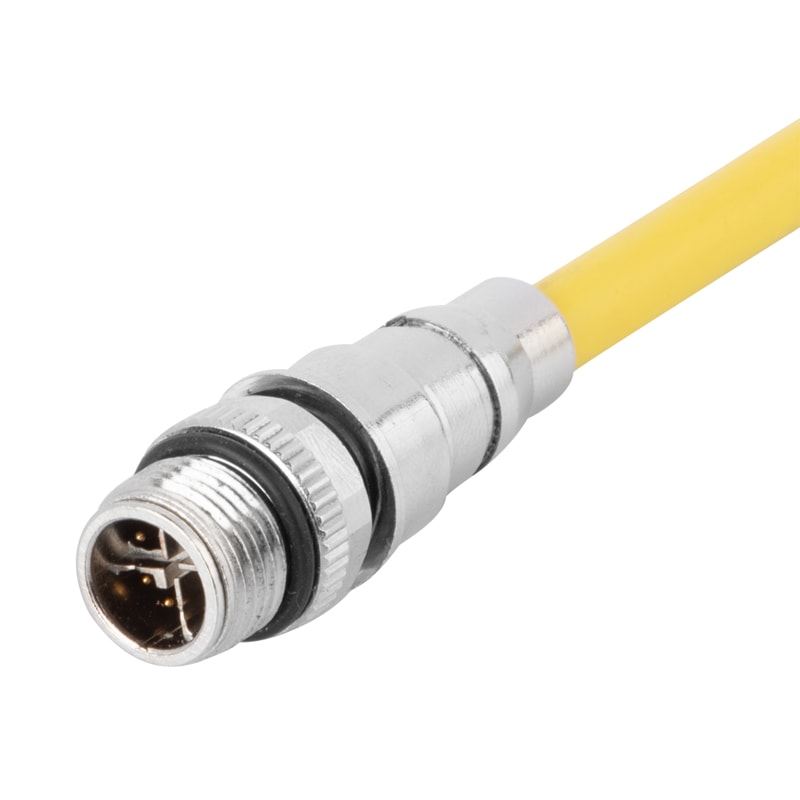

P/N: AM12M0811X003
M12 data cable connector, contact: 8P, male, for pre-molding , X code, straight, 360 EMC shielding, solder connection, 0.5A/60VView All -
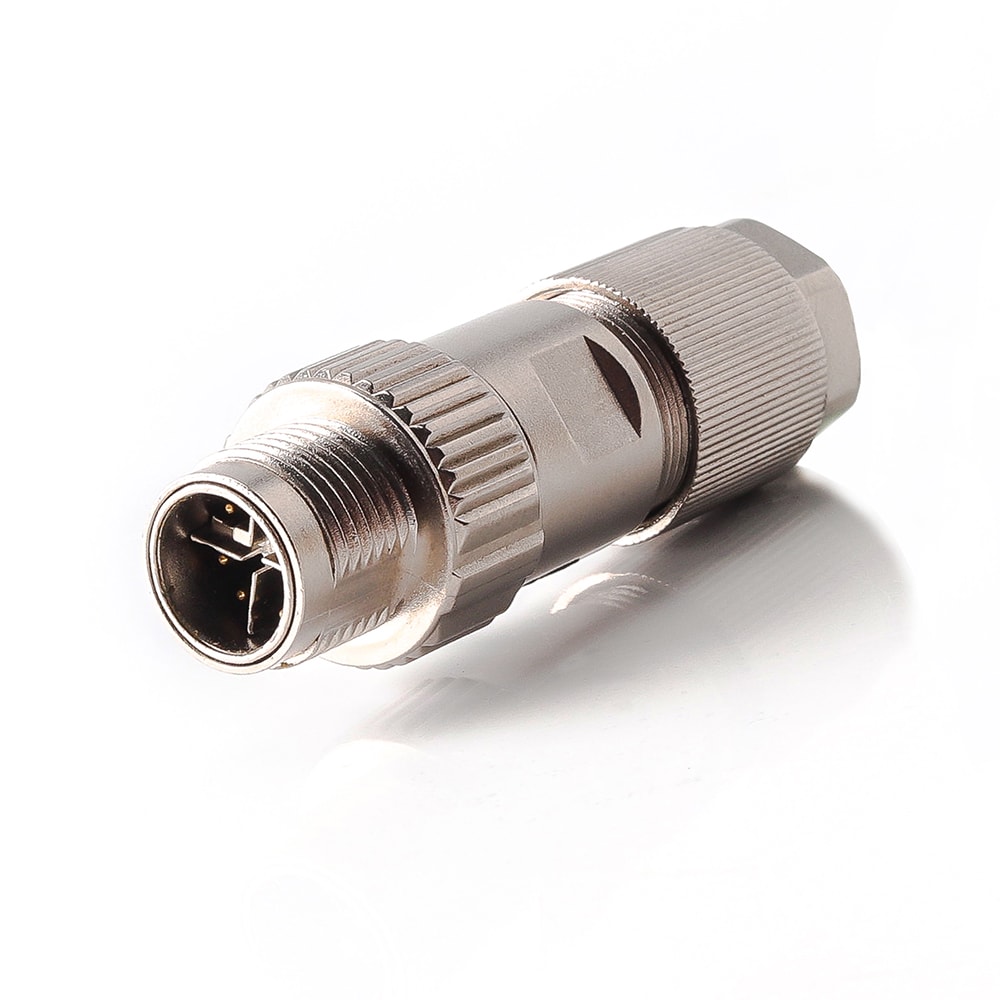

P/N: AM12M0844X003
M12 X Code Field Assembly Connector Male EMC Shielded Straight IP67 Crimp ContactsView All -
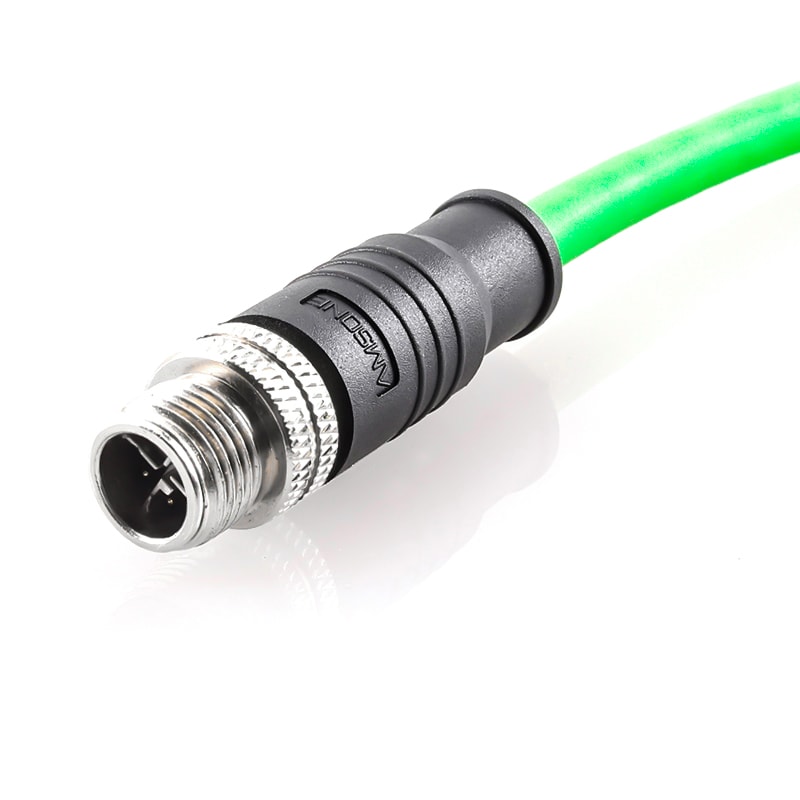

P/N: AM12M0811X233-100
M12 Pre-molded Cable Connector 8Pole Male X Code EMC Profinet/Ethernet Cable StraightView All -
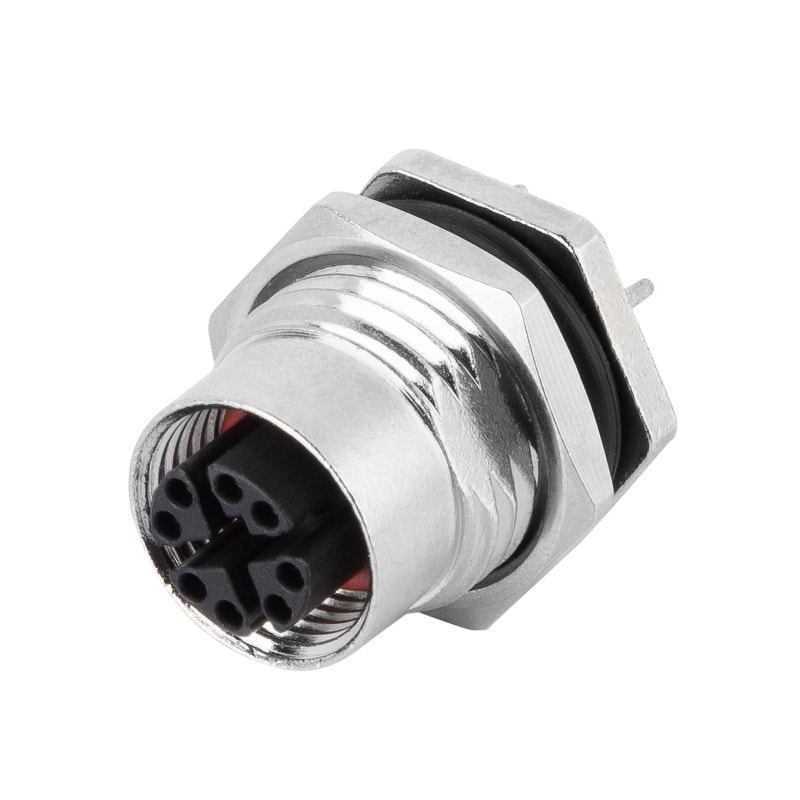

P/N: AM12F0822X002
M12 X Code Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female PCB DIP Connection M16*1.5View All -
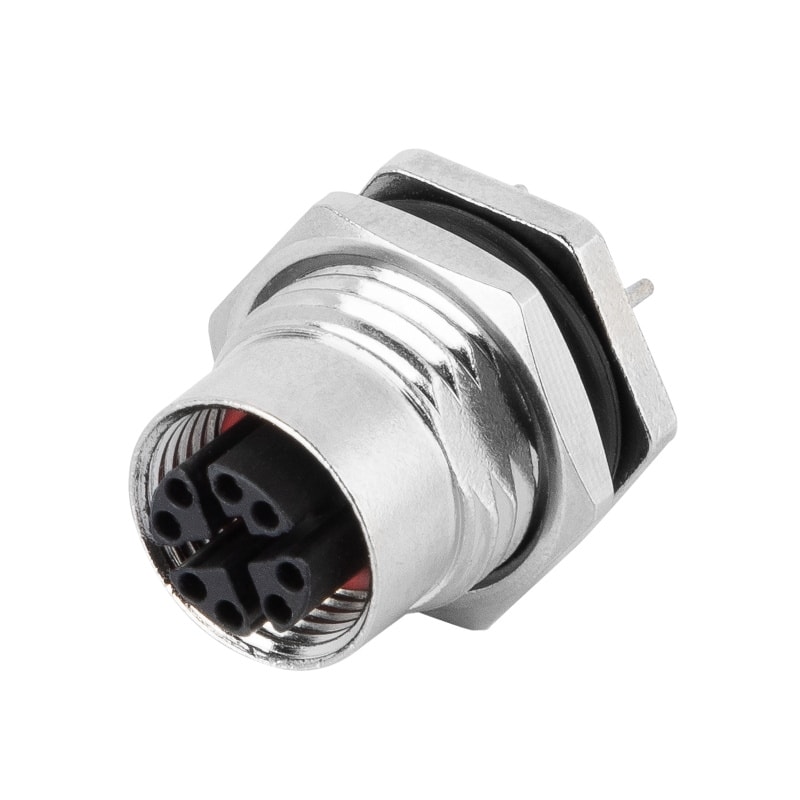

P/N: AM12F0822X001
M12 X Code Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female PCB DIP Connection PG9View All -
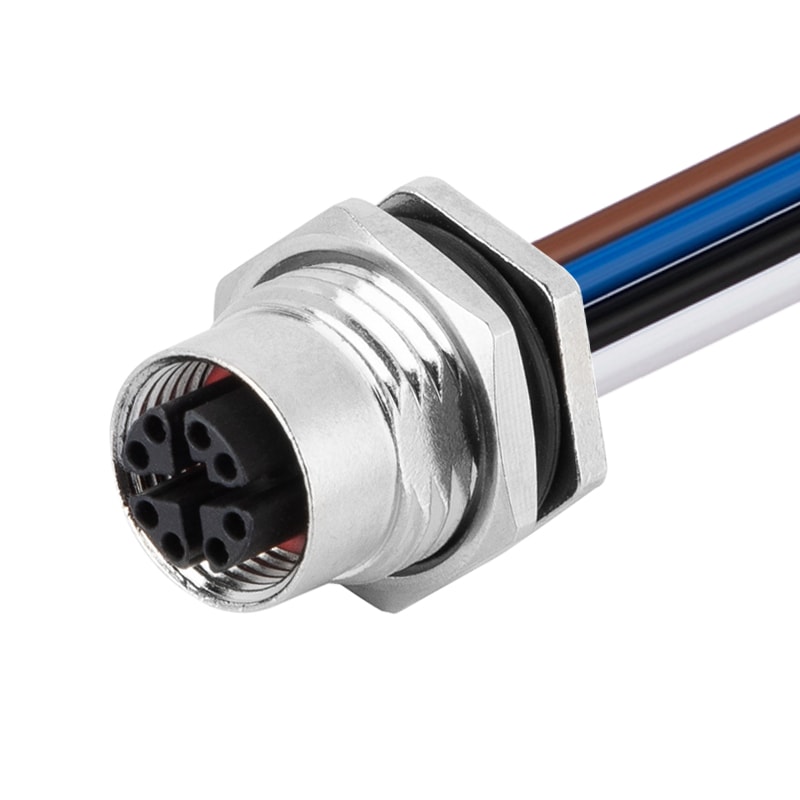

P/N: AM12F0812X001
M12 X Code Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female For Solder Wires ConnectionView All
-

P/N: AM12F0822Y002
M12 Hybrid Connector,Y Code,Female,Panel Mount Receptacle,M12 Device ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM12M0822Y002
M12 Hybrid Connector,Y Code,Male,Panel Mount Receptacle,M12 Device ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM12M0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Male,M12 Y-Coded Power Signal Ethernet CableView All -

P/N: AM12F0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Power Signal,M12 Y-Coded CablesView All -

P/N: AM12F0812Y003
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Panel Mount Shielded,M12 Y-CodedView All
-

P/N: AM12F0434T001
M12 cable connector, female, contacts: 4, field assembly type, screw connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0434T001
M12 cable connector, male, contacts: ,4, field assembly type, screw connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0412T171 -XXX
M12 panel receptacle, female, contacts: 4, solder connection for wires, T code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0412T171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, male, contacts: 4, solder connection for wires, T code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0322T001
M12 panel receptacle, female, contacts: 3,PCB dip-solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0322T001
M12 panel receptacle, male, contacts: 3,PCB dip-solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0311TXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts: 3,solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -
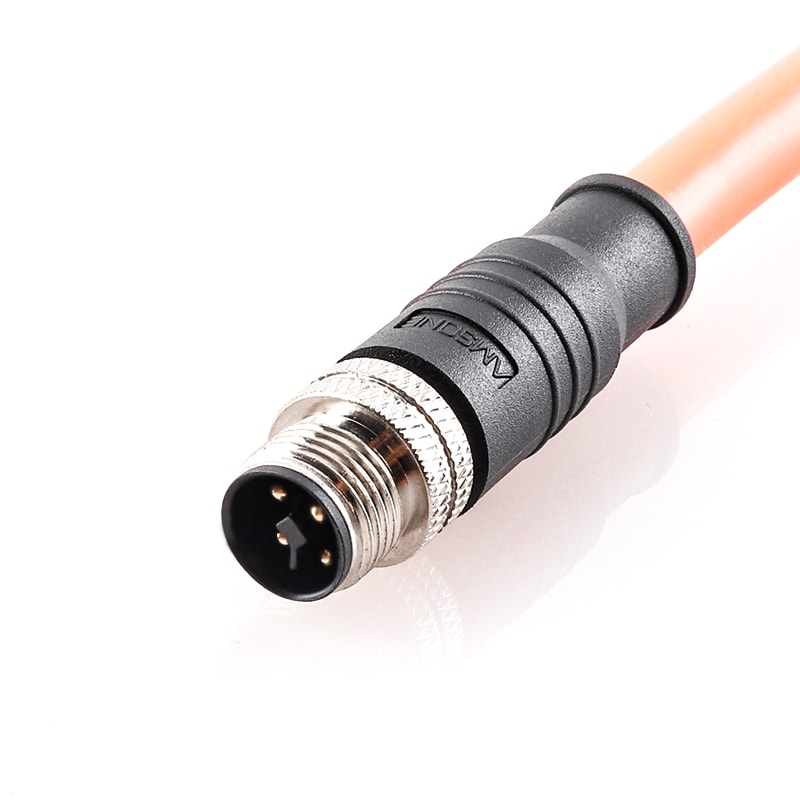

P/N: AM12M0311TXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:3, solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All
-
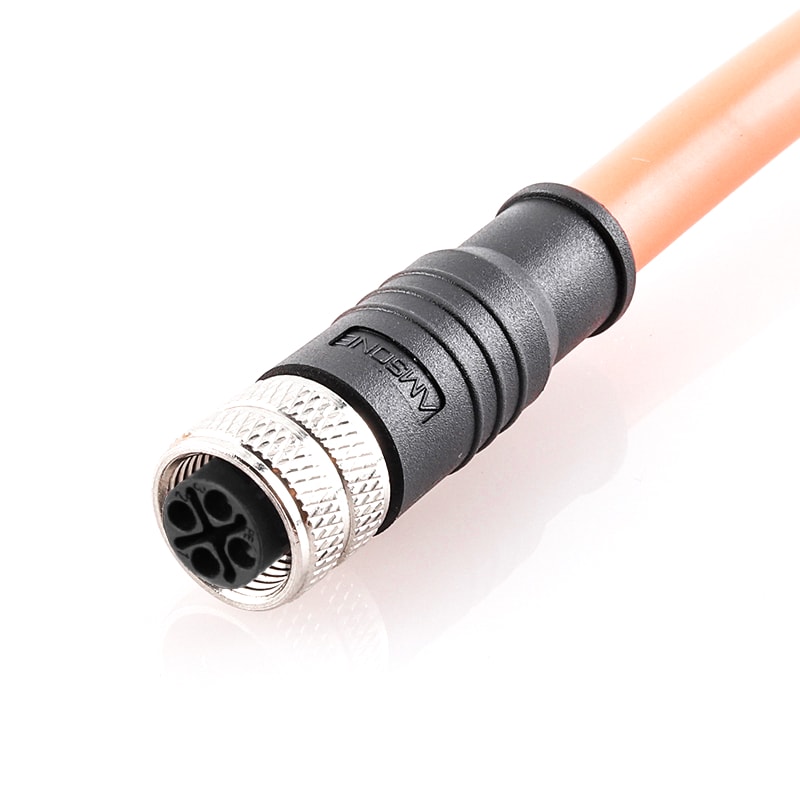

P/N: AM12F0411SXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4(3+PE), solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -
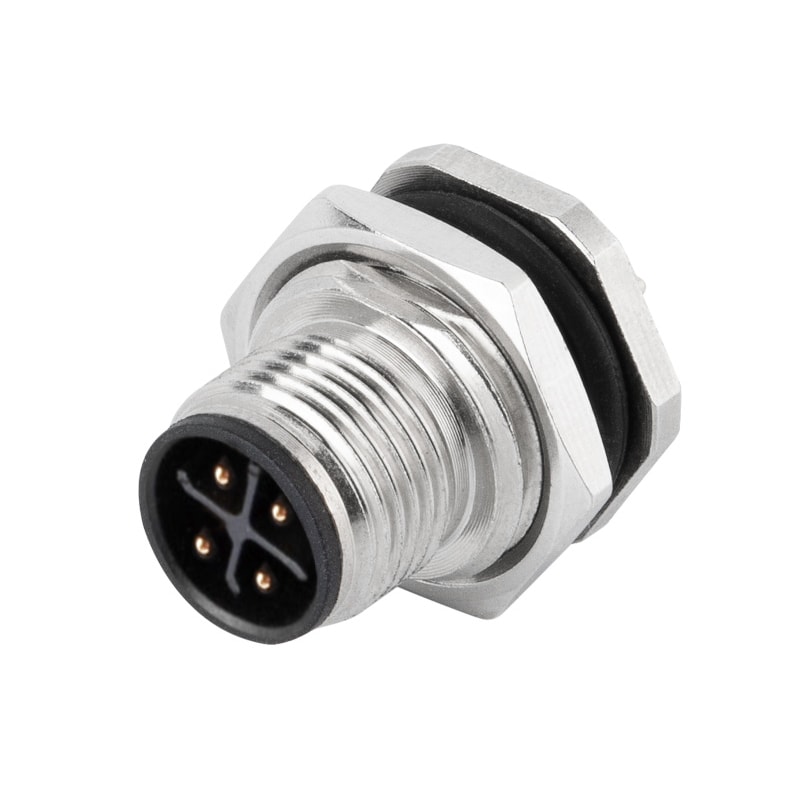

P/N: AM12M0322S001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:3(2+PE),PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0412S171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, S code, straight, IP67View All -
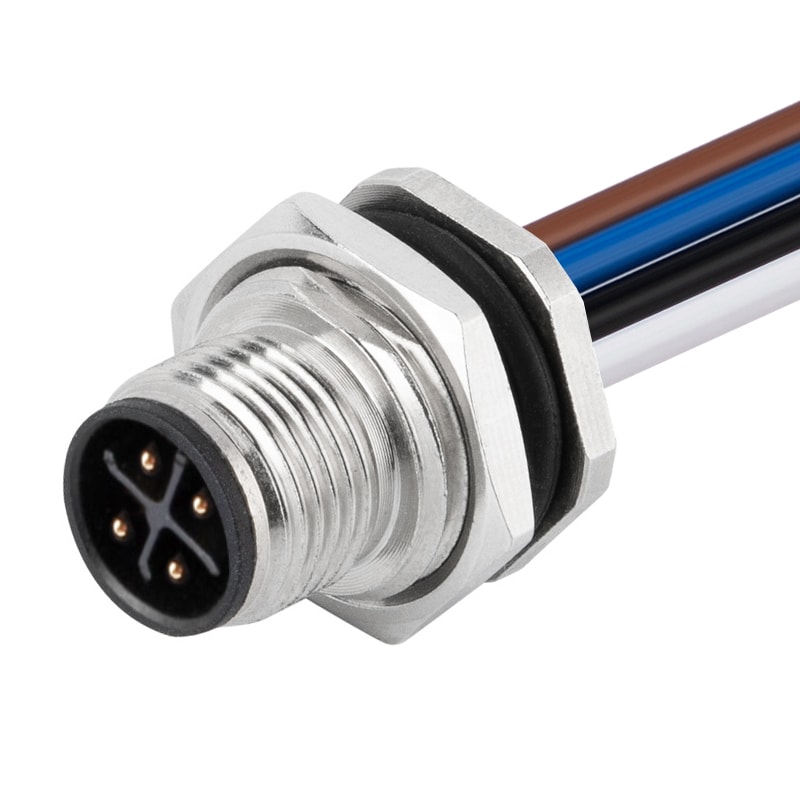

P/N: AM12M0412S171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, S code, straight, IP67View All -
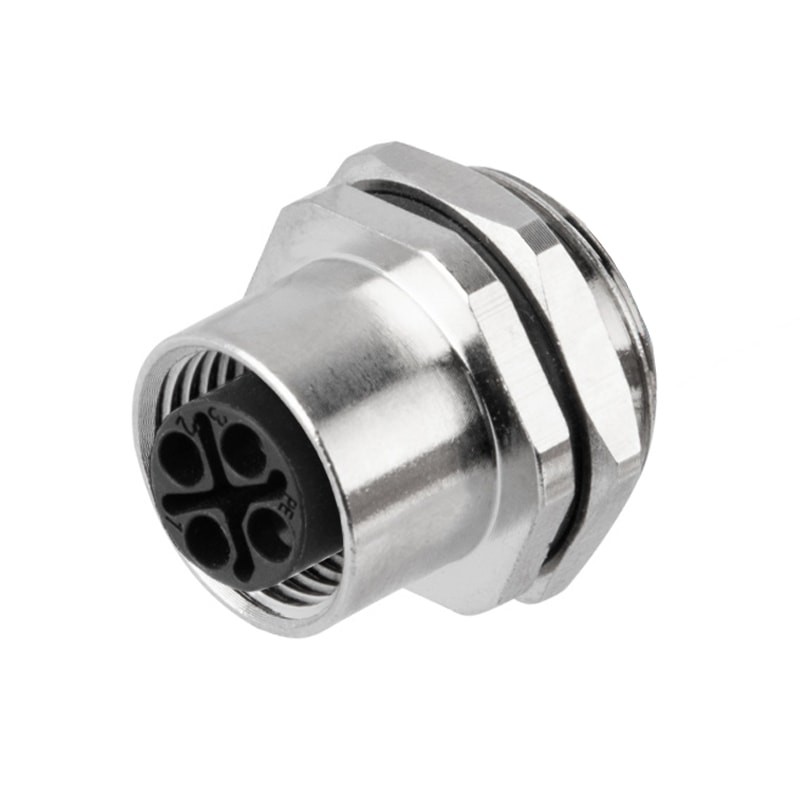

P/N: AM12F0322S001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:3(2+PE),PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -
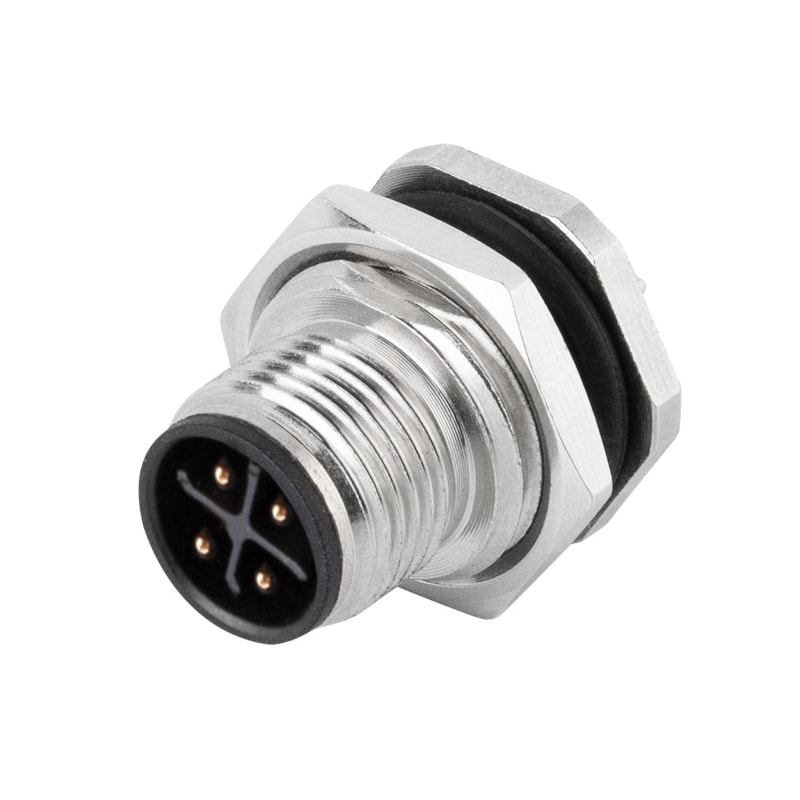

P/N: AM12M0422S001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:,4(3+PE), PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -
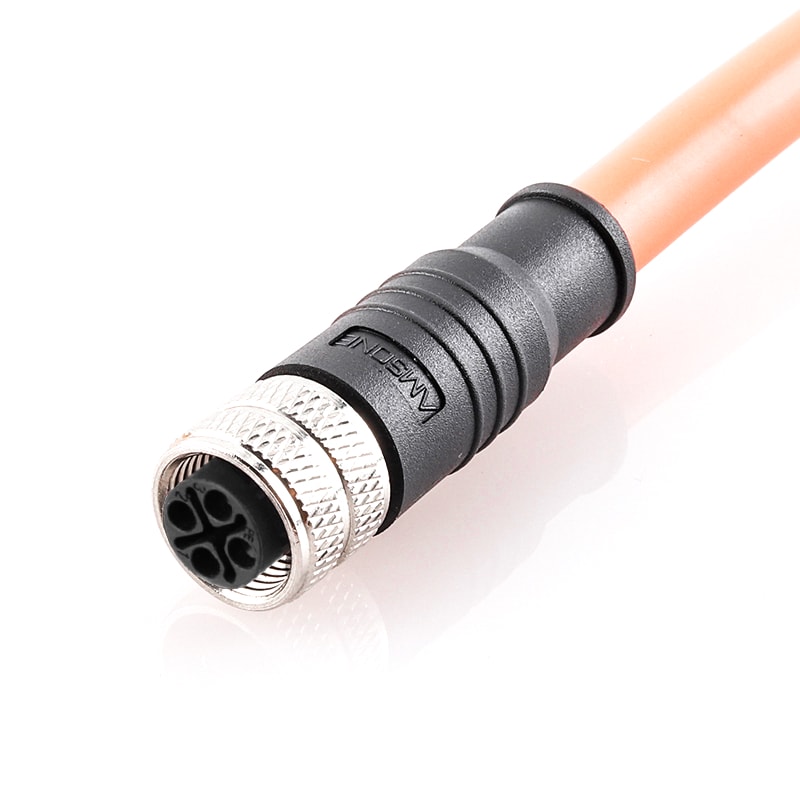

P/N: AM12F0311SXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:3(2+PE), solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -
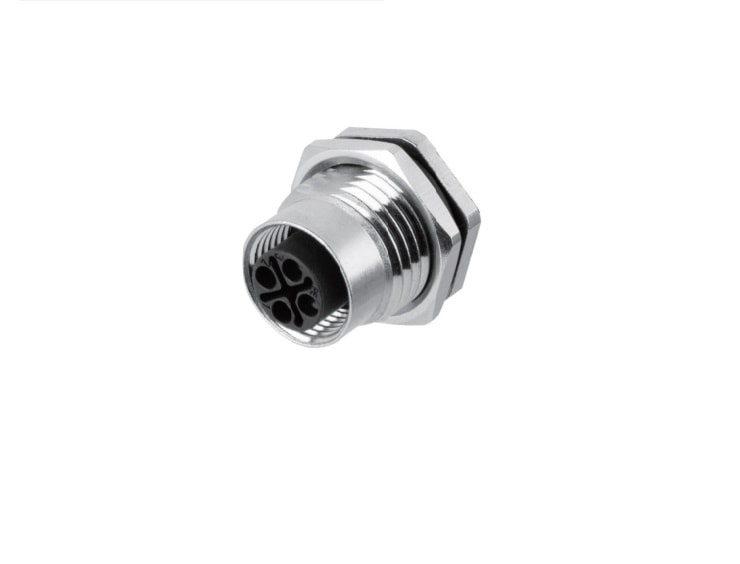

P/N: AM12F0322S002
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:3(2+PE), PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All
-

P/N: AM12M0511Lxx1-xxx
M12 L Coded Power 5P Connector Male Drag Chain Pre-Molded CableView All -

P/N: AM12M0412L171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0522L001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:5, PCB dip-solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0411LXX2-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0411LXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:4, solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0322L001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:3, PCB dip-solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0422L001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4,PCB dip-solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0311LXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:3, solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All
-
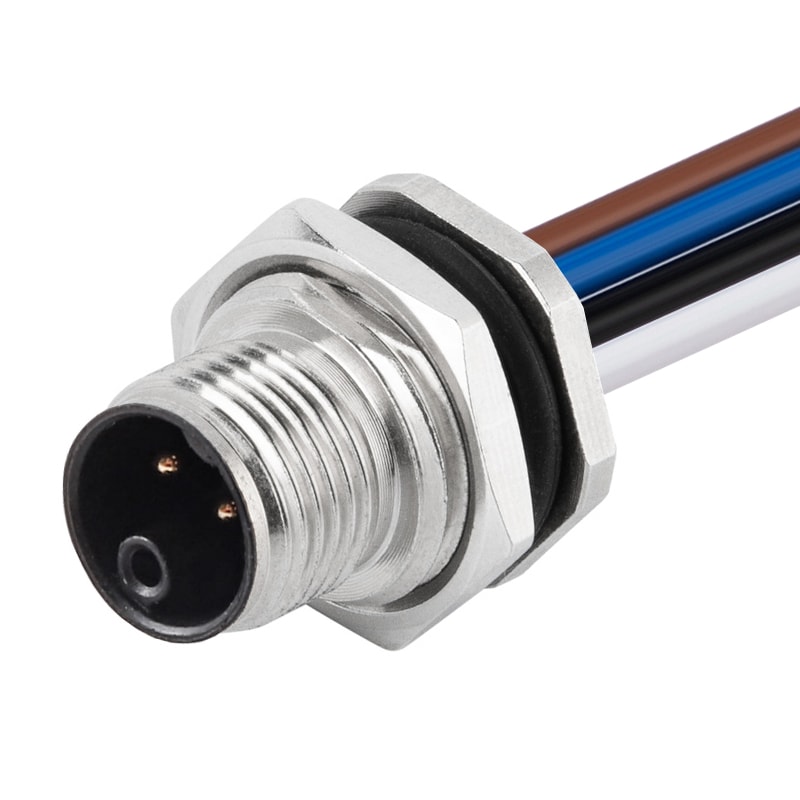

P/N: AM12M0312K171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:3,solder connection for wires, K code, straight, IP67View All -
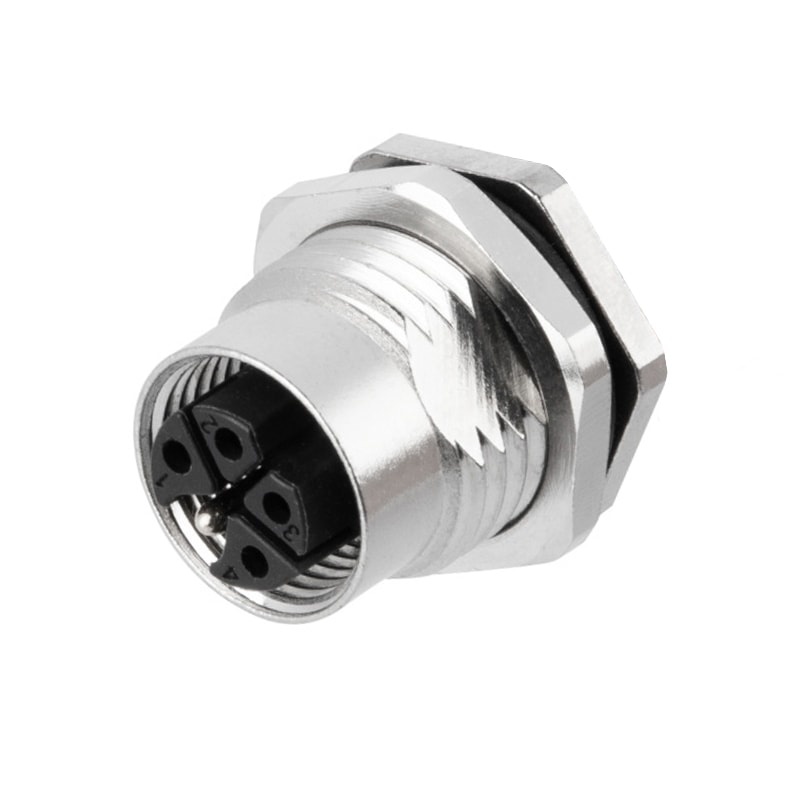

P/N: AM12F0522K001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:5, PCB dip-solder connection, K code, straight, IP67View All -
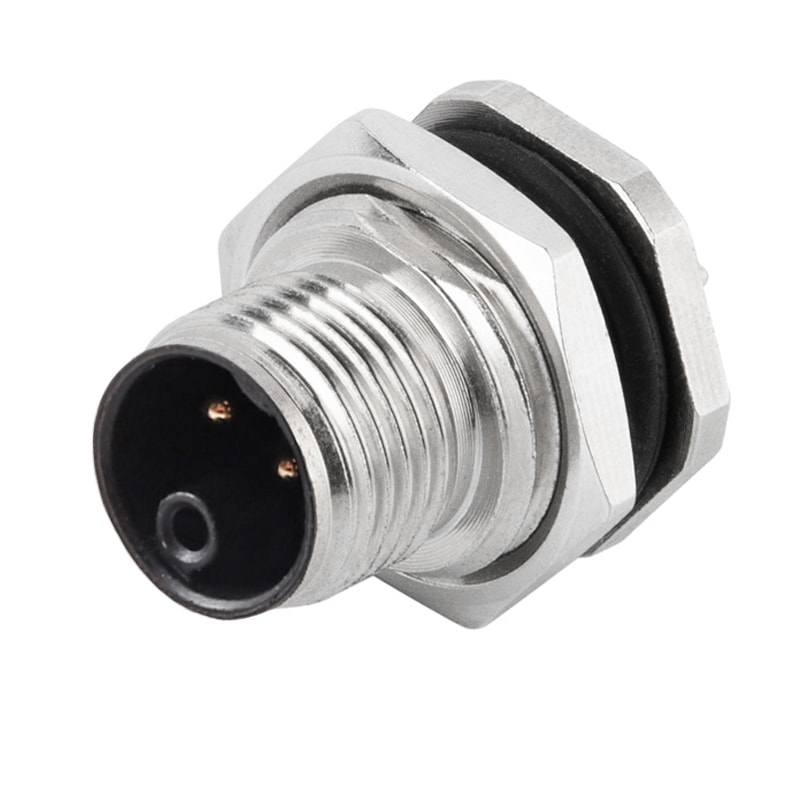

P/N: AM12M0522K001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:5,PCB dip-solderconnection, K code, straight, IP67View All -
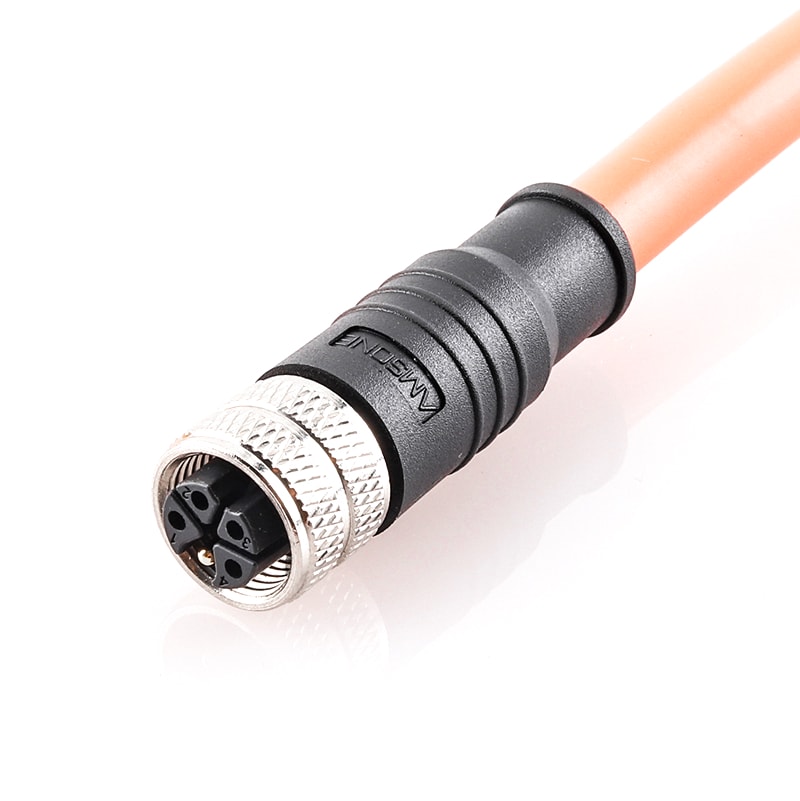

P/N: AM12F0311KXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:3, solder connection, K code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0311KXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:3, solder connection, K code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0513K371-005
M12 K Code 5P(4+PE) Female Panel Front Mount Receptacle ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM12F0312K171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:3, solder connection for wires, K code, straight, IP67View All
-

P/N: AM12M0512M371-XXX
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Male 5Pin Connector For WiresView All -

P/N: AM12F0322M001
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Female 3Pin PCB ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM12F0612M171-XXX
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Female 6Pin Connector For WiresView All -

P/N: AM12M0612M371-XXX
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Male 6Pin Connector For WiresView All -

P/N: AM12M0522M001
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Male 5Pin PCB ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM12F0611MXX1-XXX
M12 M Code 5+PE Pre-molded Cable 6Pin Female Straight ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM12M0611MXX1-XXX
M12 M Code 5+PE Pre-molded Cable 6Pin Male Straight ConnectorView All -
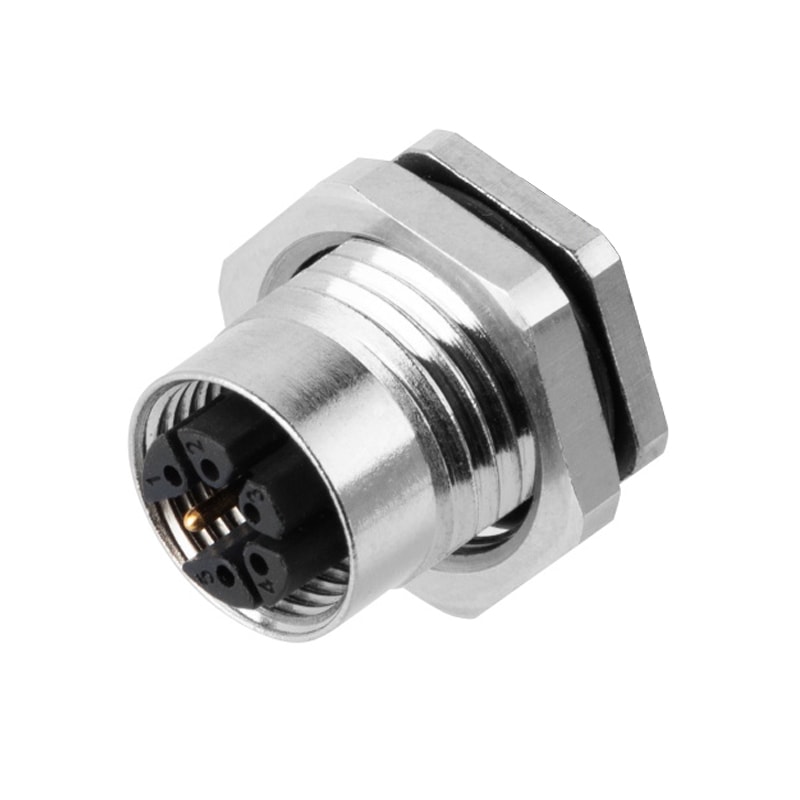

P/N: AM12F0522M001
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Female 5Pin PCB ConnectorView All
-
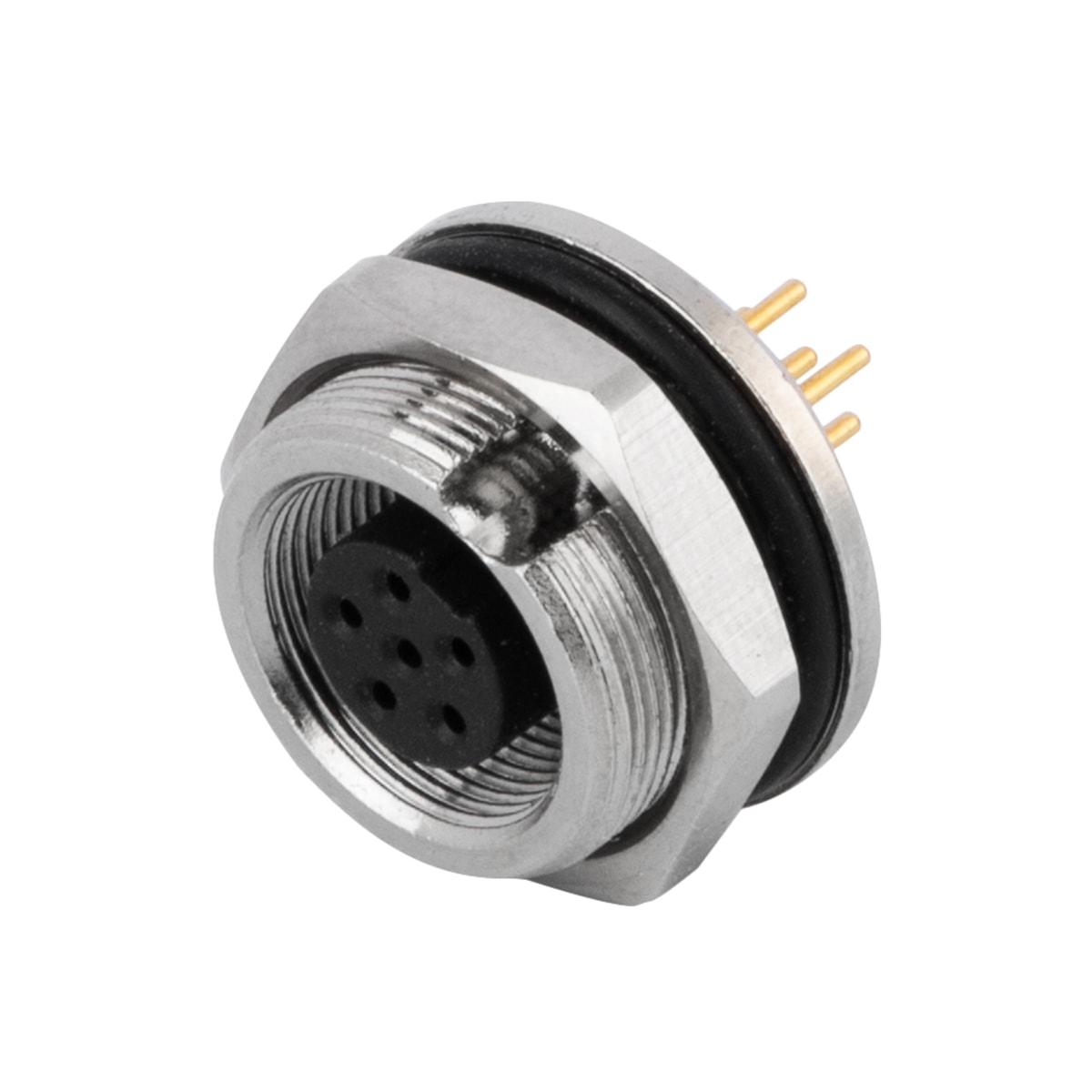

P/N: AM09F0522A001
M9 Connector Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female 5Pole PCB Dip-solderView All -
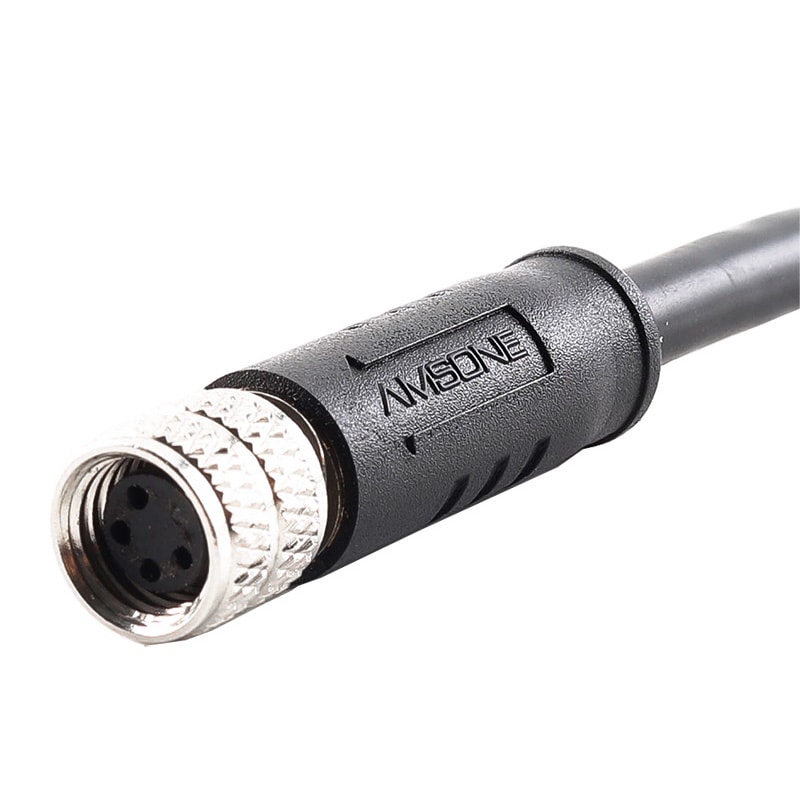

P/N: AM09F0411A001
M9 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM09F0311A001
M9 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts: 3, solder connection, straight, IP67View All -
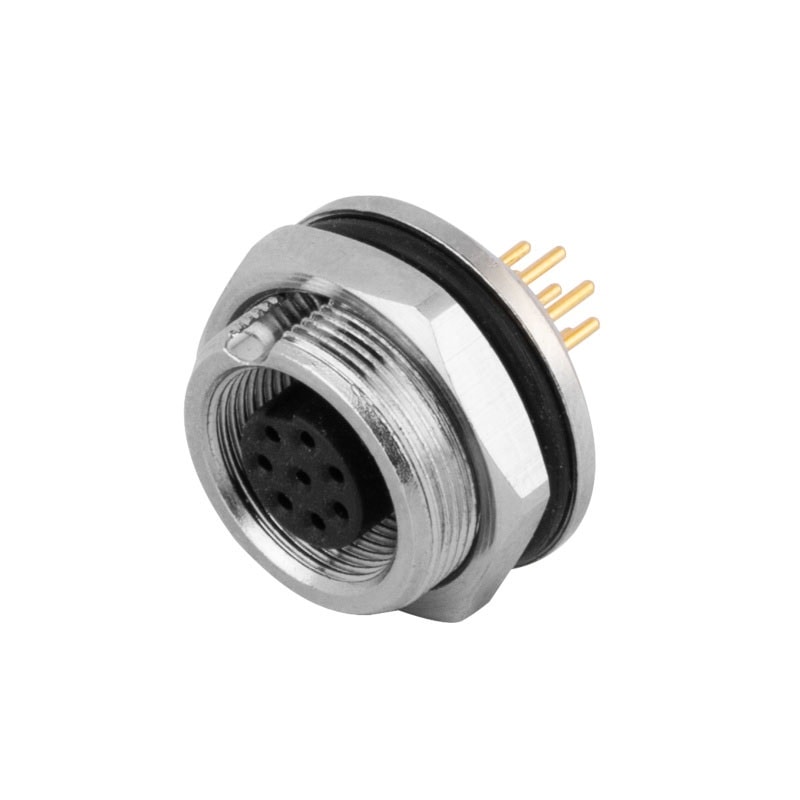

P/N: AM09F0822A001
M9 Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle 8Pin PCB Waterproof ConnectorView All -
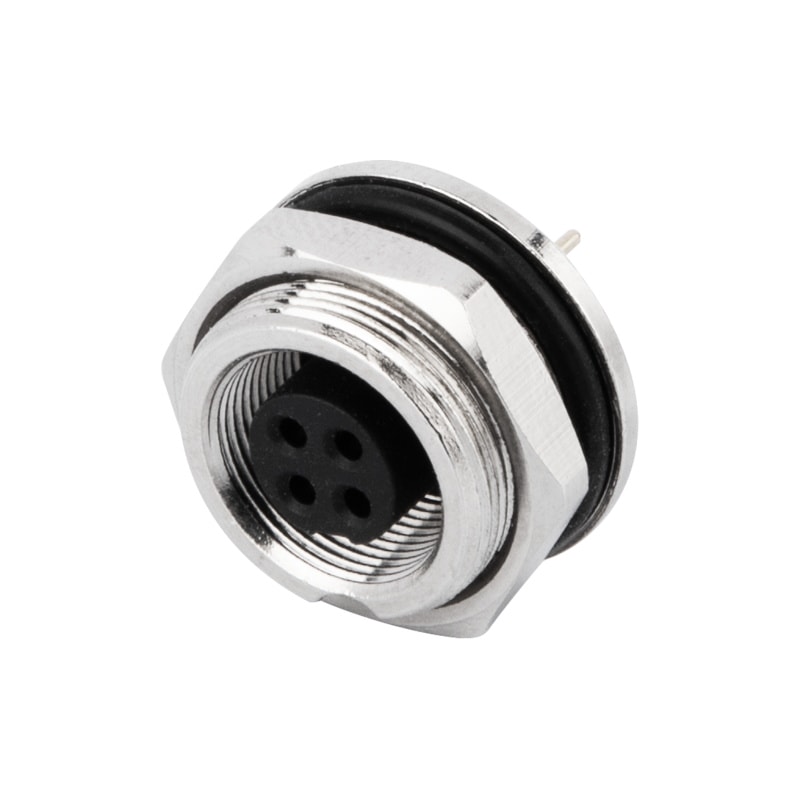
P/N: AM09F0422A001
M9 4P Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle PCB Waterproof ConnectorView All -
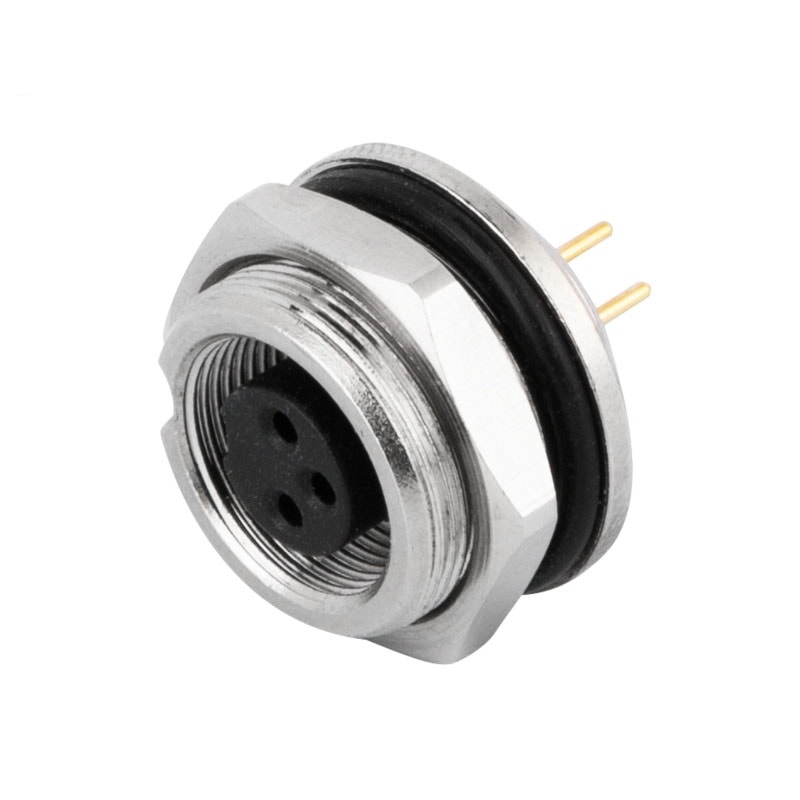

P/N: AM09F0322A001
M9 3Pole Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle PCB Waterproof ConnectorView All -
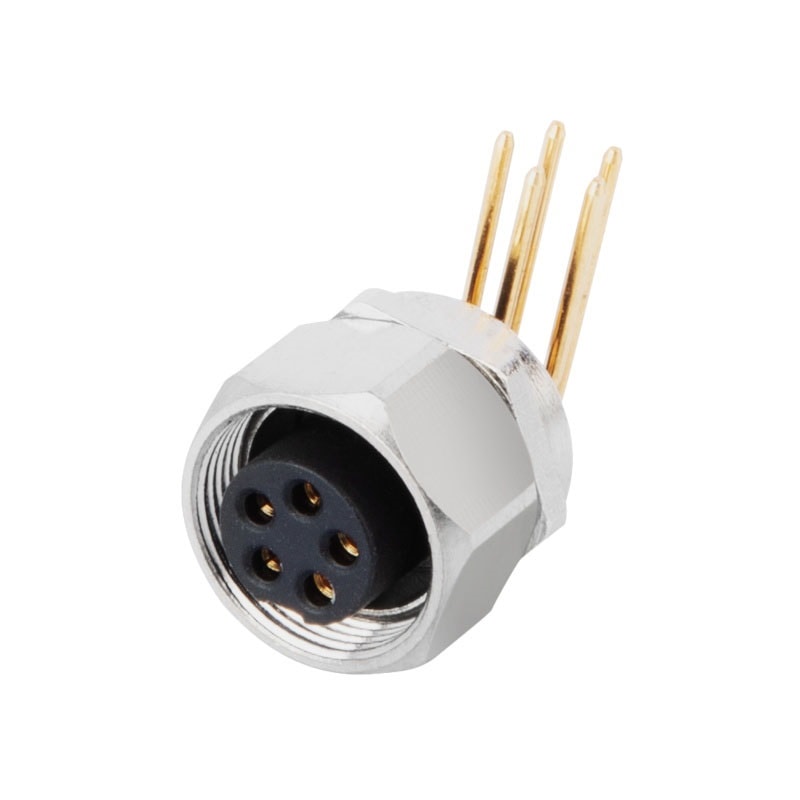

P/N: AM09F0522A201
M9 Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle 5Pin PCB Connector Right AngledView All
-
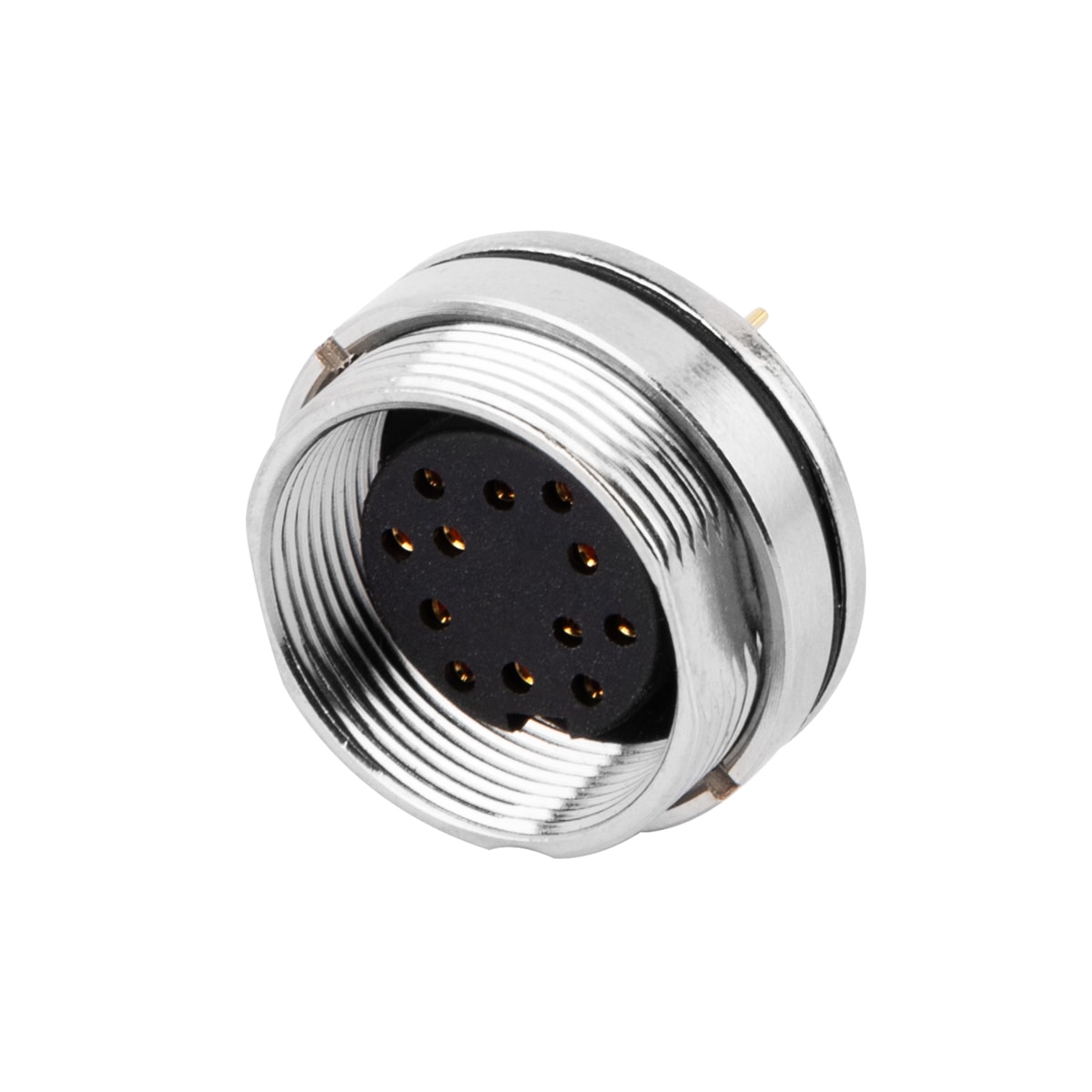

P/N: AM16F2422A001
M16 panel receptacle,rear mount,Female, contacts:24, PCB dip- solder connection,straight,IP67,UL certifiedView All -
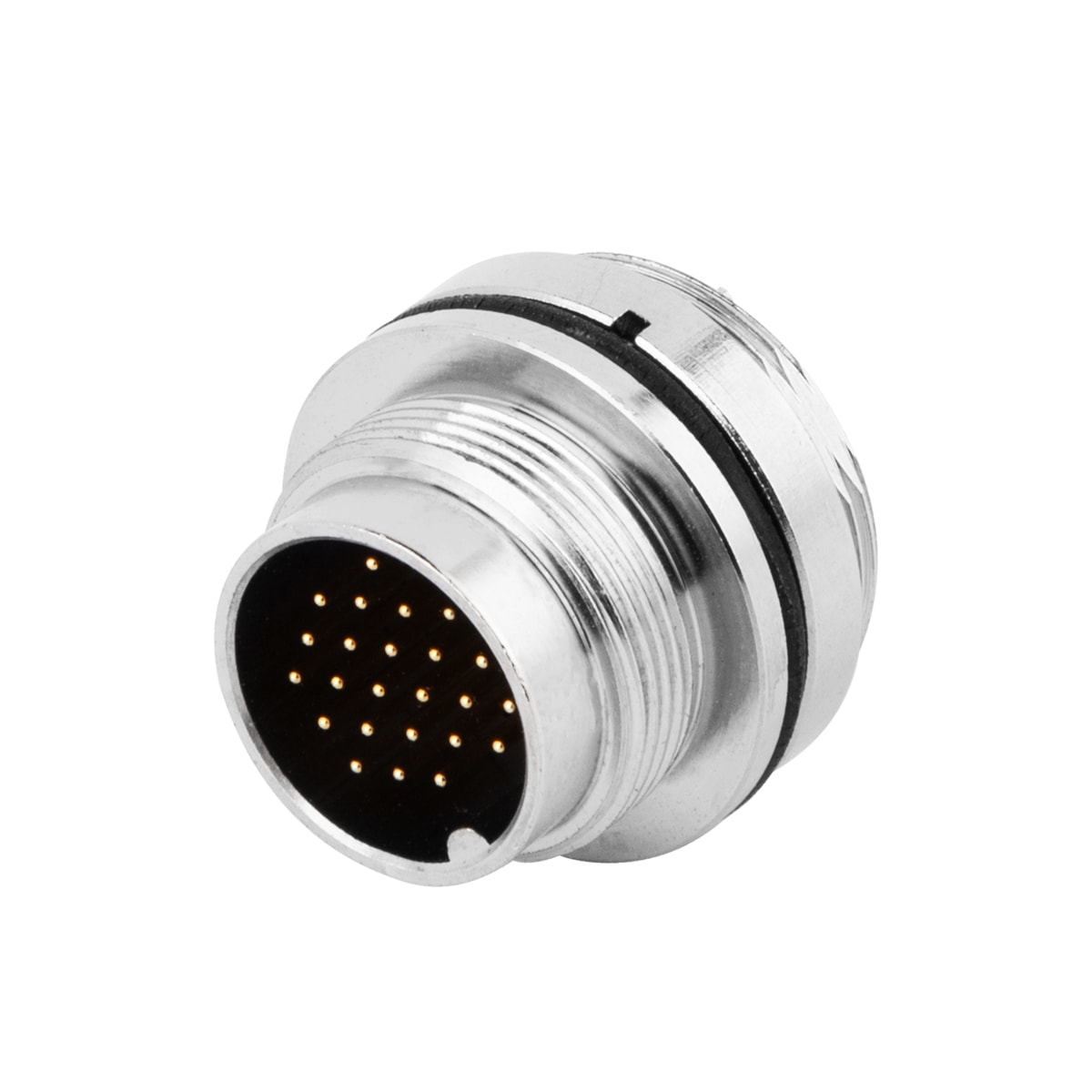

P/N: AM16M2422A001
M16 panel receptacle,rear mount,male, contacts:24, PCB dip- solder connection,straight,IP67,UL certifiedView All -
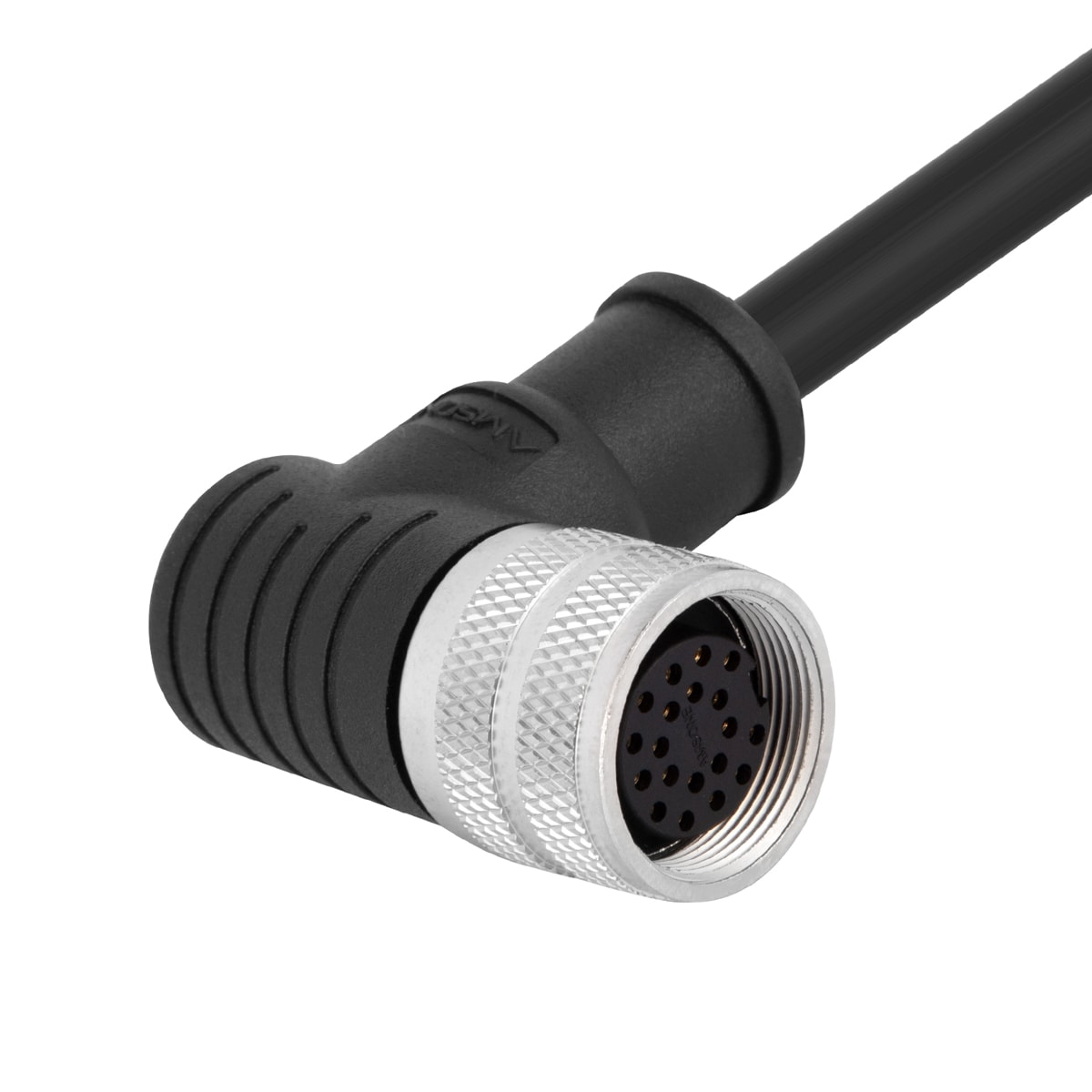

P/N: AM16F2411AXX2-XXX
M16 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:24, solder connection, right angled, IP67, shieldable, UL certifiedView All -
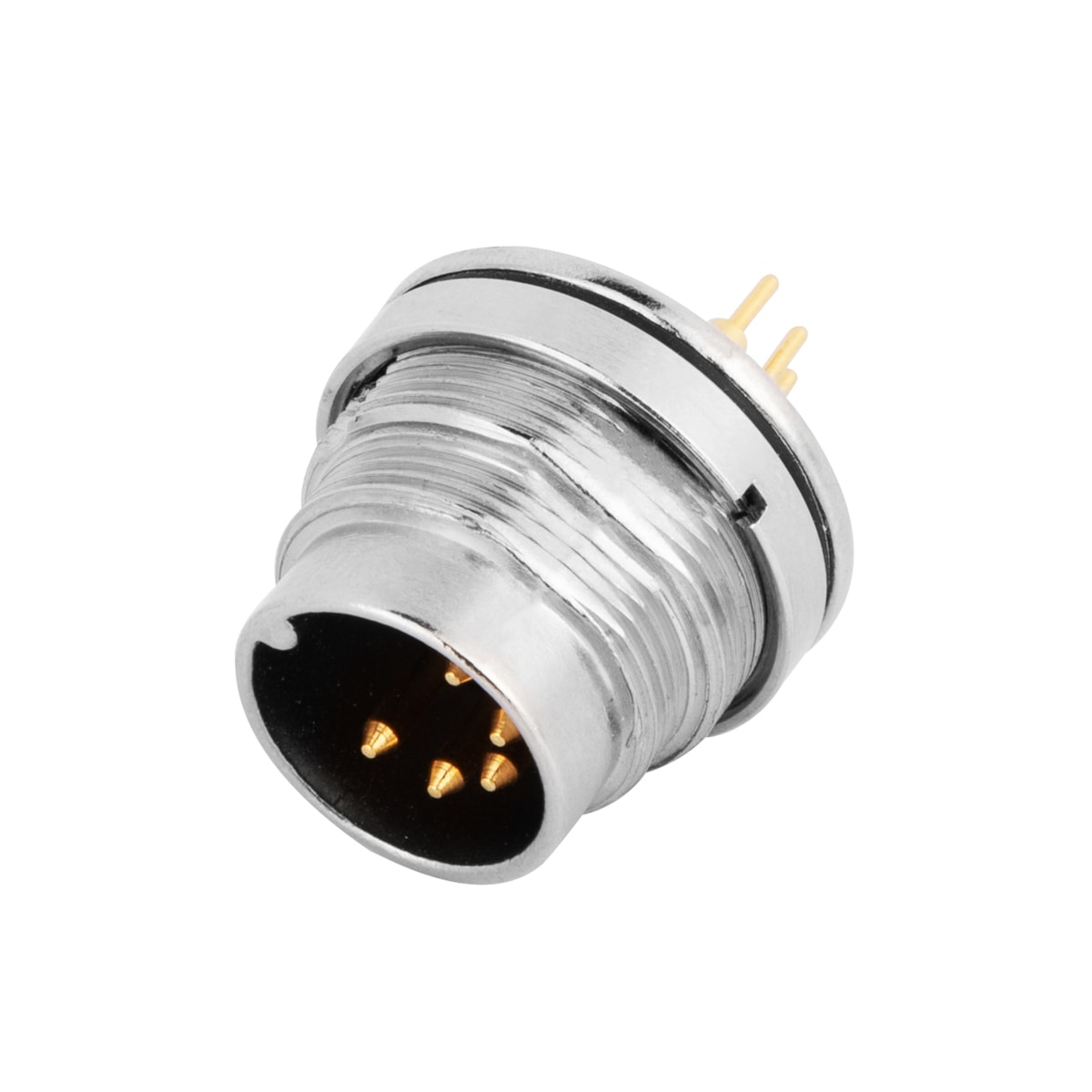

P/N: AM16M0522B001
M1M16 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:5, PCB dip-solderconnection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All -
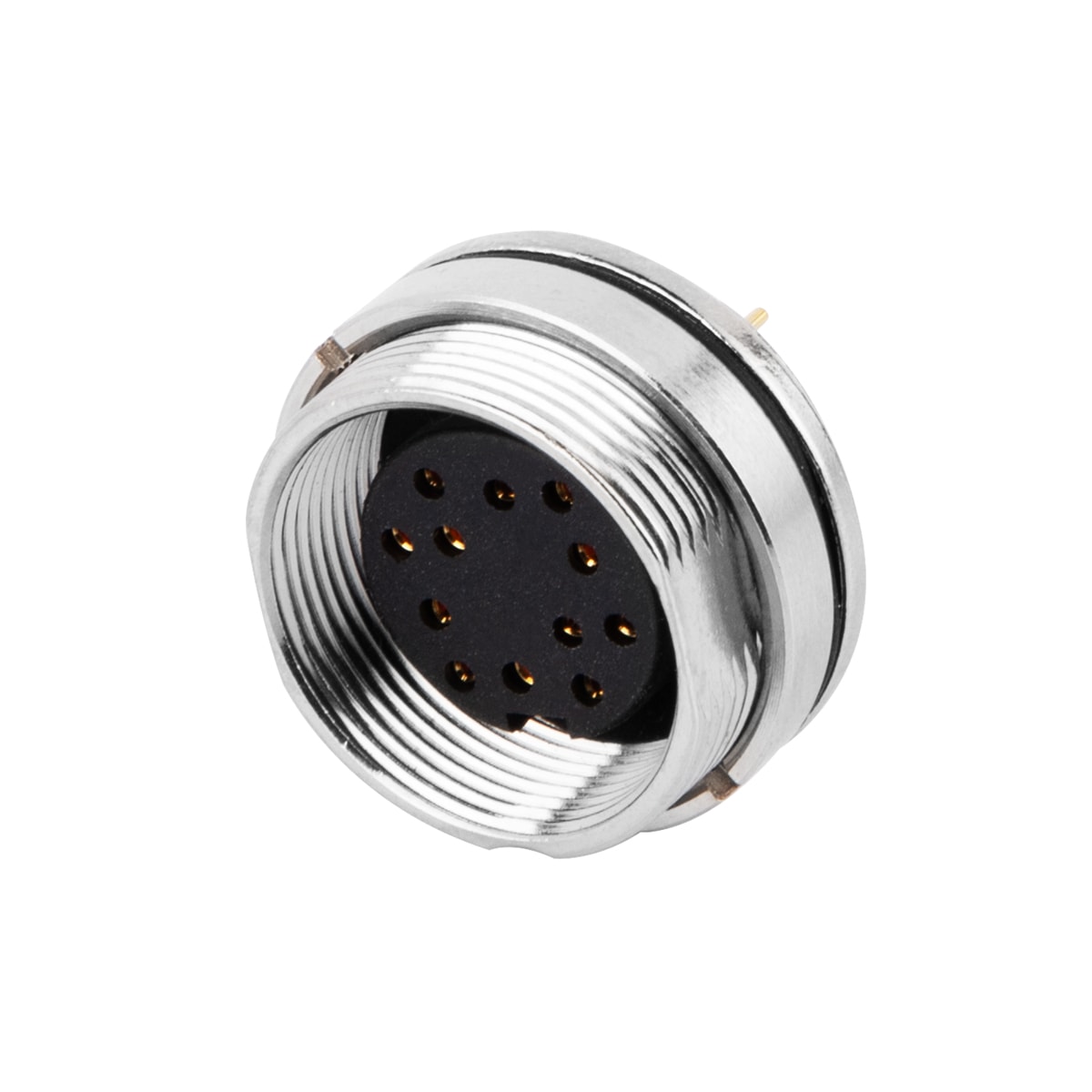

P/N: AM16F1222A001
M16 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:12,PCB connection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All -
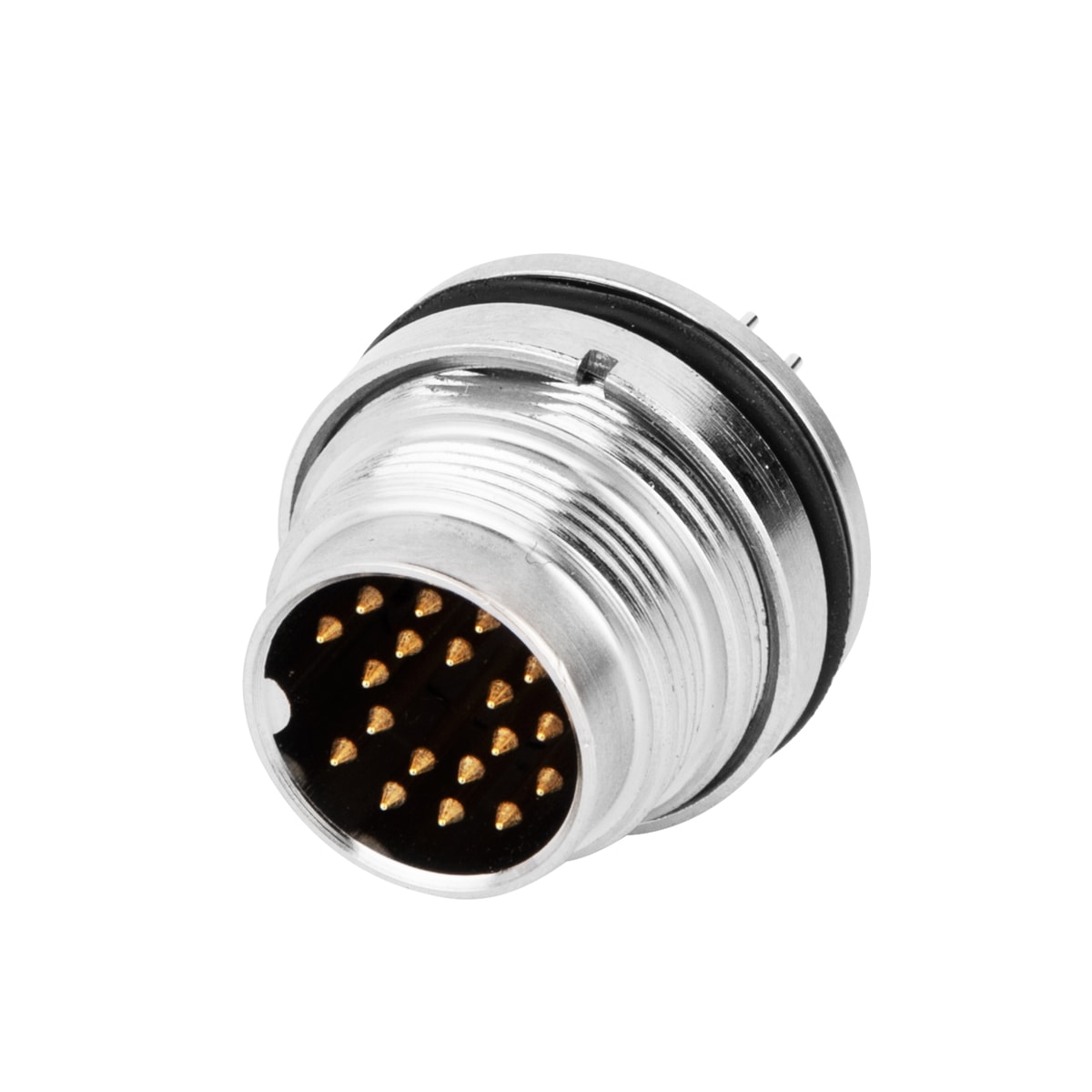

P/N: AM16M1222A001
M16 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:12,PCB dip-solder connection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All -

P/N: AM16M2411AXX1-XXX
M16 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:24, solder connection, straight, IP67, shieldableView All -
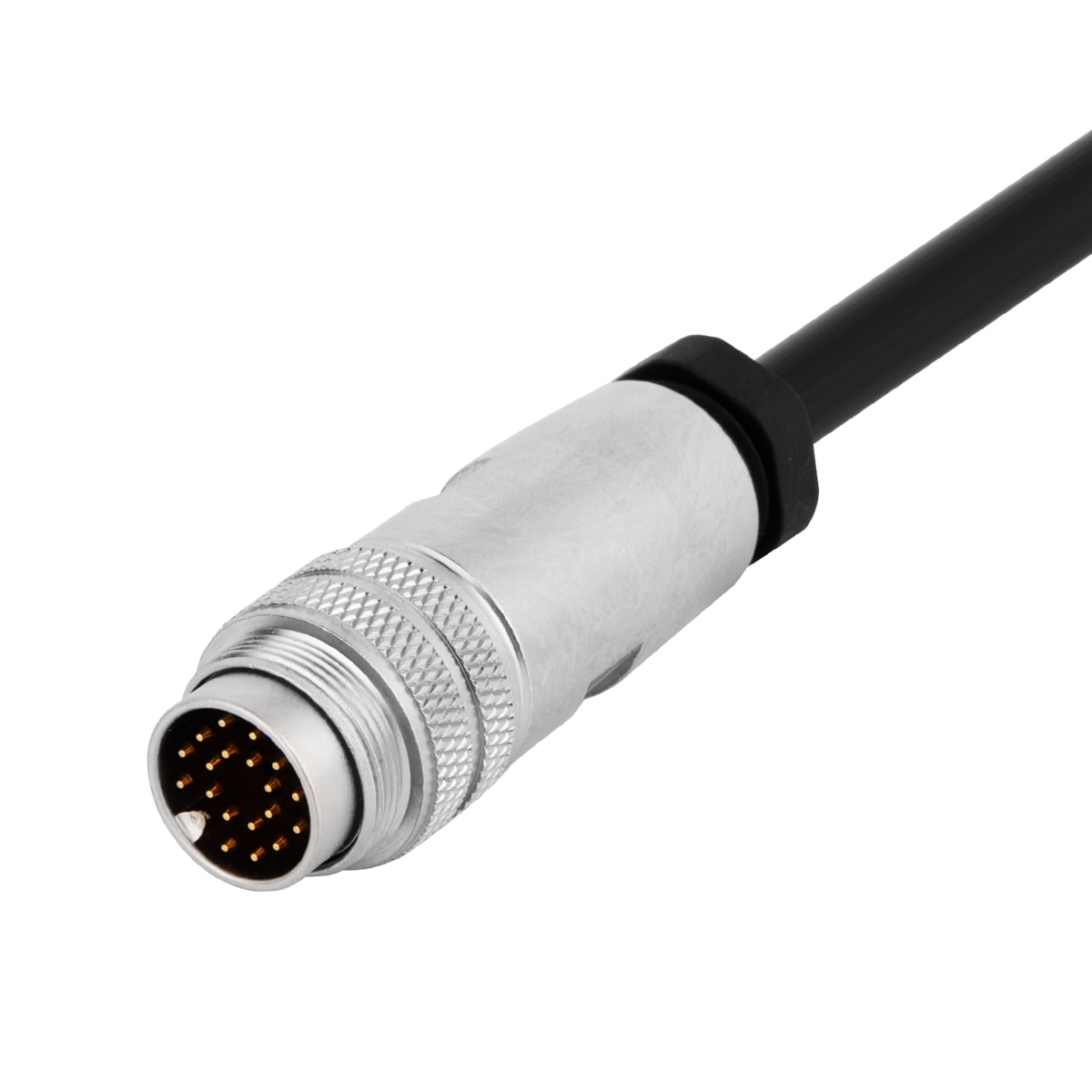

P/N: AM16M1214A001
M16 cable connector, male, contacts:12,field assembly type, solder connection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All
-
P/N: AM78F0511A162-010
MINI-Change 7/8View All -
P/N: AM78M0522A001
MINI-Change 7/8-16UNF Panel Rear Mount Receptacle Male 5Pin PCB ConnectorView All -
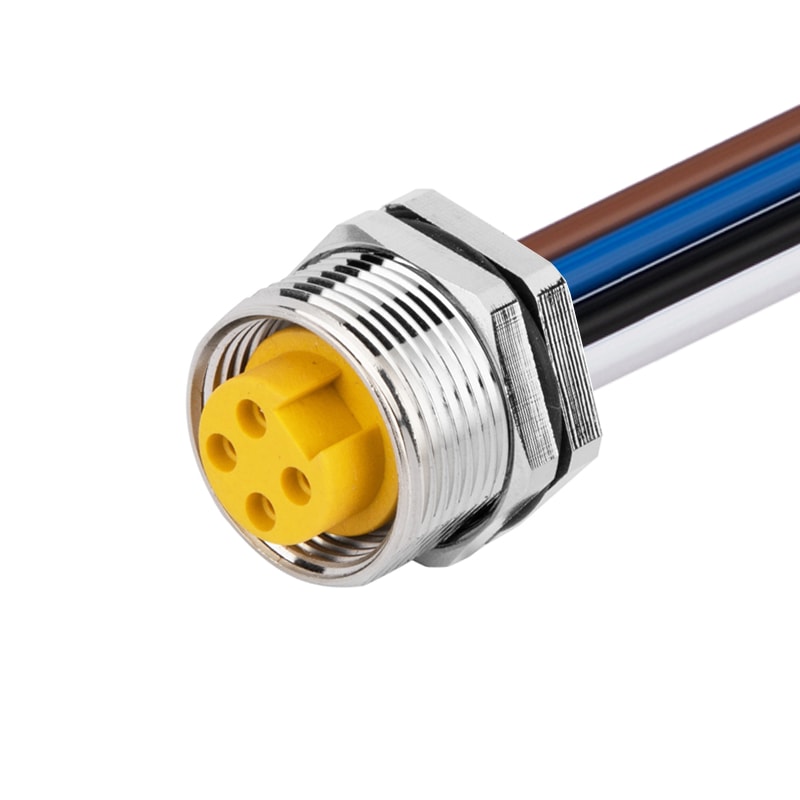

P/N: AM78F0412A371-050
7/8View All -
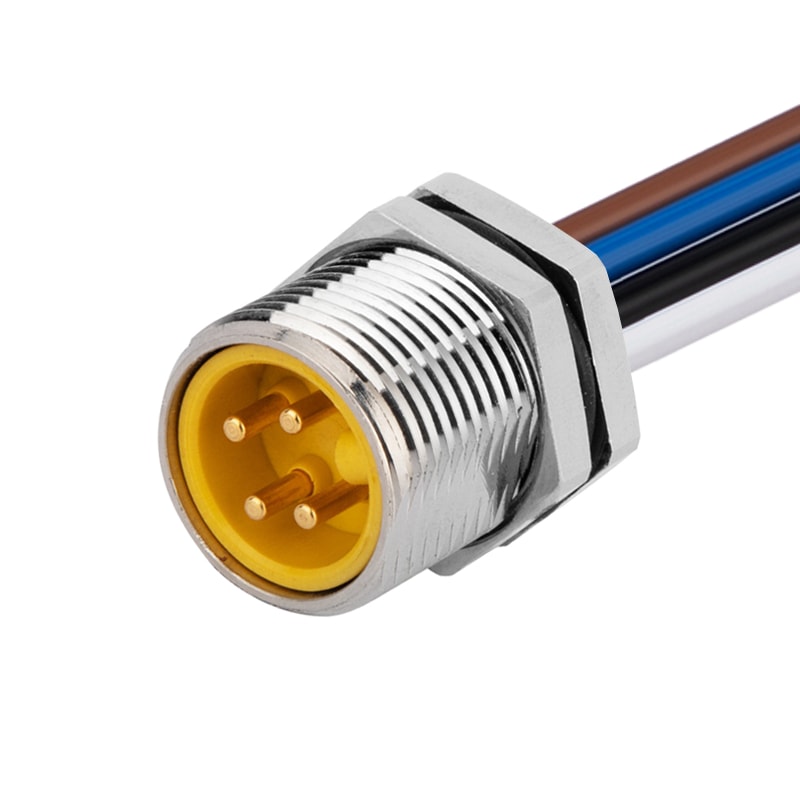

P/N: AM78M0412A371-050
7/8View All -
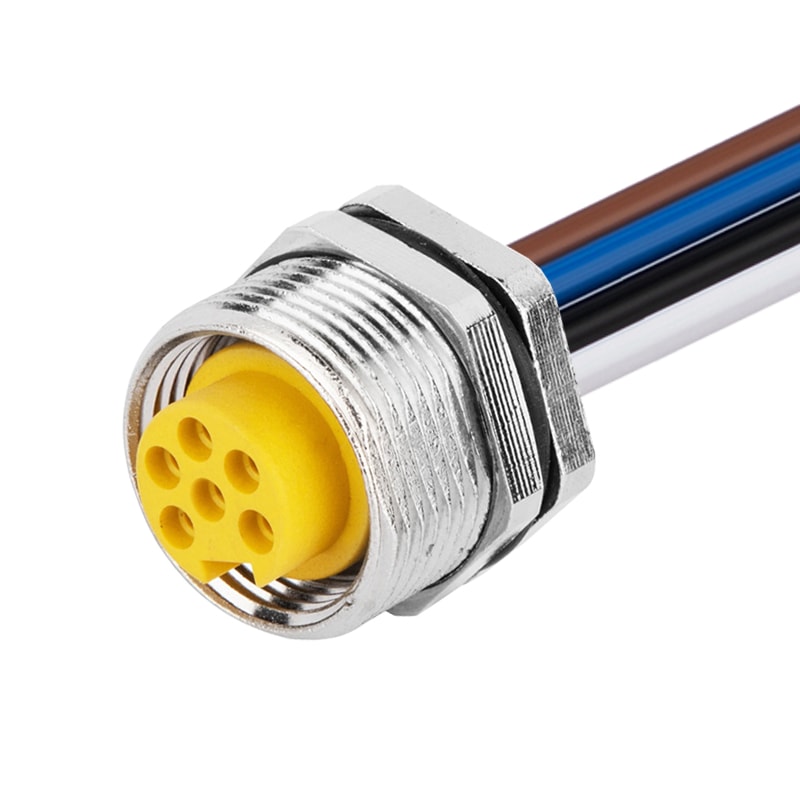

P/N: AM78F0512A371-050
7/8View All -

P/N: AM78M0512A371-050
7/8View All -

P/N: AM78F0312A371-050
7/8View All -

P/N: AM78M0312A371-050
7/8View All
-
P/N: AM23M1912A002
M23 Panel Receptacle Rear Mount Male 19P(16+3) Solder Connection For Wires Straight IP67View All -

P/N: AM23F1911AXX1-XXX
M23 Pre-molded Cable Connector Female 19P(16+3) Solder Connection Straight IP67View All -
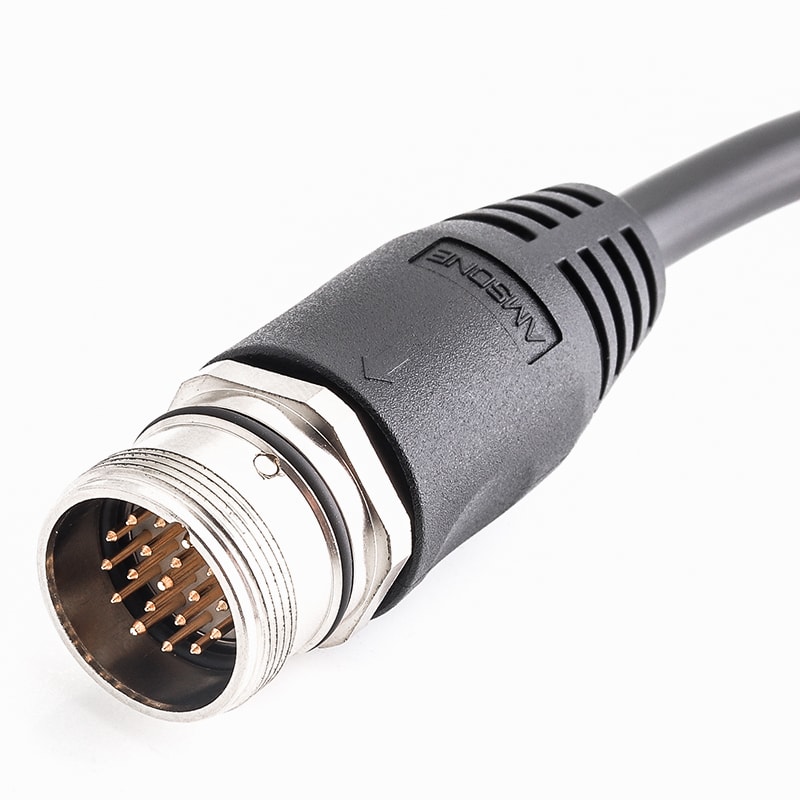

P/N: AM23M1911AXX1-XXX
M23 Pre-molded Cable Connector Male 19P(16+3) Solder Connection Straight IP67View All
-
P/N: BM24F0212A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 2P Receptacle Panel Mount Solder ConnectView All -
P/N: BM24M0214A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 2P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24M0314A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 3P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24F0312A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 3P Receptacle Panel Mount Solder ConnectView All -
P/N: BM24M0414A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 4P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24F0412A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 4P Receptacle Panel Mount Solder ConnectView All -
P/N: BM24M1214A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 12P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24F1222A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 12P Receptacle Panel Mount PCB ConnectView All
Industrial Cable Harnesses
-

P/N: AM12F0411D241-010
M12 4P D Code Pre-molded Cable Connector Female Straight IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0411D241-010
M12 pre-molded cable connector male solder connection D code straight IP67View All -
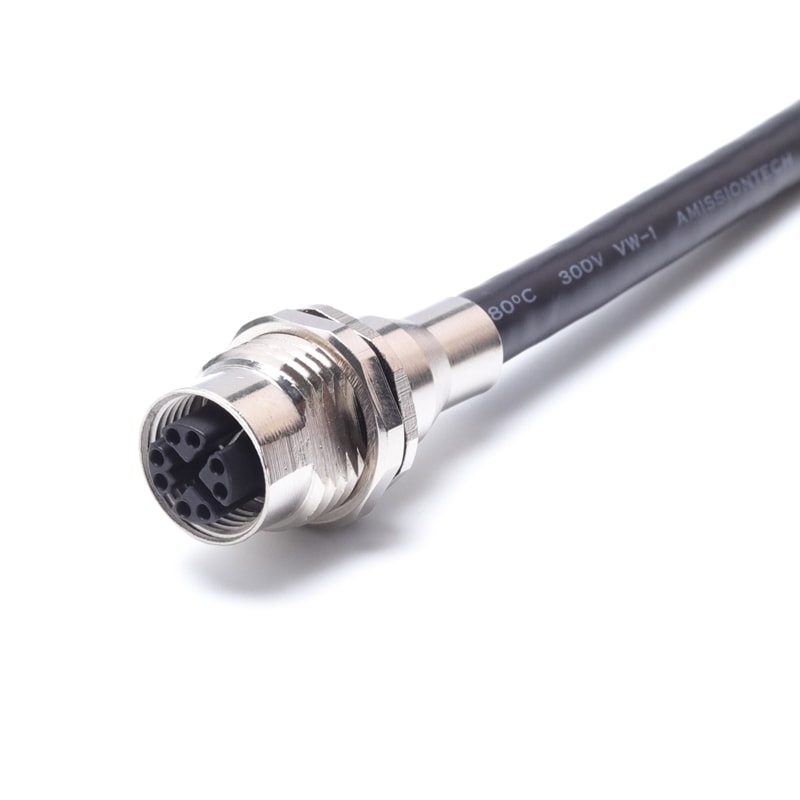

P/N: AM12F0812X003
M12 Device Connector X Code Female EMC Shielded Panel Rear Mount ReceptacleView All -
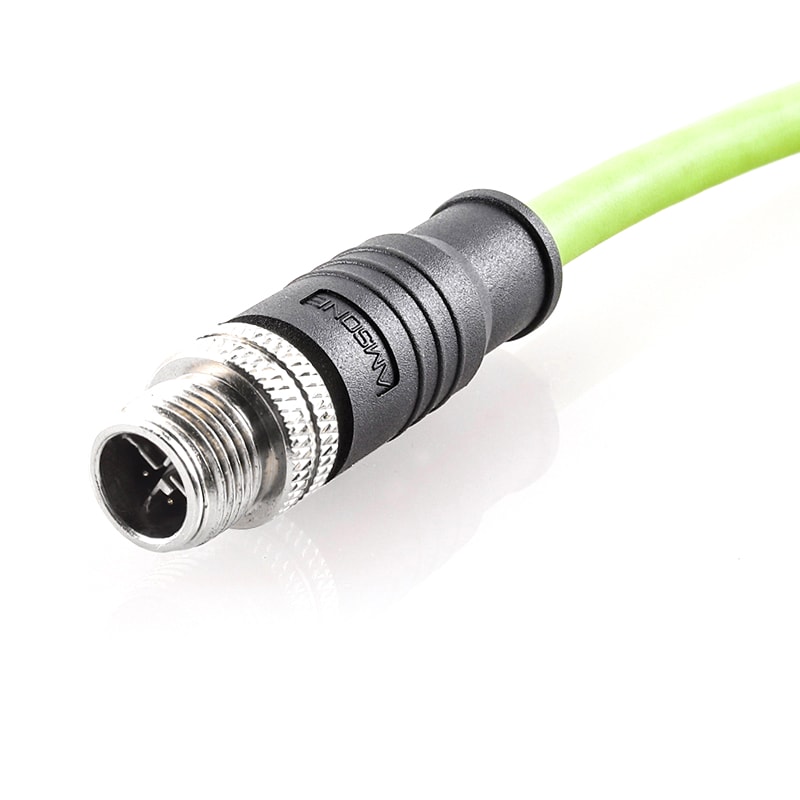

P/N: AM12M0811X231-030
M12 Pre-molded Cable Connector 8Pole Male X Code Cable StraightView All -
P/N: AM12F0411BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -
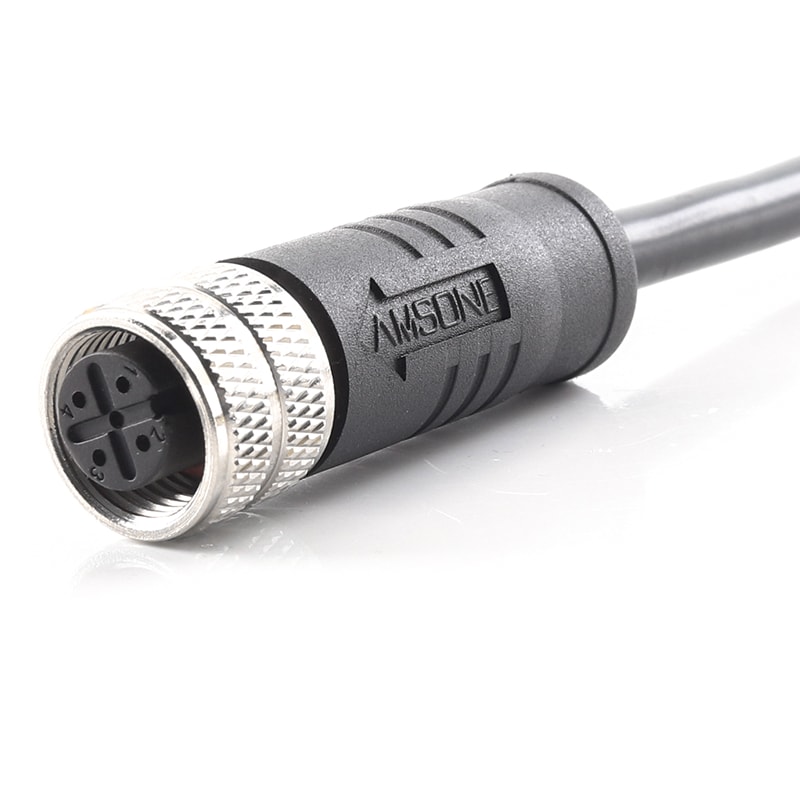

P/N: AM12F0511A241-010
M12 FieldBUS Cable Industrial Automation DeviceNet CanOpen CableView All -
P/N: EhterNet Cable
EhterNet Cable CAT5/CAT6/CAT7 PROFIBUS Industrial Network cableView All -
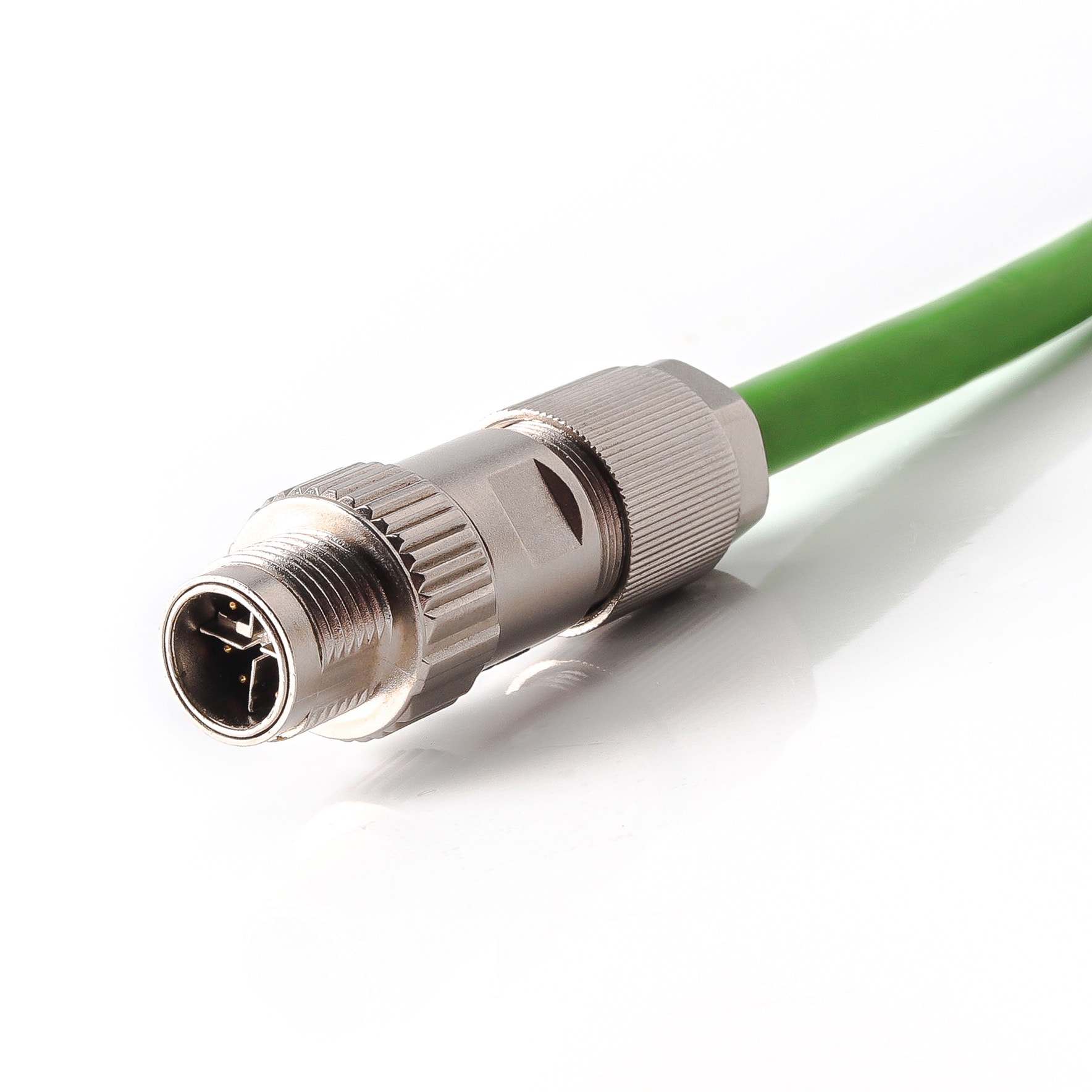

P/N: AM12M0814X221-010
M12 X Code Male ProfiNET/EtherNET Cable M12 Connector X CodedView All
-

P/N: AM12F0411D241-010
M12 4P D Code Pre-molded Cable Connector Female Straight IP67View All -
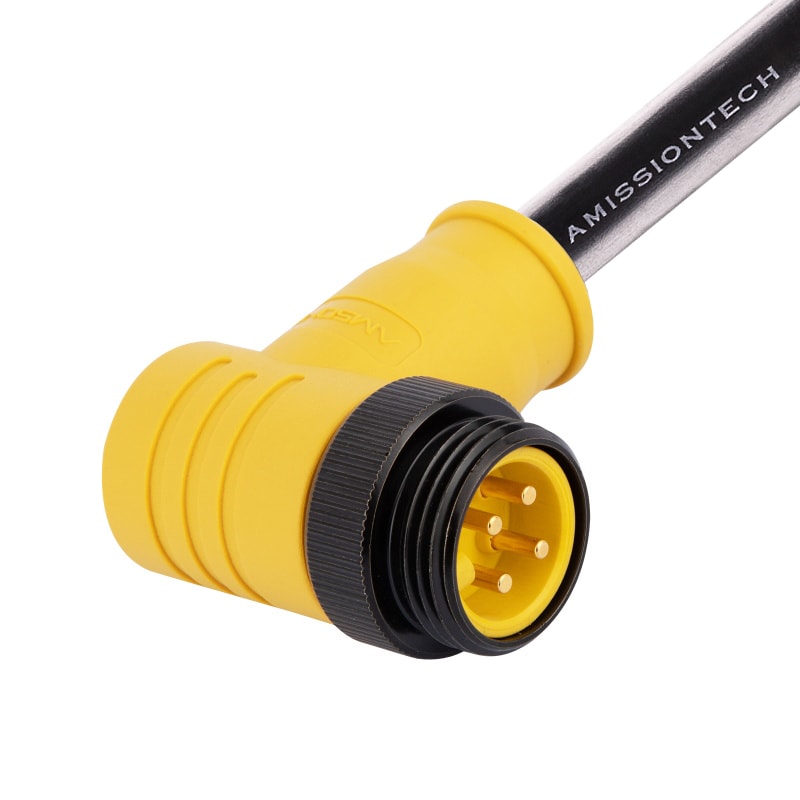

P/N: AM78M0411A272-050
DeviceNET 7/8View All -
P/N: AM12F0411BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0511A241-010
M12 FieldBUS Cable Industrial Automation DeviceNet CanOpen CableView All -
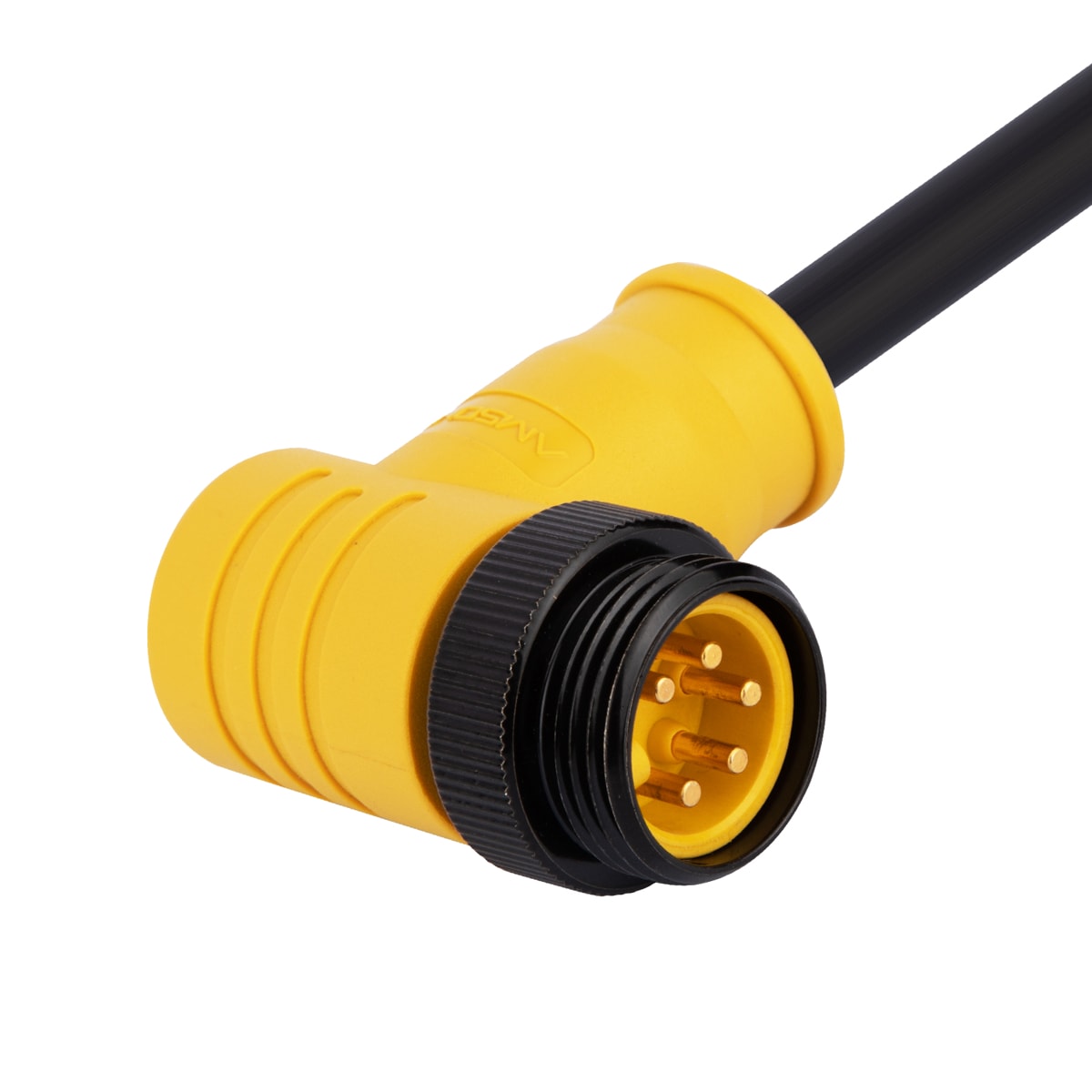

P/N: AM78M0511A172-030
MINI-Change 7/8View All
-

P/N: AM12M0411D241-010
M12 pre-molded cable connector male solder connection D code straight IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0812X003
M12 Device Connector X Code Female EMC Shielded Panel Rear Mount ReceptacleView All -

P/N: AM12M0811X231-030
M12 Pre-molded Cable Connector 8Pole Male X Code Cable StraightView All -
P/N: EhterNet Cable
EhterNet Cable CAT5/CAT6/CAT7 PROFIBUS Industrial Network cableView All -

P/N: AM12M0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Male,M12 Y-Coded Power Signal Ethernet CableView All -

P/N: AM12F0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Power Signal,M12 Y-Coded CablesView All -

P/N: AM12F0812Y003
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Panel Mount Shielded,M12 Y-CodedView All
-
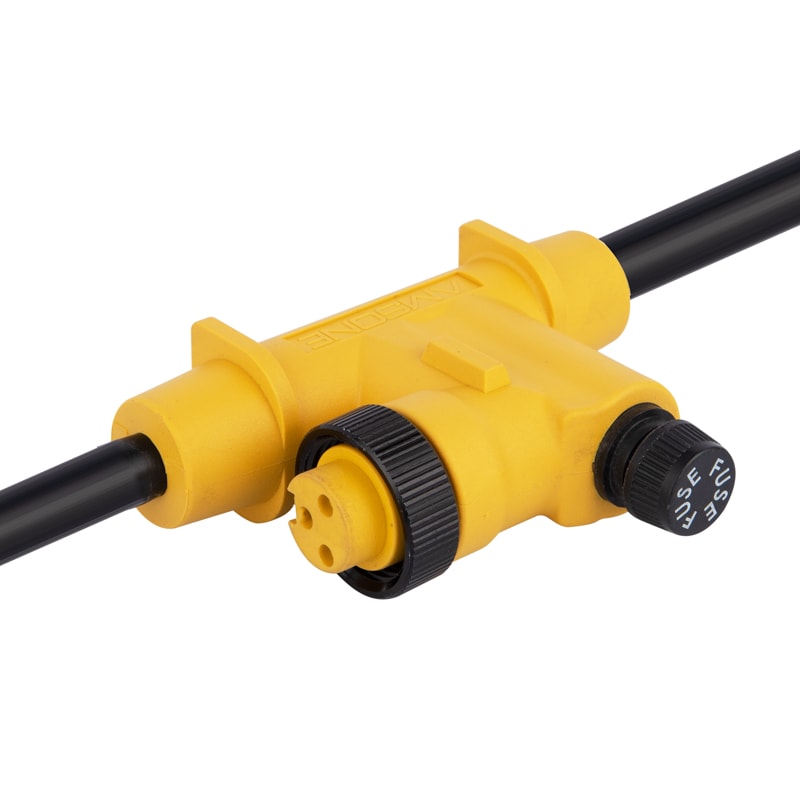

P/N: AM78H0511A433-XXX
Electrical Automation Power Supply Connector Cable 7/8-16UNF Pre-molded H-SplitterView All -
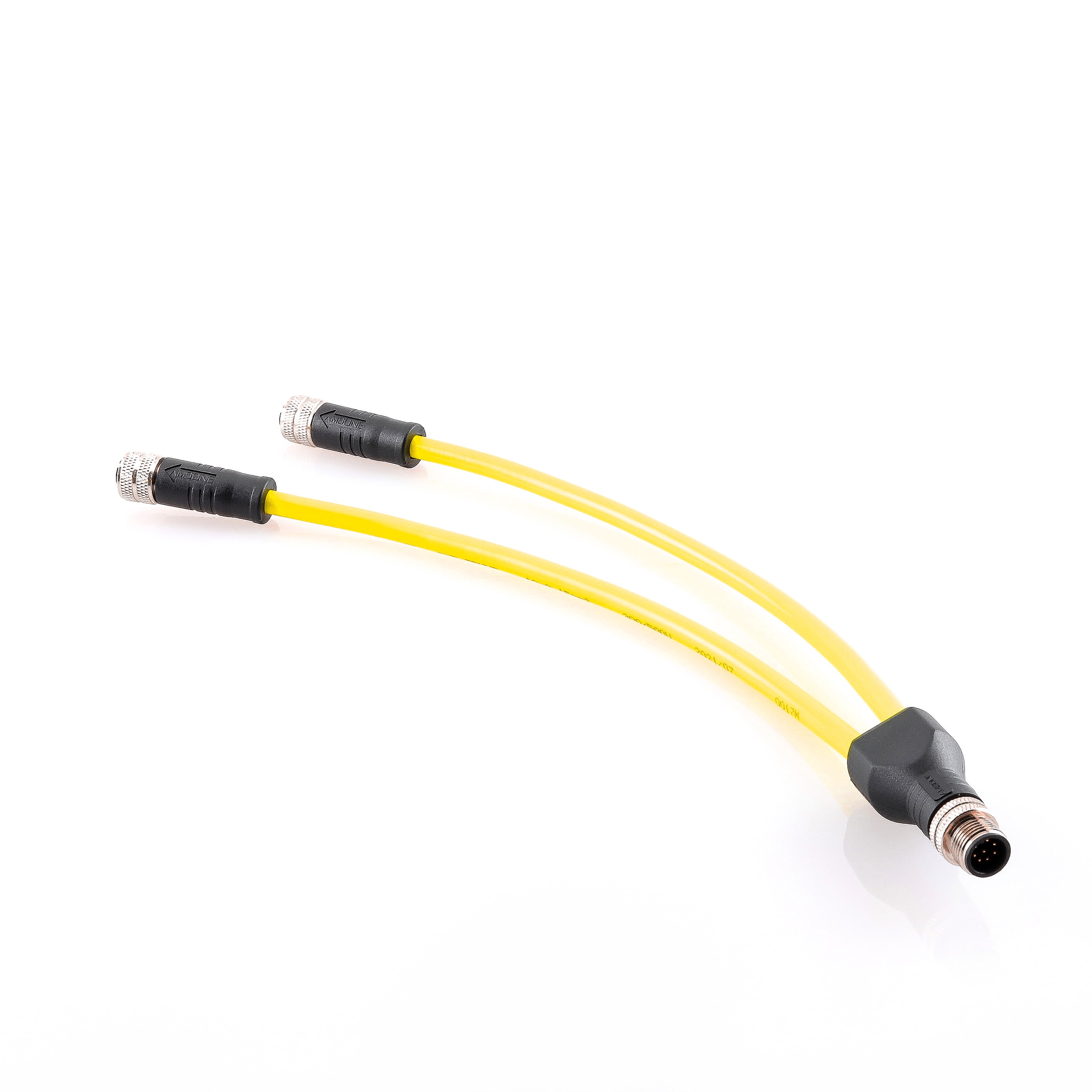

P/N: AM12H0811AXX1-XXX
M12 A Code 8P/4P Connector Y-Splitter Industrial Automation Sensor CableView All -
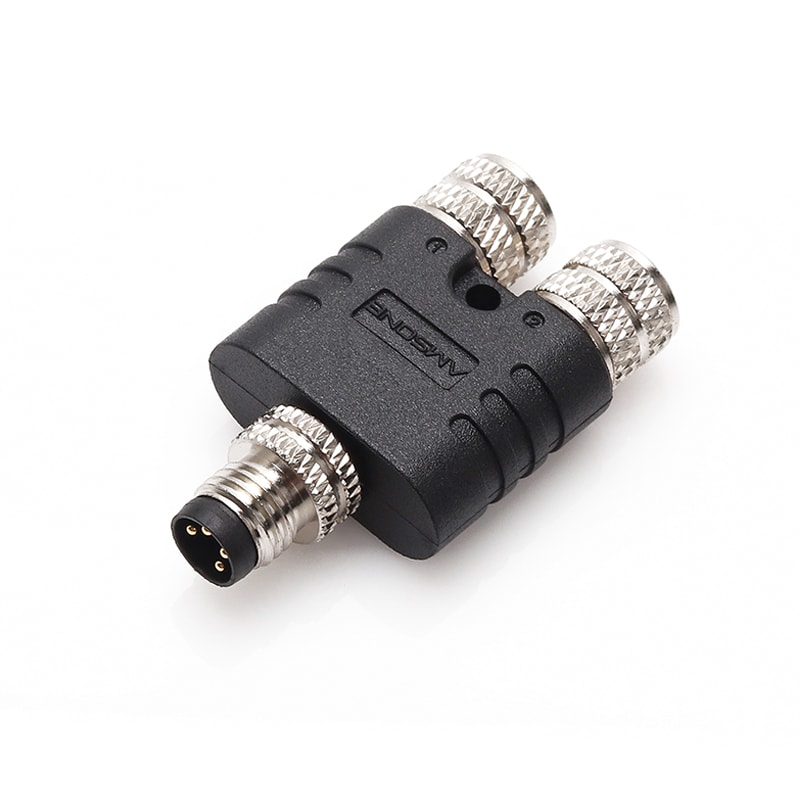

P/N: AM08Y0411A001-000
M8 Y-Splitter Electrical Automation Sensor Connector AdapterView All
Underwater Connectors and Cables
-

P/N: RMK5F
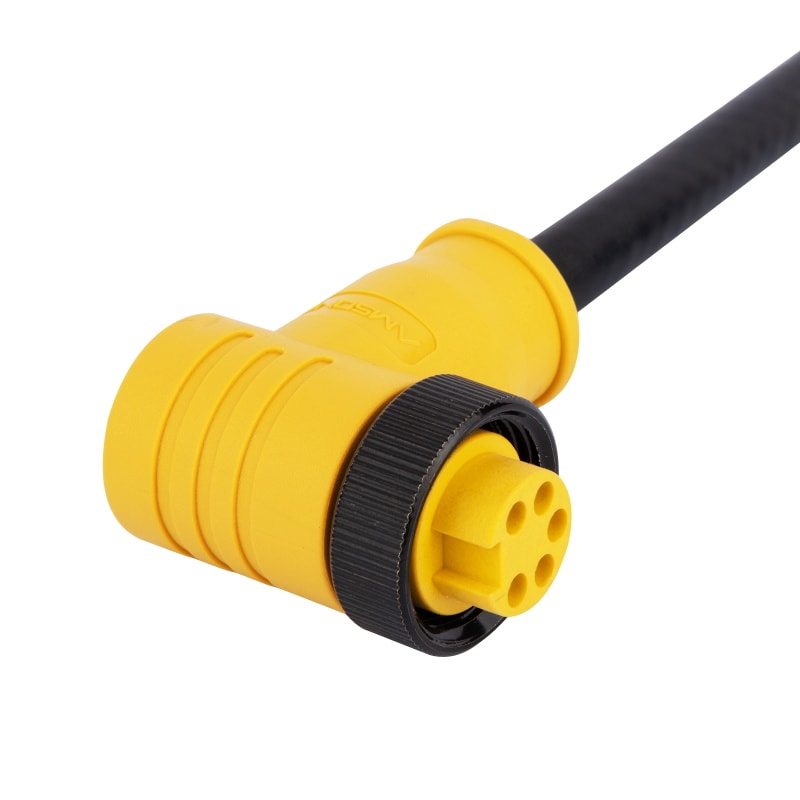
RMK5F 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 And 8 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: MCDLS-F
MCDLS-F 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 8 contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: MCBH5MTI
MCBH5MTI 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 And 8 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: HPBH9M
HPBH9M 9 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: HF75 50CXBH6F
HF75 50CXBH6F 6 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: DMCIL13F M
DMCIL13F M 13 contacts Underwater cable connectorView All -

P/N: AWQ7-42
AWQ7-42 24, 28, 32, 36, 42 contacts Underwater cable connectorView All -

P/N: 1L25F M
1L25F M Circular 12, 16, 25 Contacts Underwater ConnectorView All
company
News
-
 Amissiontech to Showcase Smart Interconnection Solutions at SPS 2025 in NurembergView All
Amissiontech to Showcase Smart Interconnection Solutions at SPS 2025 in NurembergView All -
 2025 Tokyo International Manufacturing Expo: A Perfect ConclusionView All
2025 Tokyo International Manufacturing Expo: A Perfect ConclusionView All -
 Amissiontech to Showcase Advanced Industrial Connectors and I/O Solutions at Manufacturing World Japan 2025View All
Amissiontech to Showcase Advanced Industrial Connectors and I/O Solutions at Manufacturing World Japan 2025View All -
 Amissiontech Reflects on a Successful Participation at ProPak China 2025View All
Amissiontech Reflects on a Successful Participation at ProPak China 2025View All -
 Amissiontech Team-Building Activity at Hailing IslandView All
Amissiontech Team-Building Activity at Hailing IslandView All -
 Dragon Boat Festival Greetings: Celebrating Tradition with AmissiontechView All
Dragon Boat Festival Greetings: Celebrating Tradition with AmissiontechView All -
 Celebrating Women at Amissiontech on International Women’s DayView All
Celebrating Women at Amissiontech on International Women’s DayView All -
 Amissiontech Invites You to HANNOVER MESSE 2025View All
Amissiontech Invites You to HANNOVER MESSE 2025View All
-
 Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All
Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All -
 What is an M12 A coded connector?View All
What is an M12 A coded connector?View All -
 What Do You Know M12 B Coded?View All
What Do You Know M12 B Coded?View All -
 Revolutionizing Field I/O Signal Transmission with Amissiontech's IO-Link HUBView All
Revolutionizing Field I/O Signal Transmission with Amissiontech's IO-Link HUBView All -
 Exploring the Technology Behind Underwater Connectors and CablesView All
Exploring the Technology Behind Underwater Connectors and CablesView All -
 Amissiontech's IO-LINK Modules Shine at HANNOVER MESSE 2024View All
Amissiontech's IO-LINK Modules Shine at HANNOVER MESSE 2024View All -
 Circular ConnectorView All
Circular ConnectorView All -
 IO-Link Module - Connects Future Digital CommunicationsView All
IO-Link Module - Connects Future Digital CommunicationsView All
-
 Understanding Ethernet MHz Speed and Its Impact on Network PerformanceView All
Understanding Ethernet MHz Speed and Its Impact on Network PerformanceView All -
 Top 10 Cable Types and Their UsesView All
Top 10 Cable Types and Their UsesView All -
 HDMI vs VGA: Understanding the Key Differences for Industrial & Custom Cable ApplicationsView All
HDMI vs VGA: Understanding the Key Differences for Industrial & Custom Cable ApplicationsView All -
 Complete Guide to Ethernet Cable CategoriesView All
Complete Guide to Ethernet Cable CategoriesView All -
 Wire Harness Production ExplainedView All
Wire Harness Production ExplainedView All -
 Industrial HDMI Shielded Cable Technology InterpretationView All
Industrial HDMI Shielded Cable Technology InterpretationView All -
 Revolutionize Automation with DeviceNet-Compatible ToolsView All
Revolutionize Automation with DeviceNet-Compatible ToolsView All -
 Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All
Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All
Industries and Solutions
Solutions
Industries
News And Events
Application of IO-Link in Industry
In the era of Industry 4.0, intelligent automation relies on advanced control systems and continuous data exchange enabled by industrial connectivity, such as IO-Link, to unify machine devices and facilitate advanced monitoring and diagnostics.
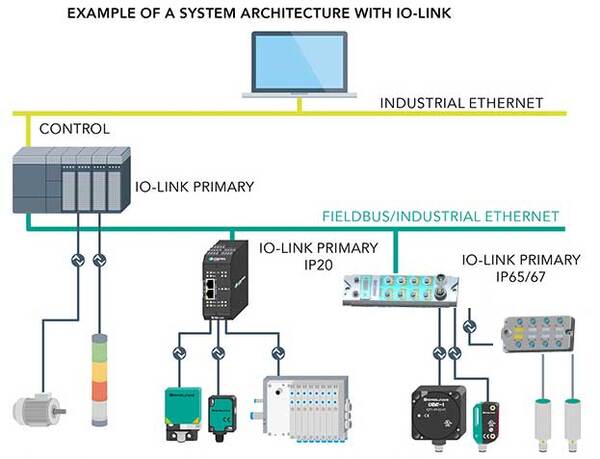
Figure 1: IO-Link complements existing network protocols by easily integrating into fieldbus or Ethernet networks via the IO-Link primary.
Standardized networks and communication-equipped devices are the foundation of industrial connectivity. While numerous protocols exist, not all meet the demands of modern automation for data exchange and intelligence. IO-Link was developed to address these requirements across a range of applications.
What is IO-Link?
IO-Link is a wired point-to-point communication protocol that enables bidirectional data exchange between devices. Local controllers typically have multiple IO-Link ports for various devices, making it a point-to-point protocol.
Introduced in 2009 by a consortium of 41 members, IO-Link has gained widespread acceptance for optimizing operations, reducing downtime, and cutting costs.
Defined by the IEC 61131-9 standard, IO-Link is supported by various manufacturers such as Siemens, Omron Automation, IFM, Balluff, Cinch Connectivity Solutions, Banner Engineering, Rockwell Automation, Sick, Pepperl+Fuchs, and others.
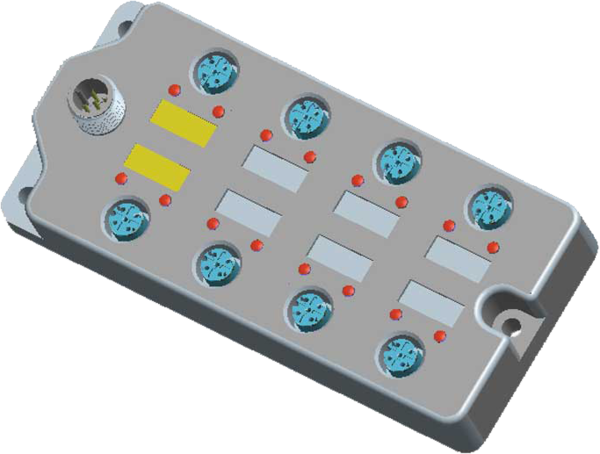

Figure 2: The choice of connector for the connecting cable is determined by the port type, and the mode of a primary's port is determined by the connected device and the ongoing operation.
Applications of IO-Link:
Actionable Status Communications

Figure 3: IO-Link enhances advanced control and automation systems. In the machine-tool industry, IO-Link sensors are extensively used for workpiece clamping verification and monitoring milling tool pressures and positions.
IO-Link devices enable machine monitoring and support system adjustments. In the machine-tool industry, IO-Link pressure sensors verify workpiece clamping, reducing rejected workpieces. These devices also aid maintenance by reporting status, like position sensors on assembly machines ensuring alignment. Analysis of IO-Link diagnostics data allows technicians to predict and prevent errors and identify areas for operational improvement.
2. Advanced Control and Automation
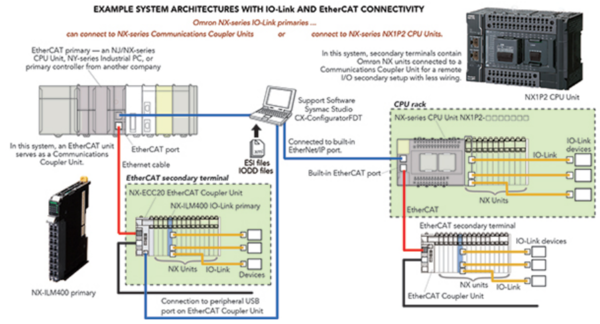
Figure 4: IO-Link enhances advanced control and automation systems. In the machine-tool industry, IO-Link sensors are extensively used for workpiece clamping verification and monitoring milling tool pressures and positions.
IO-Link supports control and automation functions, often connecting to a higher-level PLC or host system for autonomous operations. This connection typically utilizes standardized fieldbus or Ethernet protocols. Many IO-Link primaries come with fieldbus or Ethernet ports. In advanced control applications, devices integrate in one of three ways: 1) Direct connection to the host computer or PLC. 2) Connection to an IO-Link primary using the IO-Link protocol. 3) Use of IO-Link compatible communications, connecting to an IO-Link primary via an IO-Link hub. IO-Link hubs link non-IO-Link devices to the primary. With fieldbus and Ethernet connectivity, long-distance placement of IO-Link primaries is possible, whether in a control cabinet or at the outermost machine points. In advanced assembly, IO-Link primaries act as low-level controllers, handling both digital and analog signals, such as data from XY stage linear encoders. They serve as gateways, transmitting processed field-device data to PLCs or other system controllers.
3. Device Intelligence
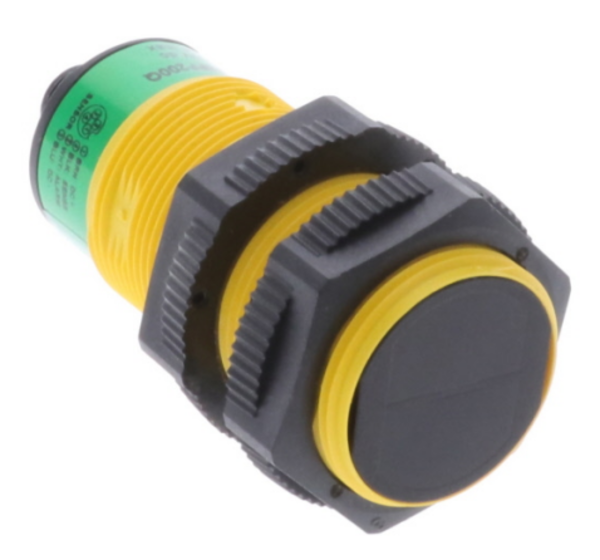

Figure 5: The IO-Link connection interface is very small and can fit on most compact field devices.
IO-Link's third application is enhancing devices' intelligence. IO-Link-enabled sensors can receive instructions, perform self-testing, and provide detailed data, beyond simple on-off signals. For instance, IO-Link temperature sensors continuously report precise temperature values for better process automation.
IO-Link's compact physical connections contrast with bulkier fieldbus and Ethernet interfaces, making it suitable for smaller field microdevices. IO-Link also enables precise control, allowing actuators to respond to specific conditions rather than basic on-off commands.
Input devices like pushbutton switches from suppliers such as Rafi can leverage IO-Link for smart features, including color-coded indicator lights.
However, IO-Link has limitations, being a wired protocol with a 20m cable length constraint and a 32-byte data transmission limit per cycle, making it unsuitable for data-intensive devices like cameras.
Summary:
IO-Link systems offer versatile applications, seamlessly integrating with existing protocols for extensive control and data collection systems. Their appeal lies in simplicity, with just an IO-Link primary, devices, and connectorized cables. Easy plug-and-play installation and cost-effectiveness further enhance IO-Link's advantages.
The IO-Link consortium's collaborative efforts have ensured broad compatibility among controllers, devices, and actuators from various manufacturers, providing design engineers with a wide array of equipment choices for specific use cases.






































