Products
I/O Systems
-
 IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All
IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBN1-354XXX
IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Metal Housing Metal Thread / Bayonet LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBN1-310XXX
IO Link Hub NPN 0.5A/channel Metal Housing Metal Thread LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP1-372XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 2A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP2-364XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 2A/channel Plastic Housing Metal Thread/Bayonet LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP1-372XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Plastic Thread LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP1-351XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 0.5A/channel Plastic Housing Metal Thread/Bayonet LockingView All -

P/N: ALD-HBP2-330XXX
IO Link Hub PNP 2A/channel Metal Housing Metal Thread LockingView All
-

P/N: ALM-MPA1-051XXX
IO Link Master Multiprotocol Plastic Housing 7/8 Power ConnectorView All -

P/N: ALM-ECA1-010XXX
IO Link Master EtherCAT Single ProtocolView All -

P/N: ALM-MPA1-041XXX
IO Link Master Multiprotocol Plastic Housing M12 L-Codedd Power ConnectorView All -

P/N: ALM-MPA1-030XXX
IO Link Master Multiprotocol Metal Housing M12 L-Codedd Power ConnectorView All -

P/N: ALM-PNA1-010XXX
IO Link Master Profitnet Single ProtocolView All
Circular Connectors
-

P/N: AM08M0411AXX1-XXX
M8 4Pin Pre-molded Cable Male Straight M8 ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM08F0822A001
M8 Device Connector Panel Rear Mount M8 8P Female ReceptacleView All -

P/N: AM08M0622A001
M8 Device Connector Panel Rear Mount M8 6P Male ReceptacleView All -

P/N: AM08M0811AXX1-XXX
M8 8Pin Pre-molded Cable Male Straight M8 ConnectorView All -
P/N: AM08M0822A003
M8 Device Connector Male 8Pin PCB Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Right Angled ShieldedView All -

P/N: AM08M0822A001
M8 Device Connector Panel Rear Mount M8 8P Male ReceptacleView All -

P/N: AM08F0811AXX3-XXX
M8 8P Female Shield Connector Pre-molded Cable Right Angled IP67View All -

P/N: AM08M0811AXX3-XXX
M8 Connector 8P Male Shield Pre-molded Cable Right Angled IP67View All
-

P/N: AM12F1211AXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts: 12,solder connection, A code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0822A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts: 8, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0522A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts: 5, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
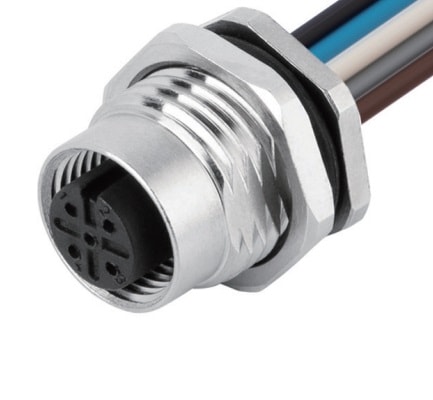

P/N: AM12F0512AXX1-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts: 5, solder connection for wires, A code, straight, IP67View All -
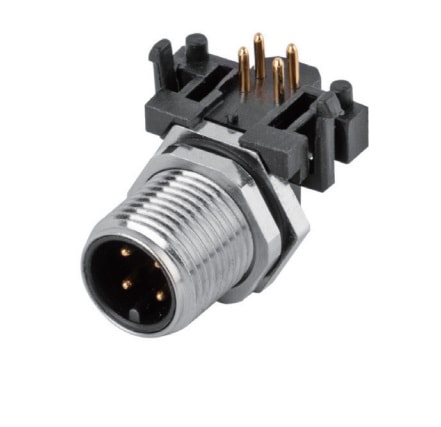

P/N: AM12M0422A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts: 4, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
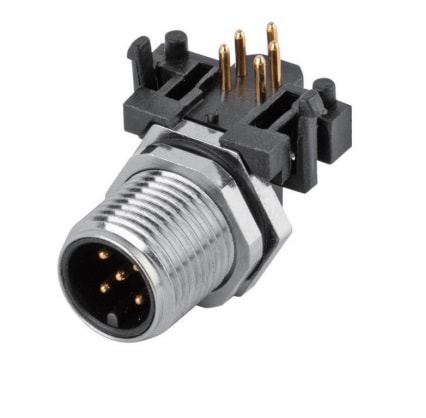

P/N: AM12M0522A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts: 5, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -
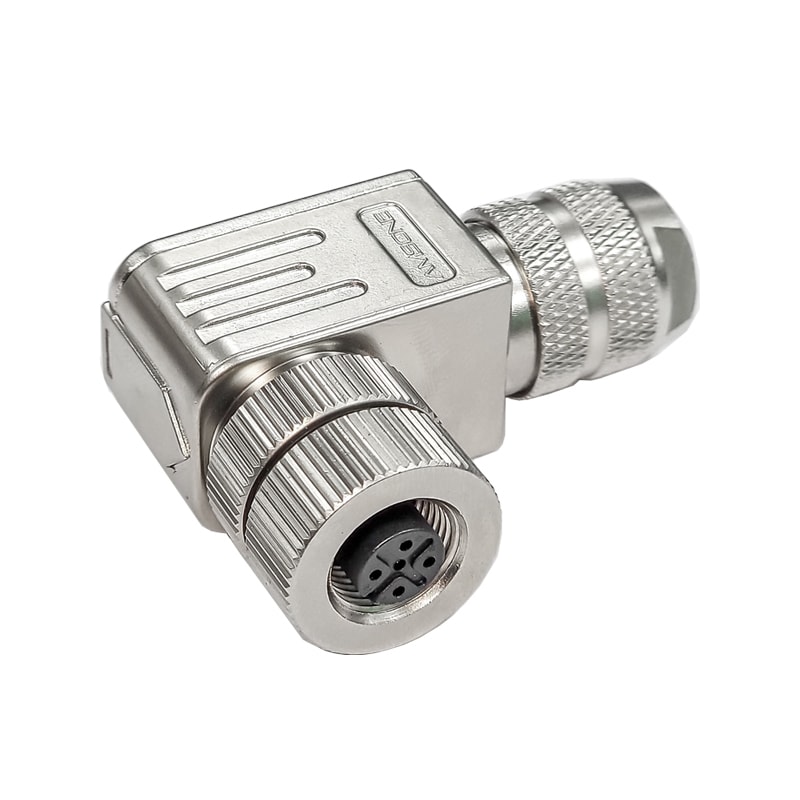

P/N: AM12F0534A007
M12 cable connector, female, contacts:5, field assembly type, screw connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0822A005
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts: 8, PCB dip-solder connection, A code, right angled, IP67View All
-

P/N: AM12F0522B001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:5, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0522B001
M12 B Code Male Panel Rear Mount Receptacle PCB Connector PG9View All -

P/N: AM12F0511BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:5, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0511BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:5, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0422B001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0422B001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0512B002
M12 5P Male B Code Panel Rear Mount Receptacle Wires Solder Connector M16*1.5View All -
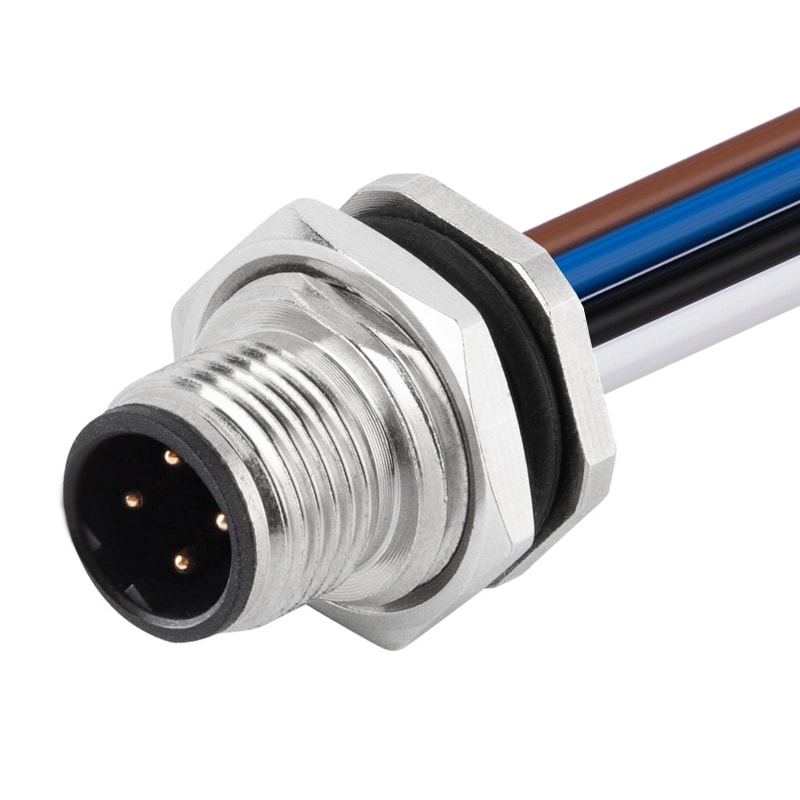

P/N: AM12M0512B001
M12 5P Male B Code Panel Rear Mount Receptacle Wires Solder Connector PG9View All
-
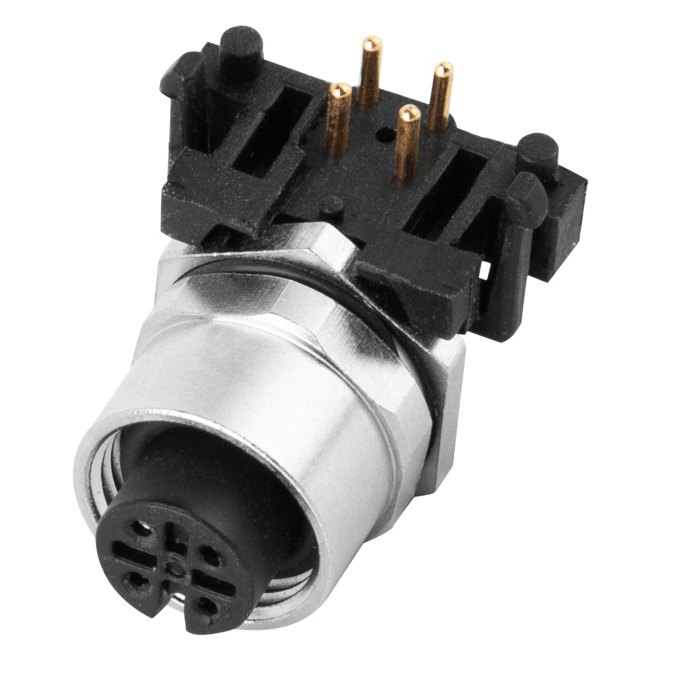
P/N: AM12F0422D006
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, D code, right angled, IP67View All -
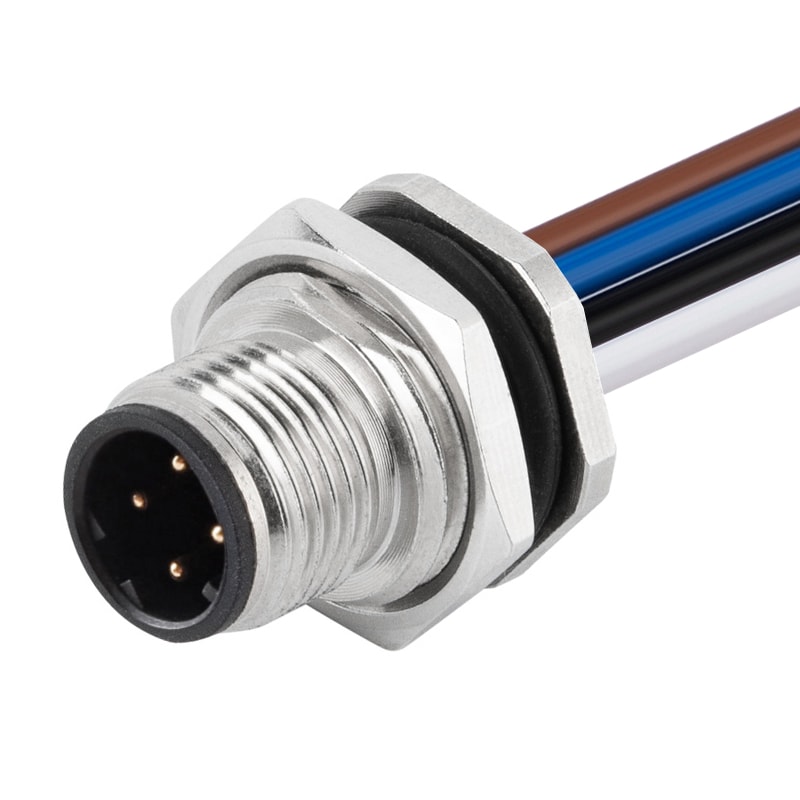

P/N: AM12M0412D001
M12 D Code Male Panel Rear Mount Receptacle For Wires Solder Connector PG9View All -
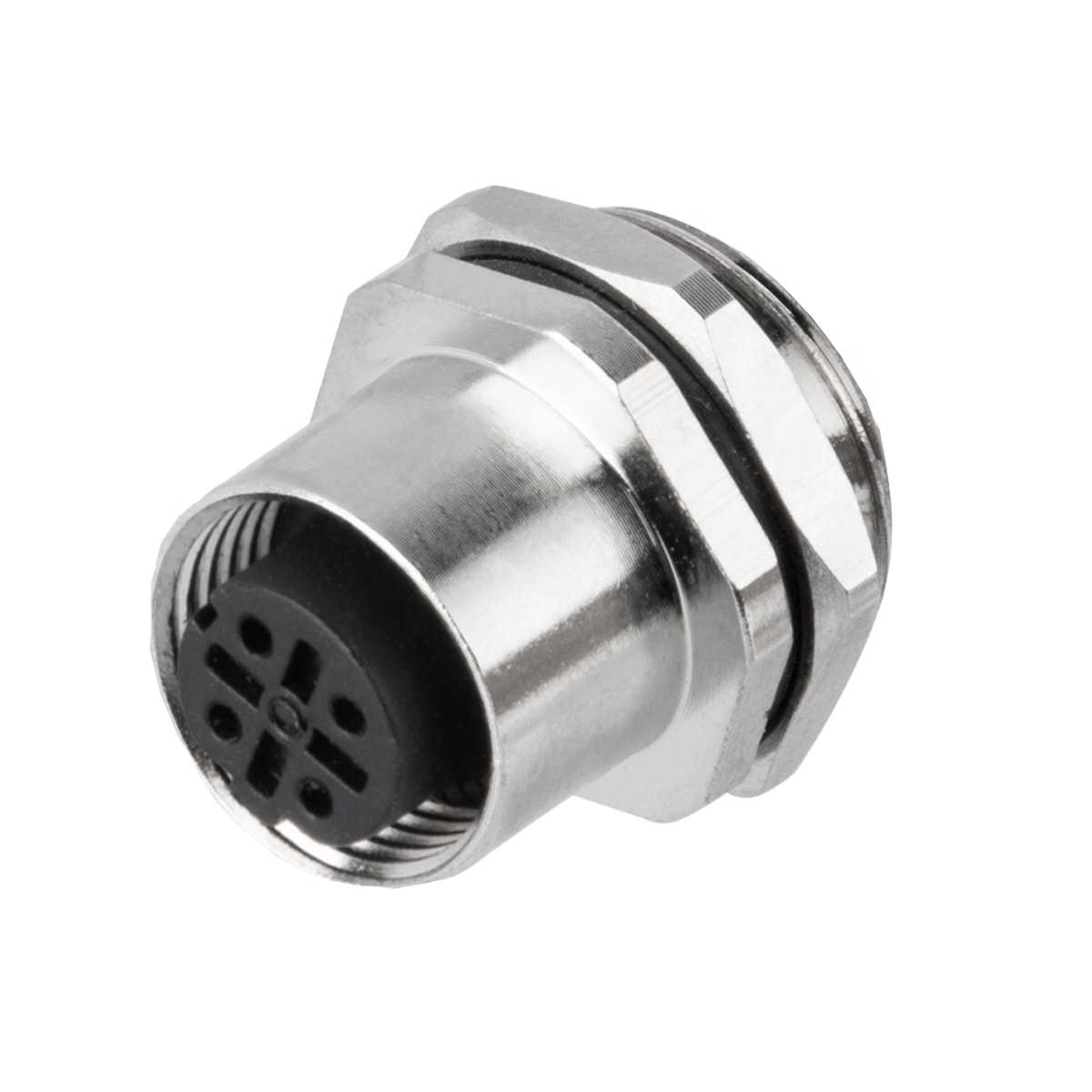

P/N: AM12F0413D001
M12 panel receptacle, front mount, female, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, D code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0413D351-005
M12 Panel Receptacle Front Mount Male 4Pin Solder Connection For Wires D Code Straight IP67View All -
P/N: AM12F0422D001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, D code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0422D001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, PCB dip-solder connection, D code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0411D241-010
M12 4P D Code Pre-molded Cable Connector Female Straight IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0411D241-010
M12 pre-molded cable connector male solder connection D code straight IP67View All
-
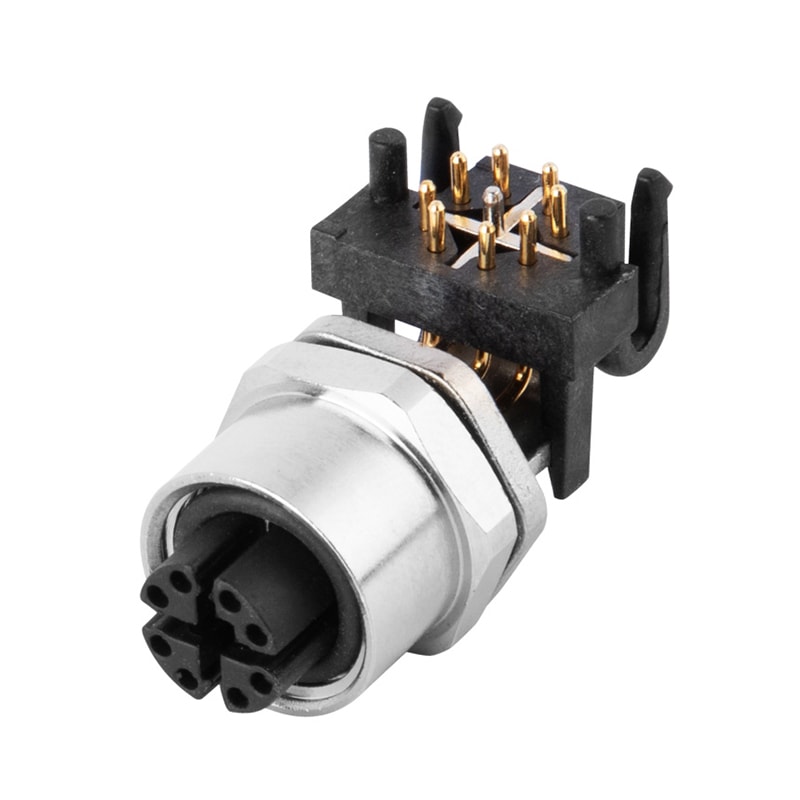

P/N: AM12F0822X008
M12 X Code 8Pole Panel Receptacle Rear Mount Female PCB Dip-solder Connection Right Angled IP67View All -
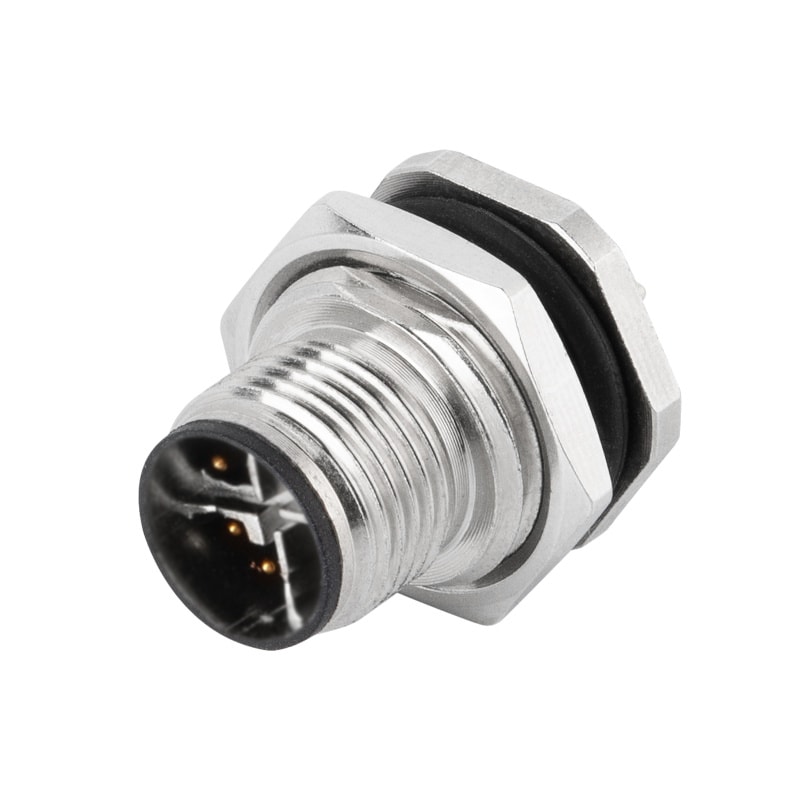

P/N: AM12M0822X001
M12 Panel Receptacle Rear Mount Male PCB DIP Solder X Code StraightView All -
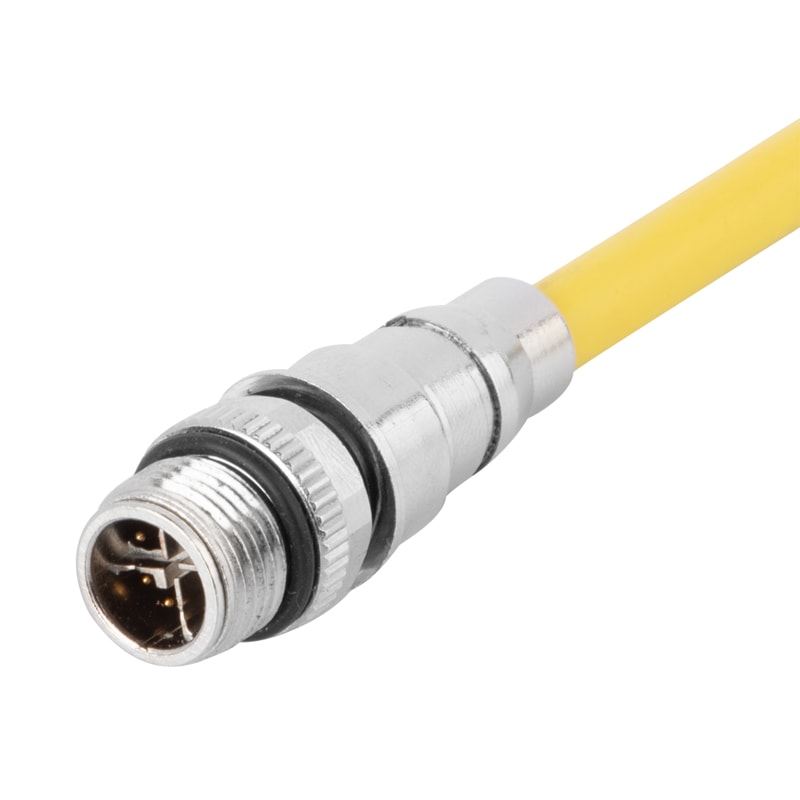

P/N: AM12M0811X003
M12 data cable connector, contact: 8P, male, for pre-molding , X code, straight, 360 EMC shielding, solder connection, 0.5A/60VView All -
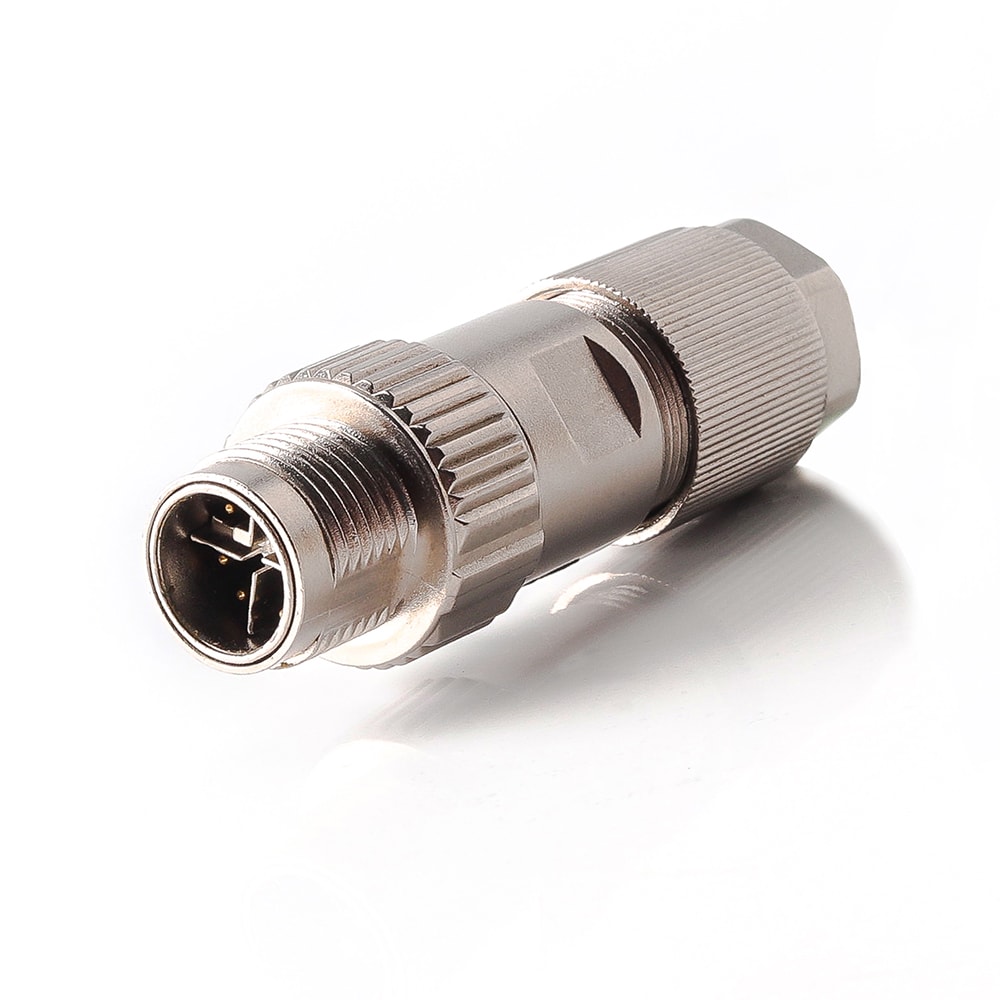

P/N: AM12M0844X003
M12 X Code Field Assembly Connector Male EMC Shielded Straight IP67 Crimp ContactsView All -
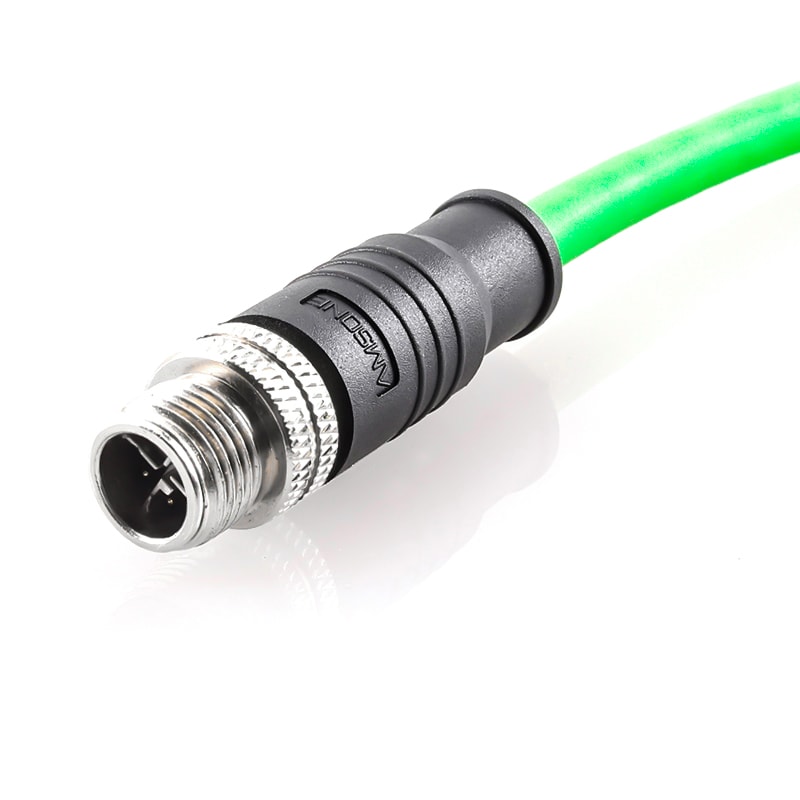

P/N: AM12M0811X233-100
M12 Pre-molded Cable Connector 8Pole Male X Code EMC Profinet/Ethernet Cable StraightView All -
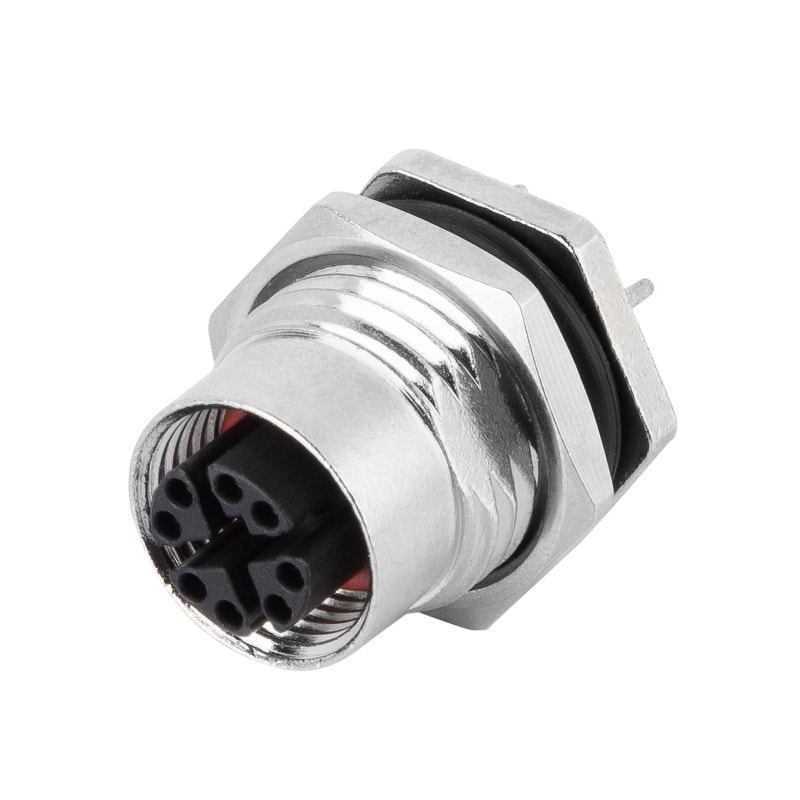

P/N: AM12F0822X002
M12 X Code Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female PCB DIP Connection M16*1.5View All -
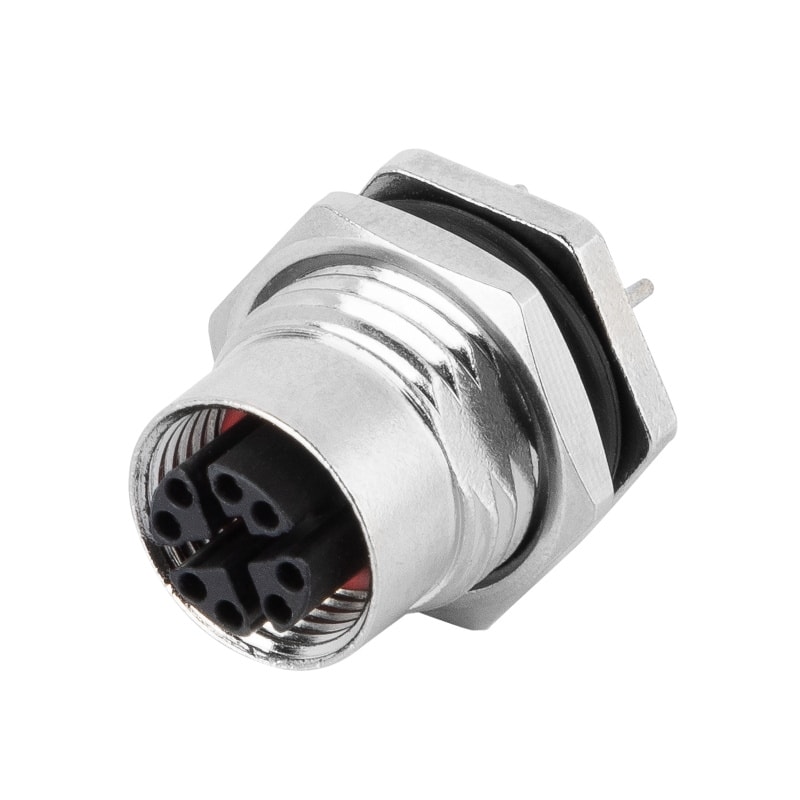

P/N: AM12F0822X001
M12 X Code Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female PCB DIP Connection PG9View All -
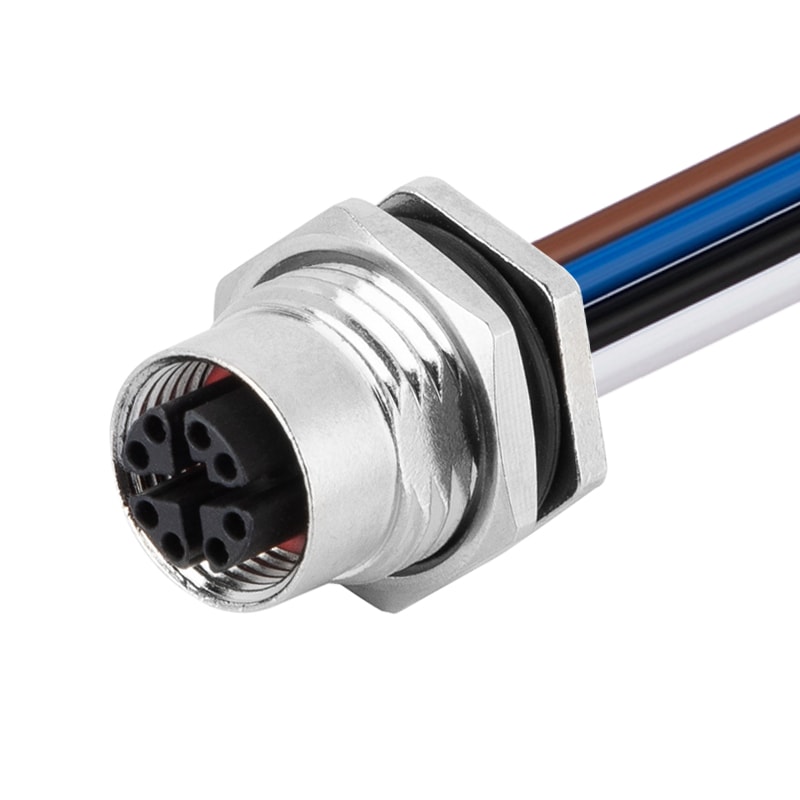

P/N: AM12F0812X001
M12 X Code Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female For Solder Wires ConnectionView All
-
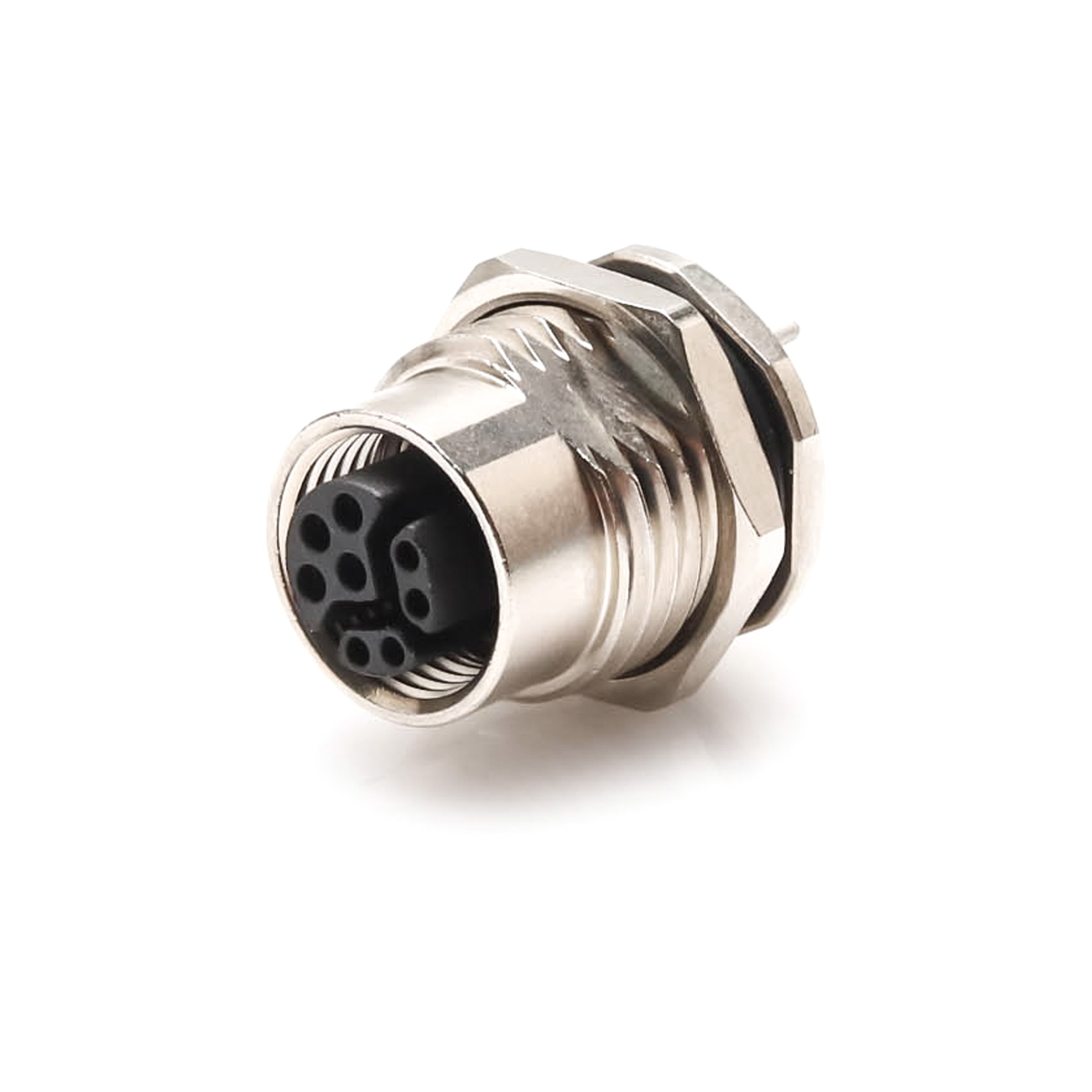

P/N: AM12F0822Y002
M12 Hybrid Connector,Y Code,Female,Panel Mount Receptacle,M12 Device ConnectorView All -
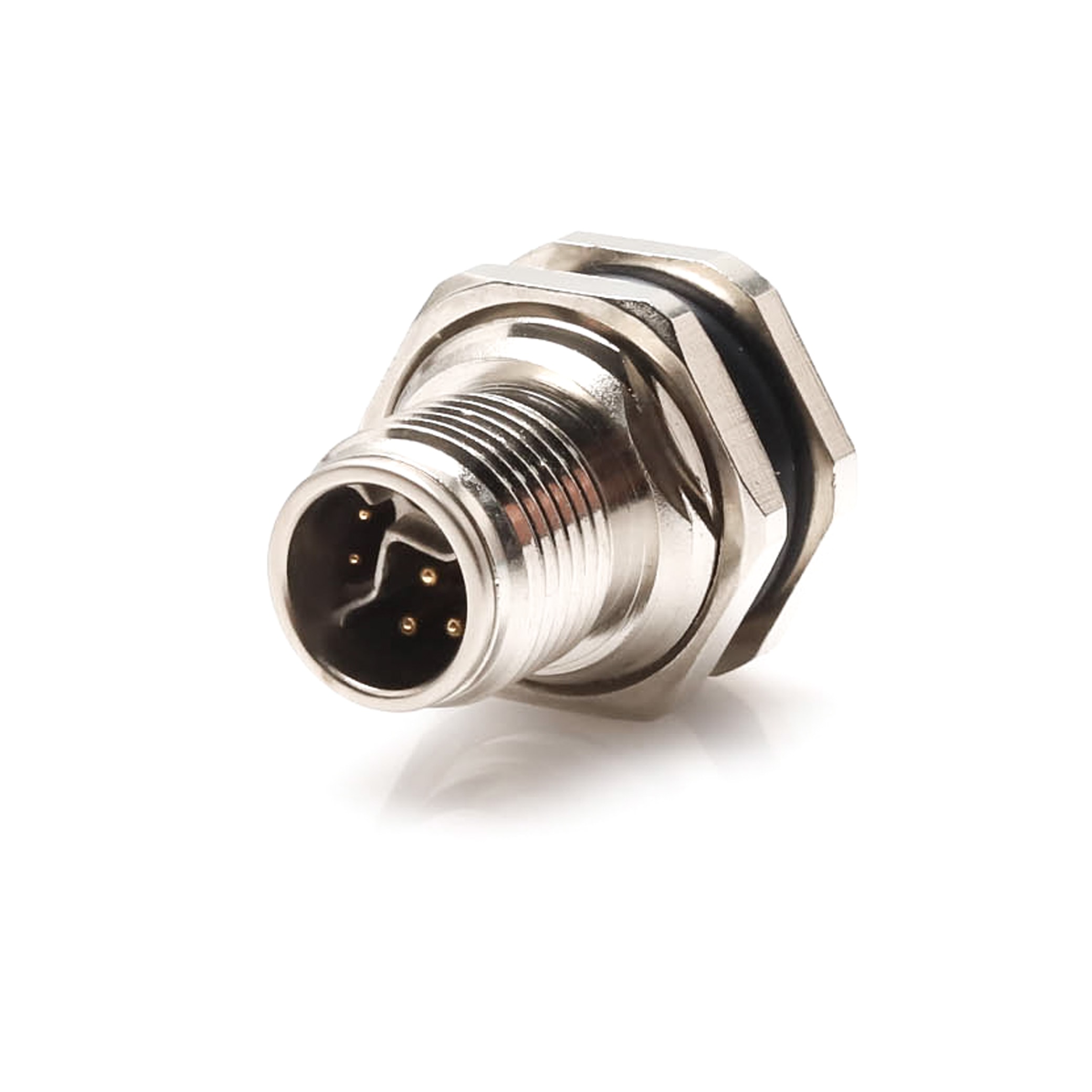

P/N: AM12M0822Y002
M12 Hybrid Connector,Y Code,Male,Panel Mount Receptacle,M12 Device ConnectorView All -
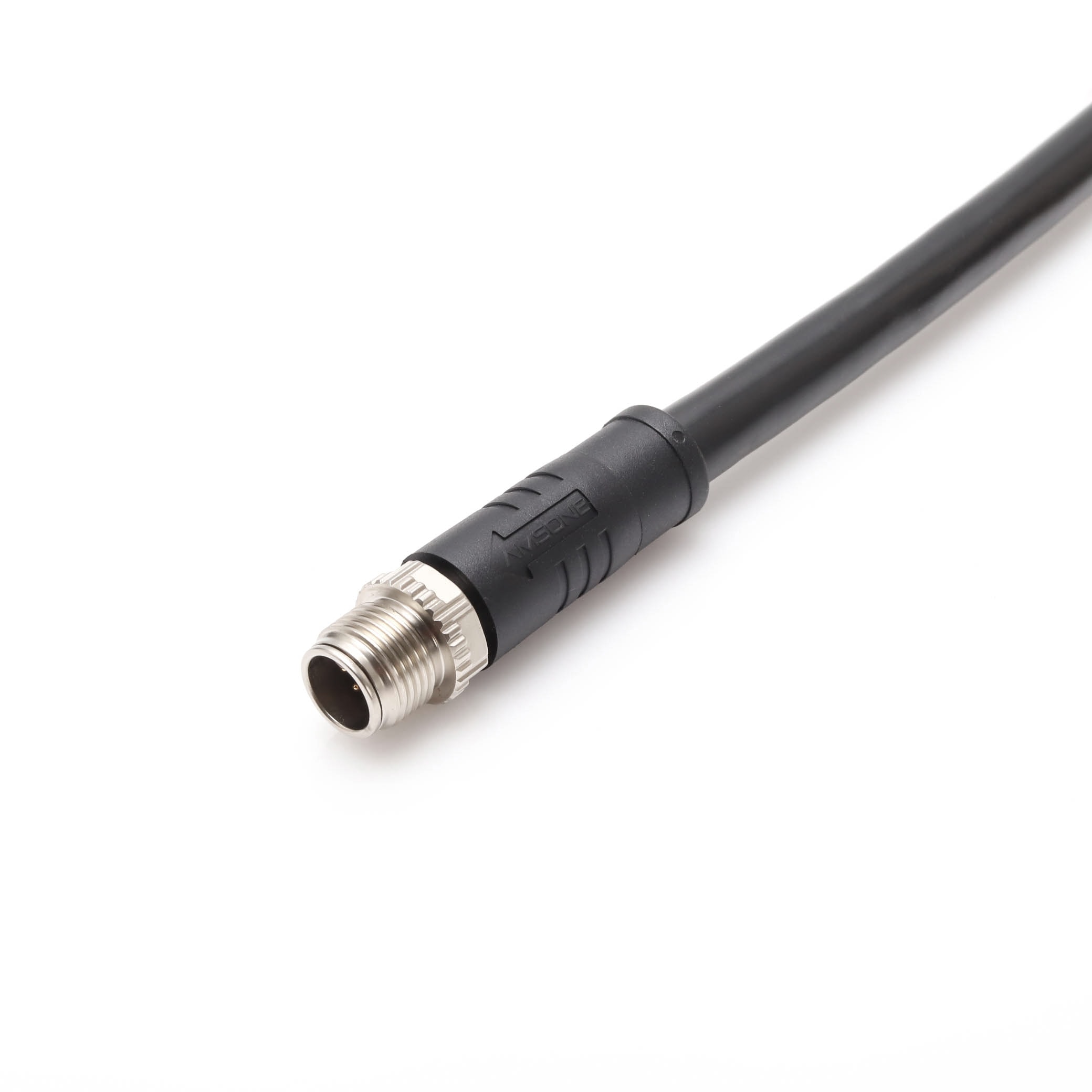

P/N: AM12M0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Male,M12 Y-Coded Power Signal Ethernet CableView All -
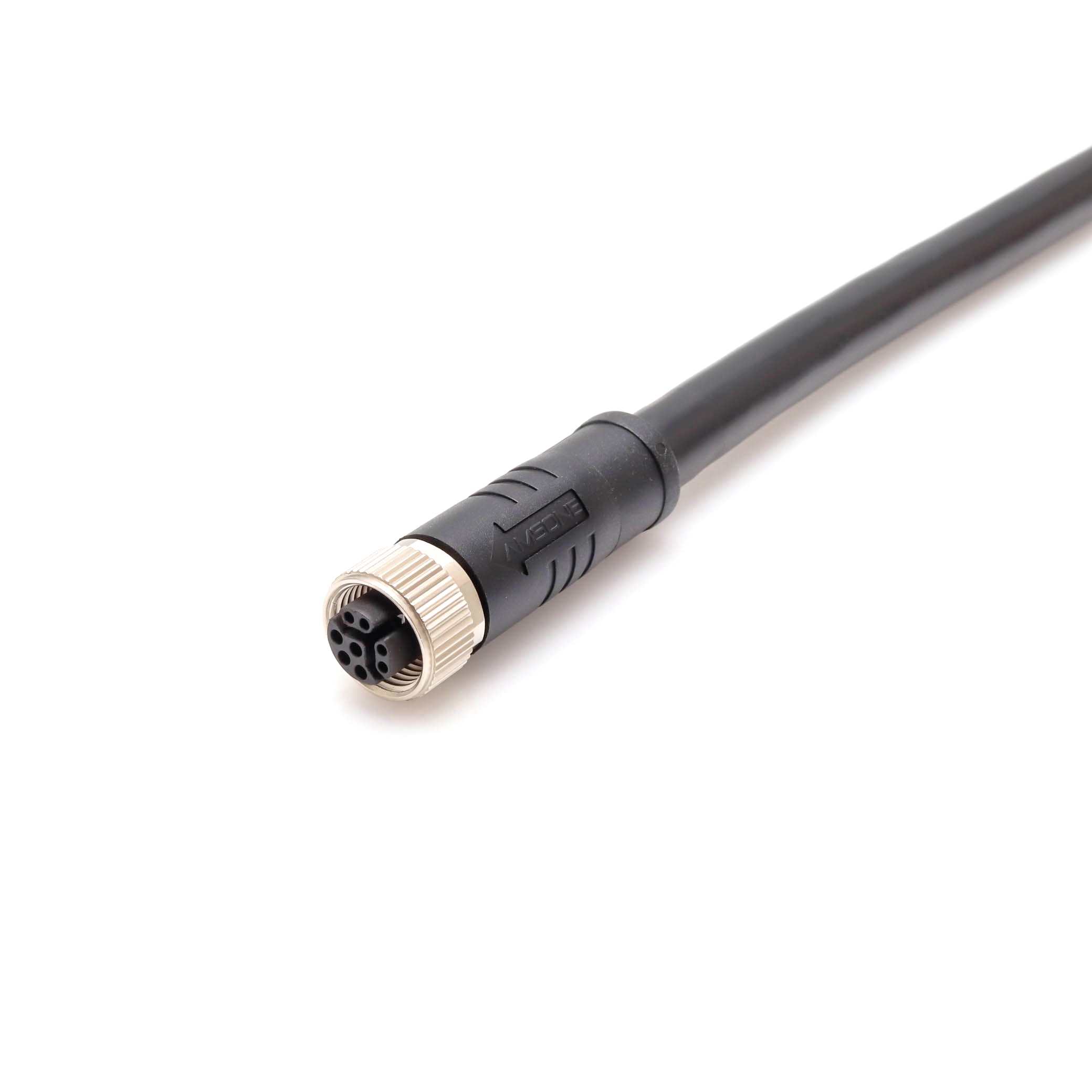

P/N: AM12F0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Power Signal,M12 Y-Coded CablesView All -
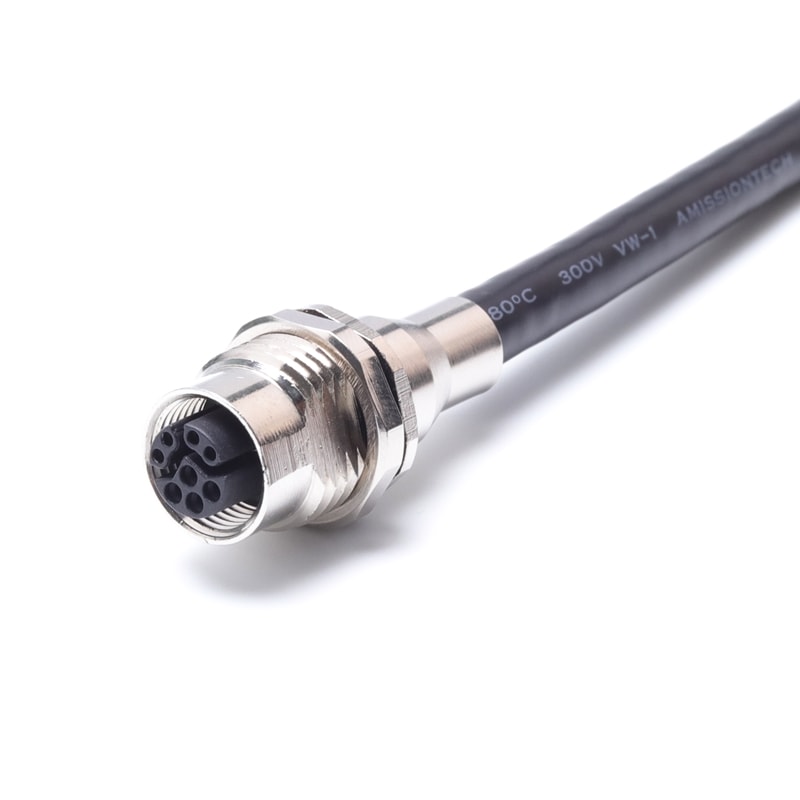

P/N: AM12F0812Y003
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Panel Mount Shielded,M12 Y-CodedView All
-
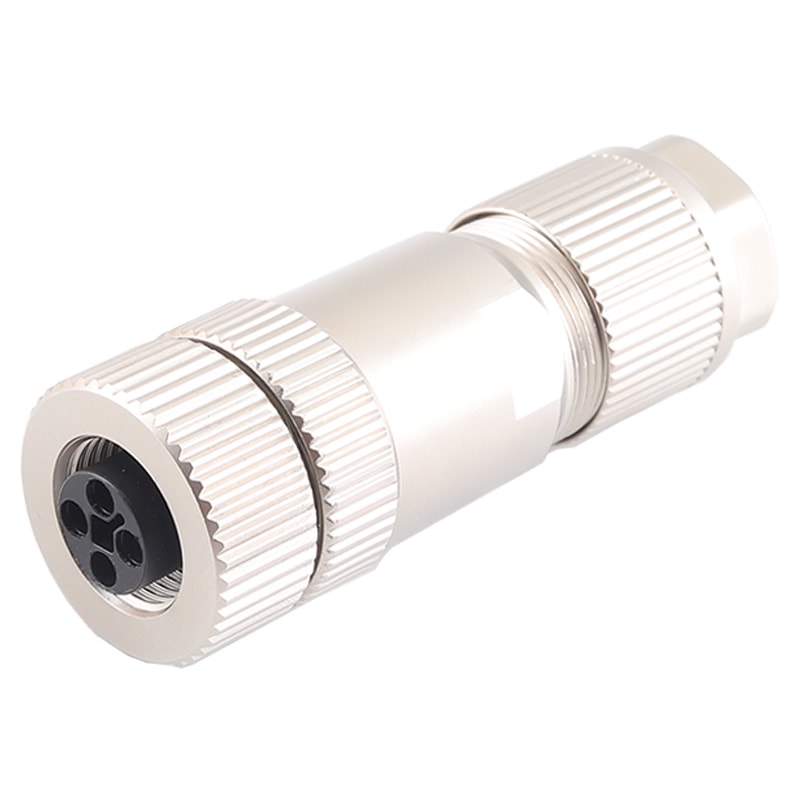

P/N: AM12F0434T001
M12 cable connector, female, contacts: 4, field assembly type, screw connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -
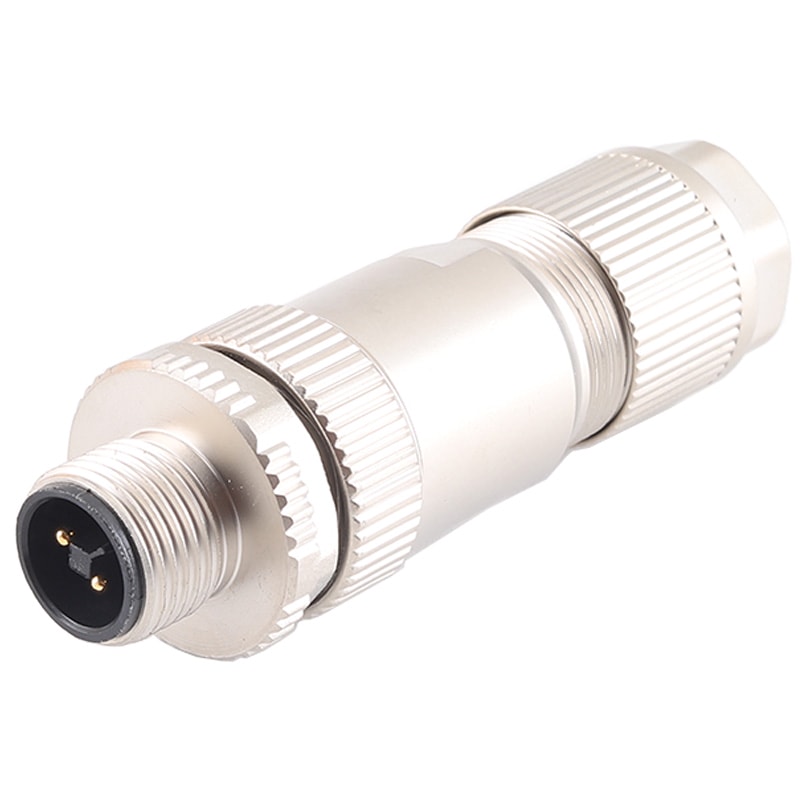

P/N: AM12M0434T001
M12 cable connector, male, contacts: ,4, field assembly type, screw connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -
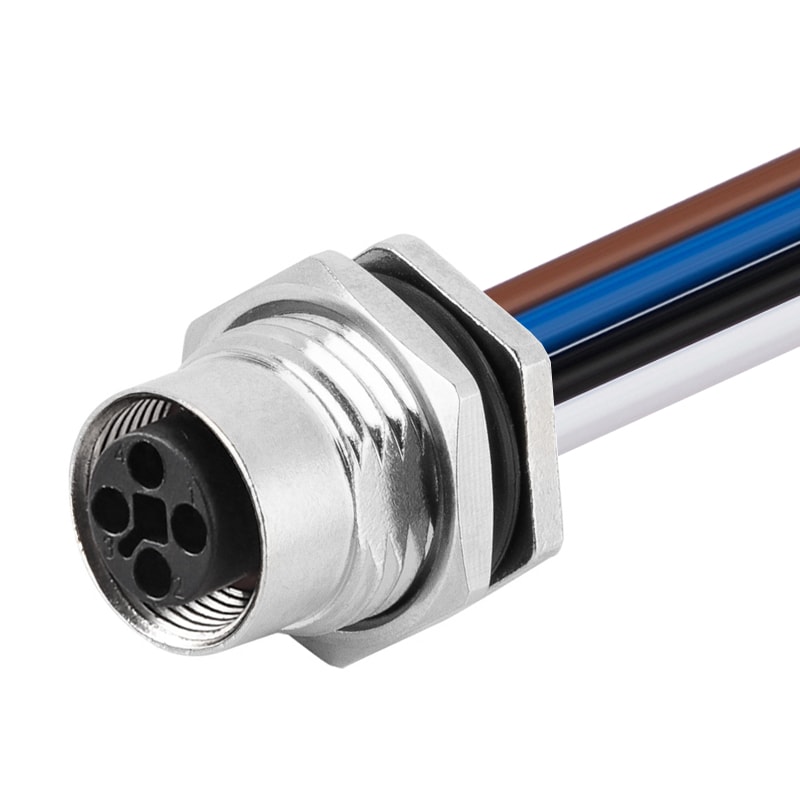

P/N: AM12F0412T171 -XXX
M12 panel receptacle, female, contacts: 4, solder connection for wires, T code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0412T171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, male, contacts: 4, solder connection for wires, T code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0322T001
M12 panel receptacle, female, contacts: 3,PCB dip-solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0322T001
M12 panel receptacle, male, contacts: 3,PCB dip-solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0311TXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts: 3,solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All -
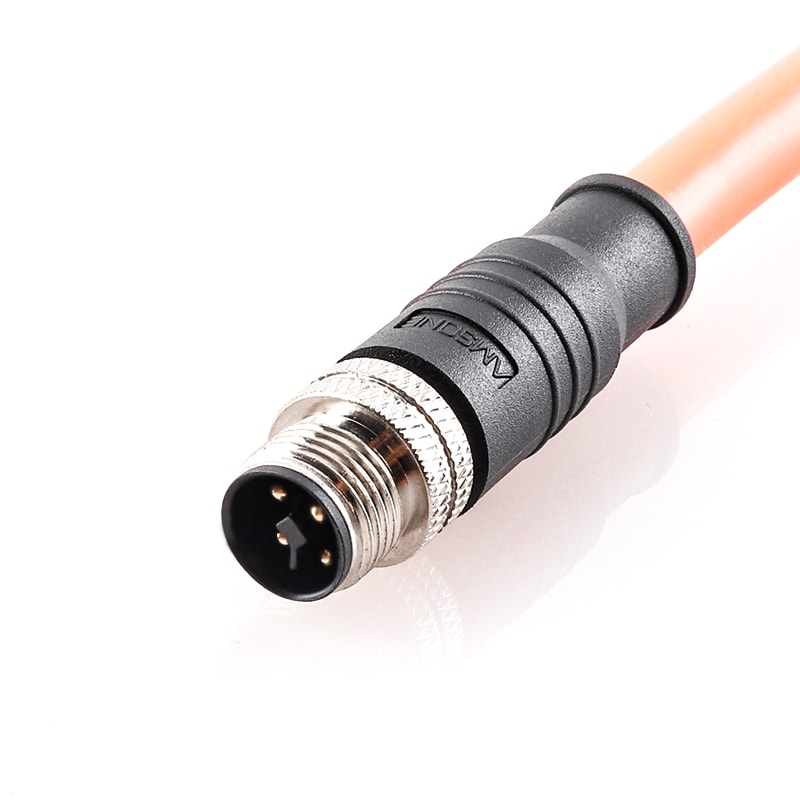

P/N: AM12M0311TXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:3, solder connection, T code, straight, IP67View All
-
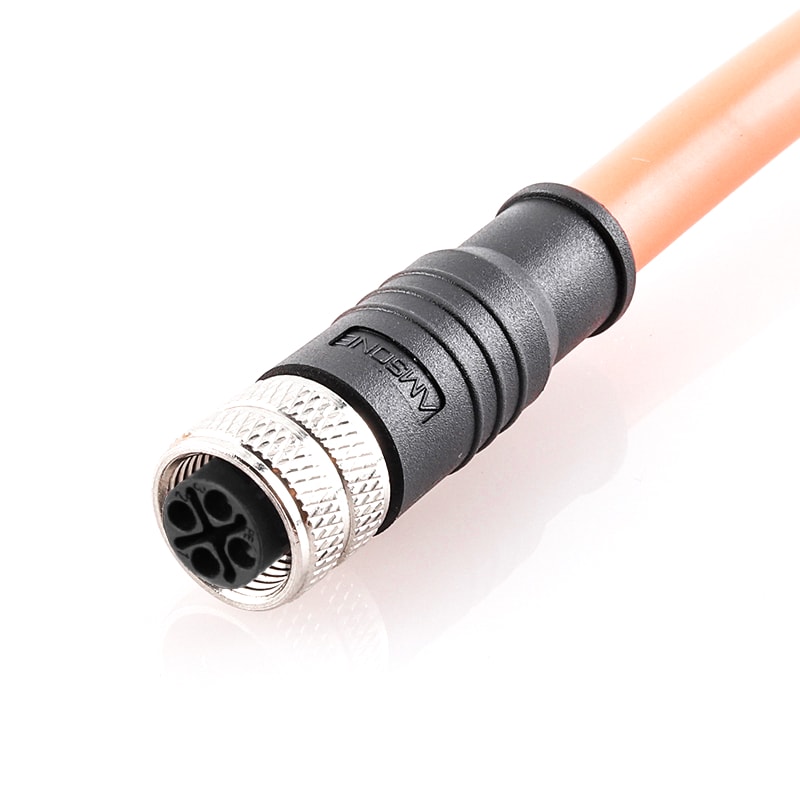

P/N: AM12F0411SXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4(3+PE), solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -
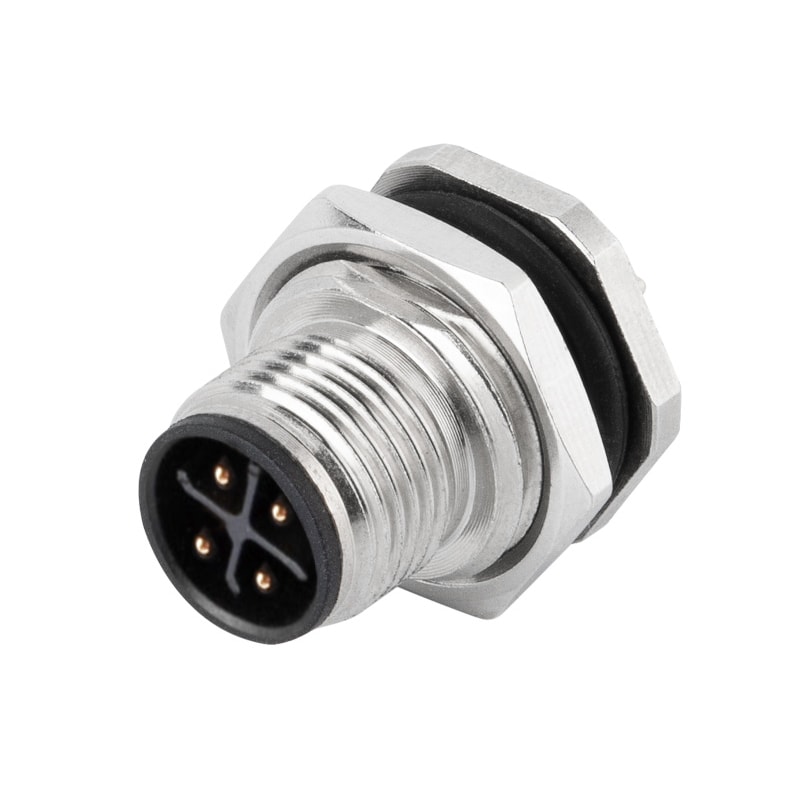

P/N: AM12M0322S001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:3(2+PE),PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0412S171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, S code, straight, IP67View All -
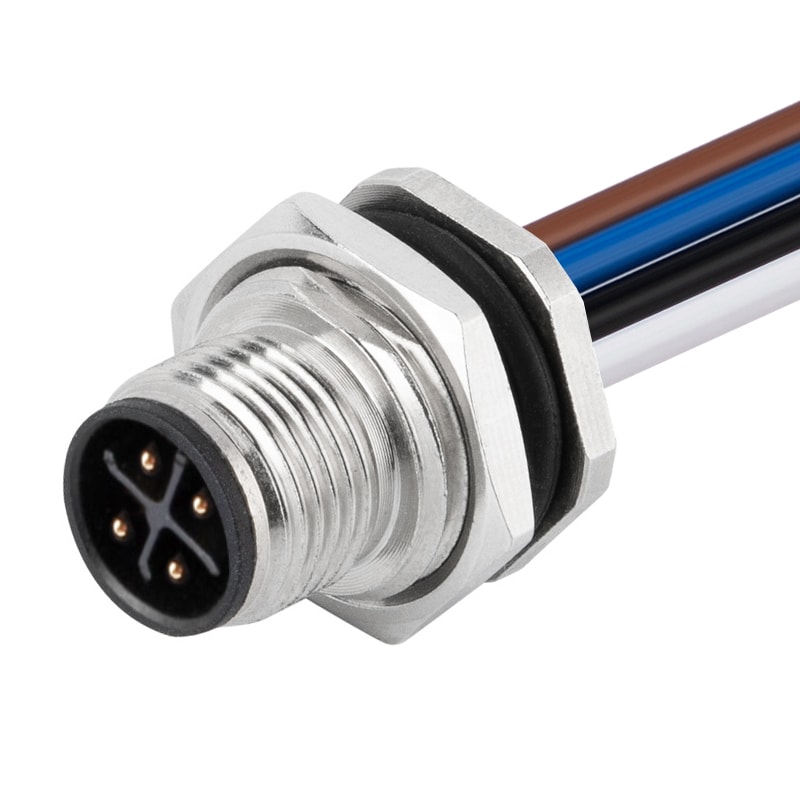

P/N: AM12M0412S171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, S code, straight, IP67View All -
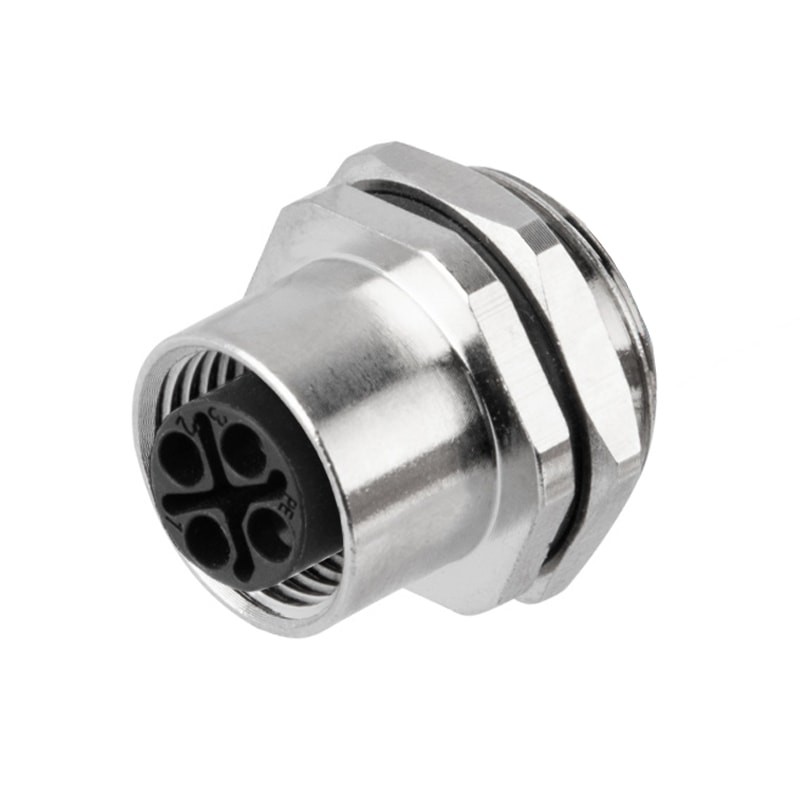

P/N: AM12F0322S001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:3(2+PE),PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -
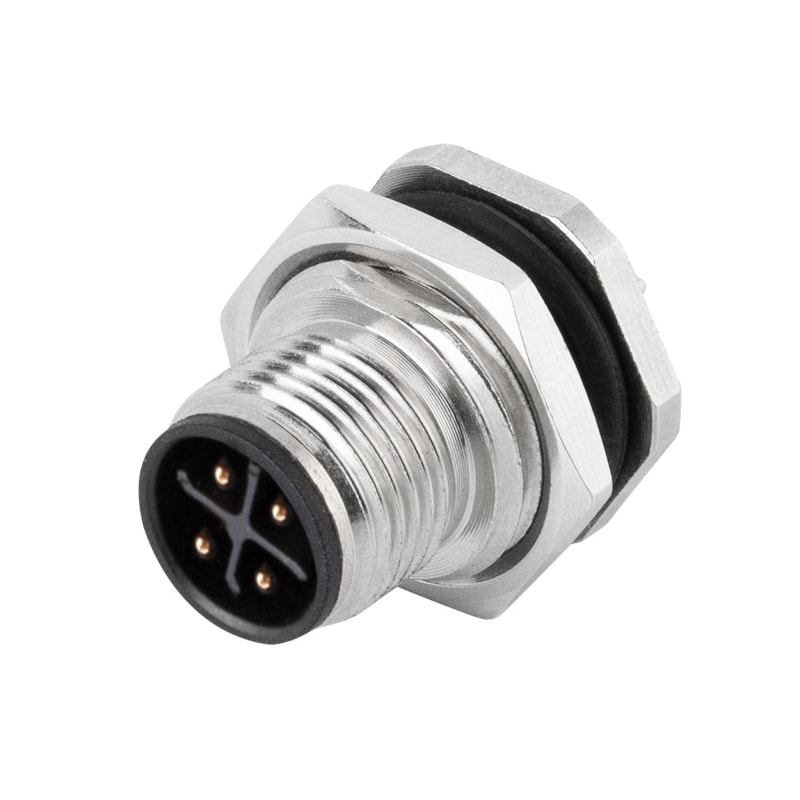

P/N: AM12M0422S001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:,4(3+PE), PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -
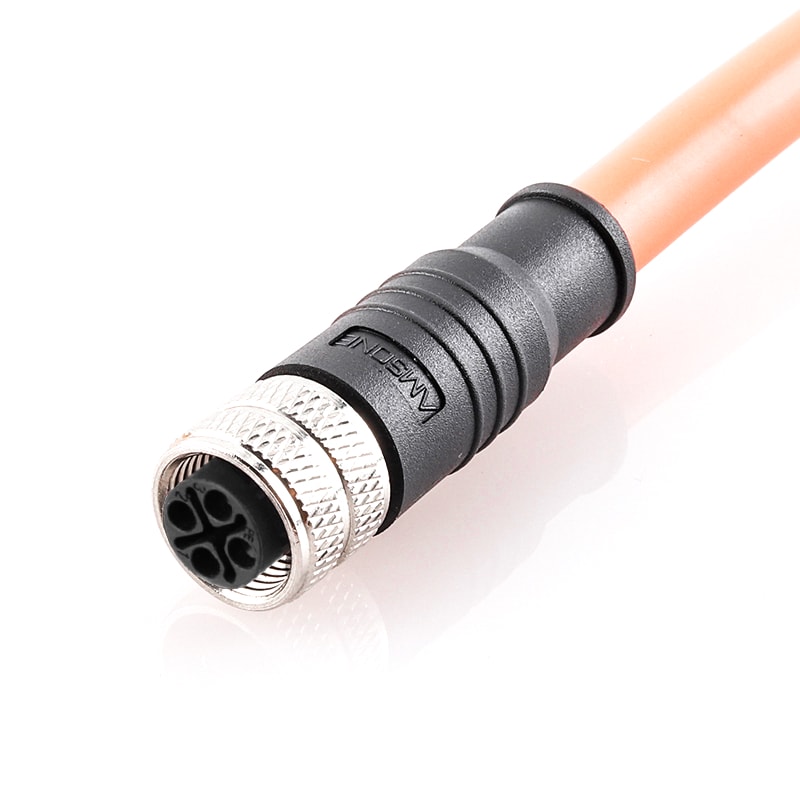

P/N: AM12F0311SXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:3(2+PE), solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All -
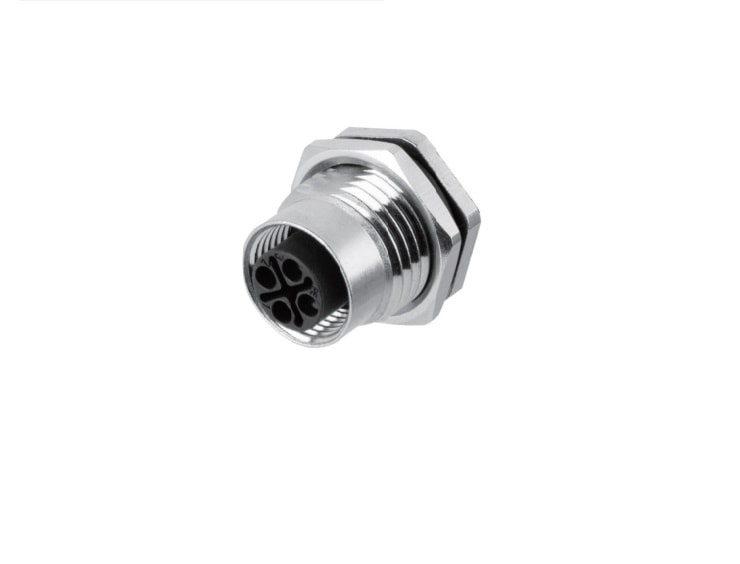

P/N: AM12F0322S002
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:3(2+PE), PCB dip-solder connection, S code, straight, IP67View All
-

P/N: AM12M0511Lxx1-xxx
M12 L Coded Power 5P Connector Male Drag Chain Pre-Molded CableView All -

P/N: AM12M0412L171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4, solder connection for wires, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0522L001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:5, PCB dip-solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0411LXX2-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0411LXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:4, solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0322L001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:3, PCB dip-solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0422L001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:4,PCB dip-solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0311LXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:3, solder connection, L code, straight, IP67View All
-

P/N: AM12M0312K171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:3,solder connection for wires, K code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0522K001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:5, PCB dip-solder connection, K code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0522K001
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:5,PCB dip-solderconnection, K code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0311KXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:3, solder connection, K code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0311KXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:3, solder connection, K code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0513K371-005
M12 K Code 5P(4+PE) Female Panel Front Mount Receptacle ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM12F0312K171-XXX
M12 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:3, solder connection for wires, K code, straight, IP67View All
-

P/N: AM12M0512M371-XXX
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Male 5Pin Connector For WiresView All -

P/N: AM12F0322M001
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Female 3Pin PCB ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM12F0612M171-XXX
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Female 6Pin Connector For WiresView All -

P/N: AM12M0612M371-XXX
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Male 6Pin Connector For WiresView All -

P/N: AM12M0522M001
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Male 5Pin PCB ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM12F0611MXX1-XXX
M12 M Code 5+PE Pre-molded Cable 6Pin Female Straight ConnectorView All -

P/N: AM12M0611MXX1-XXX
M12 M Code 5+PE Pre-molded Cable 6Pin Male Straight ConnectorView All -
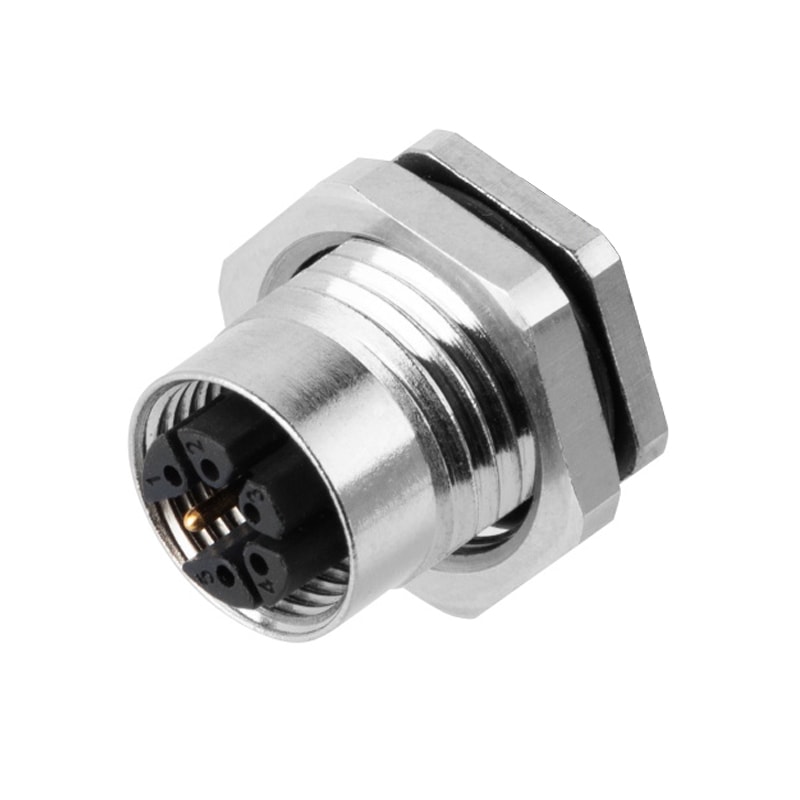

P/N: AM12F0522M001
M12 Device Receptacle M Code Panel Rear Mount Female 5Pin PCB ConnectorView All
-
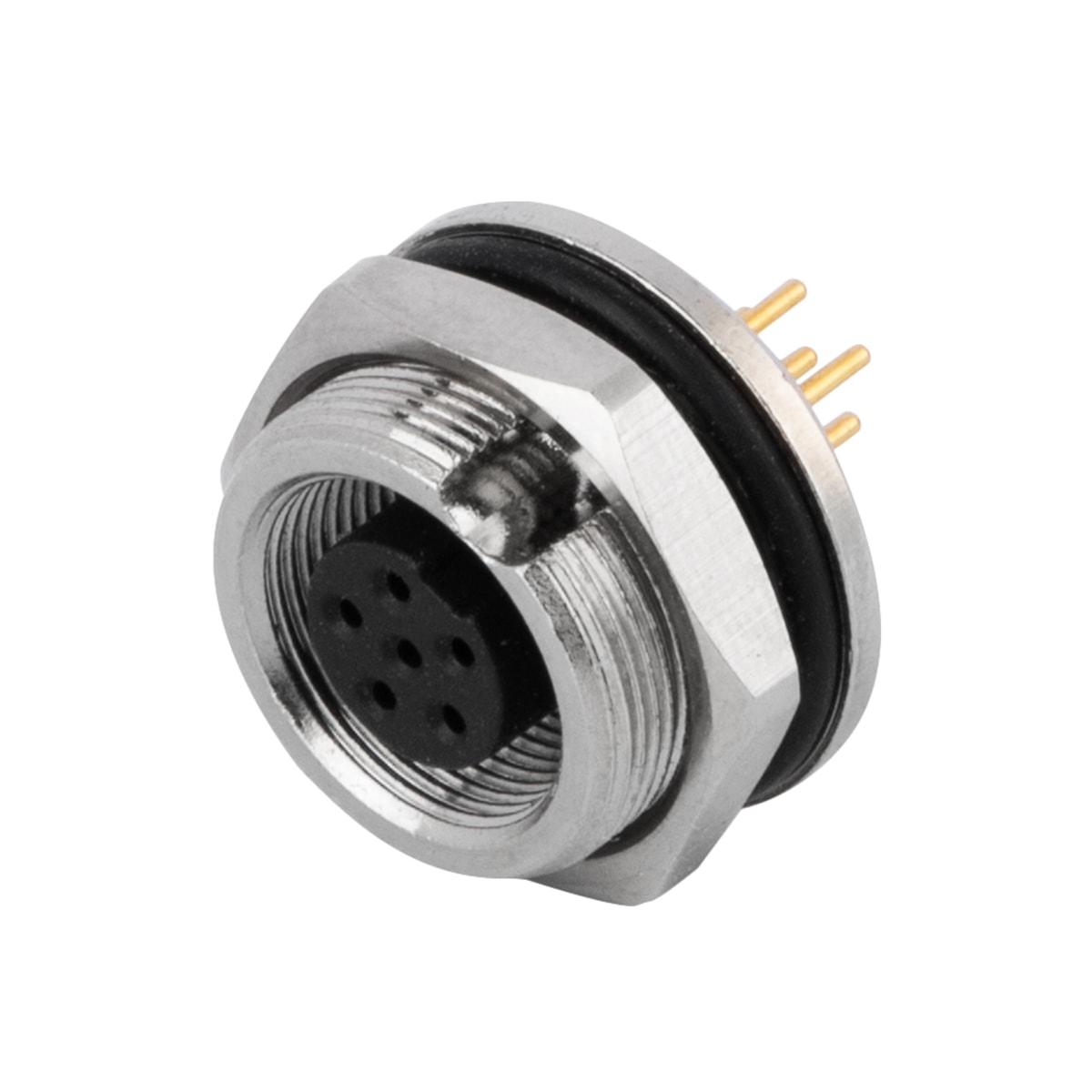

P/N: AM09F0522A001
M9 Connector Receptacle Panel Rear Mount Female 5Pole PCB Dip-solderView All -
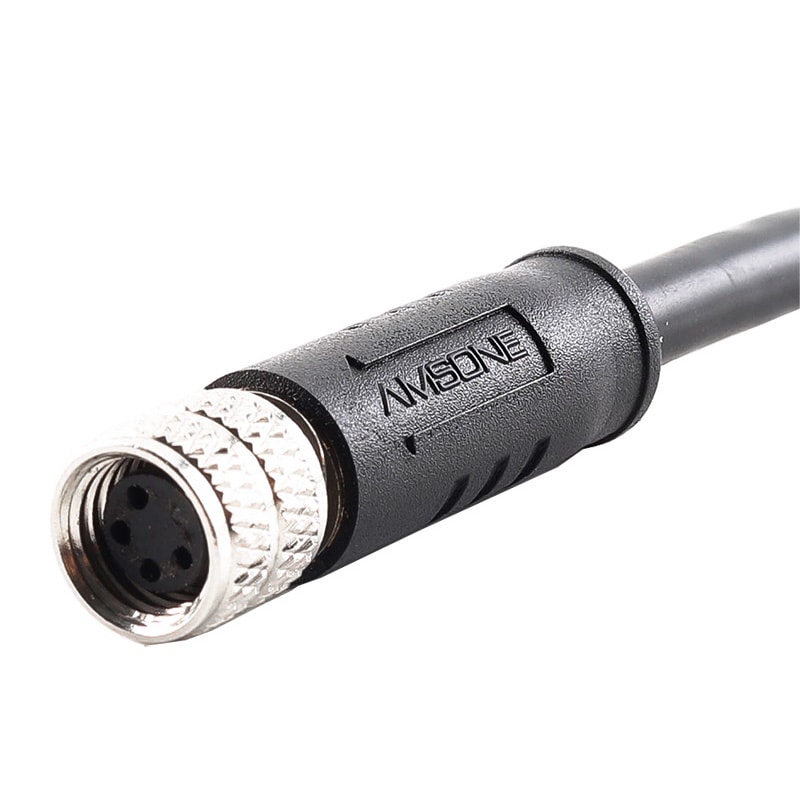

P/N: AM09F0411A001
M9 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM09F0311A001
M9 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts: 3, solder connection, straight, IP67View All -
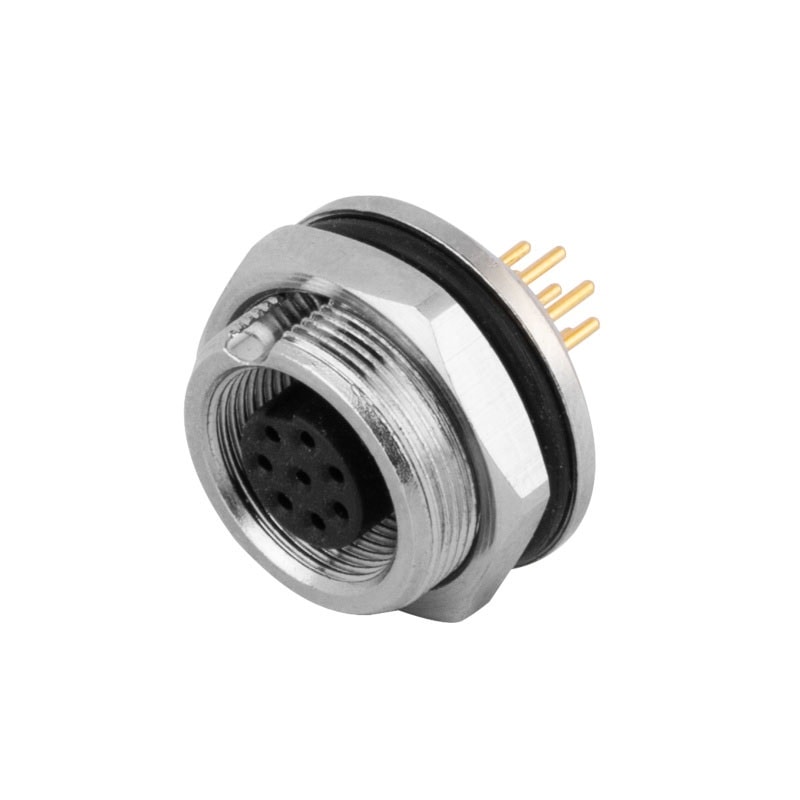

P/N: AM09F0822A001
M9 Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle 8Pin PCB Waterproof ConnectorView All -
P/N: AM09F0422A001
M9 4P Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle PCB Waterproof ConnectorView All -
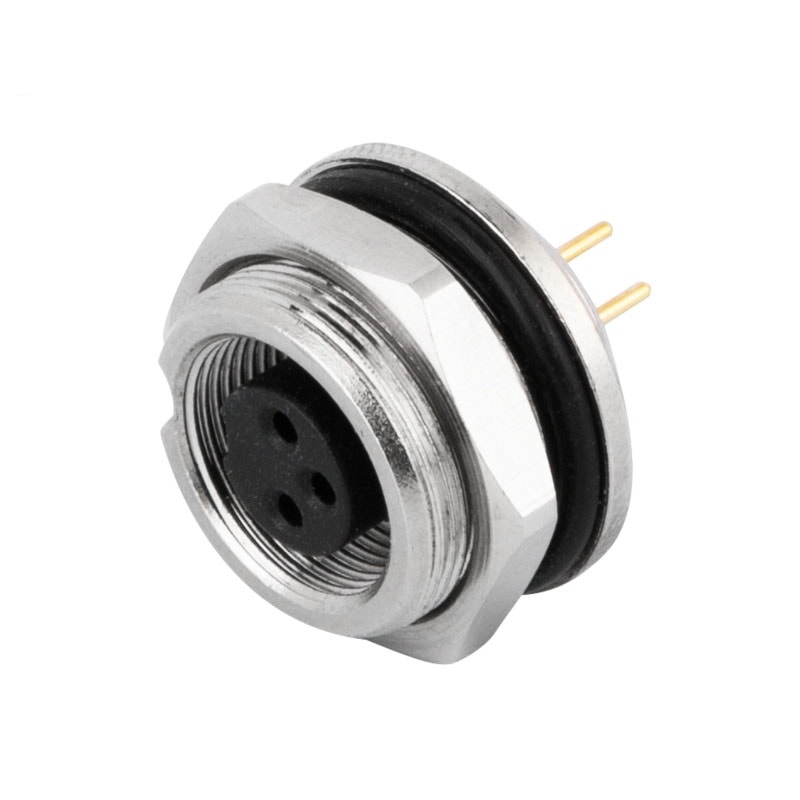

P/N: AM09F0322A001
M9 3Pole Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle PCB Waterproof ConnectorView All -
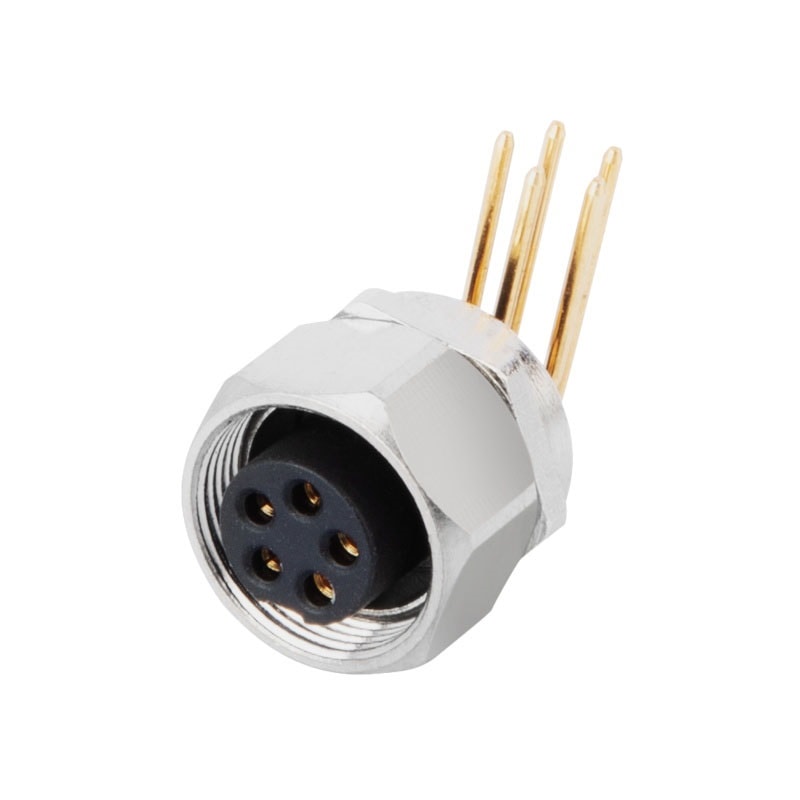

P/N: AM09F0522A201
M9 Female Panel Rear Mount Receptacle 5Pin PCB Connector Right AngledView All
-
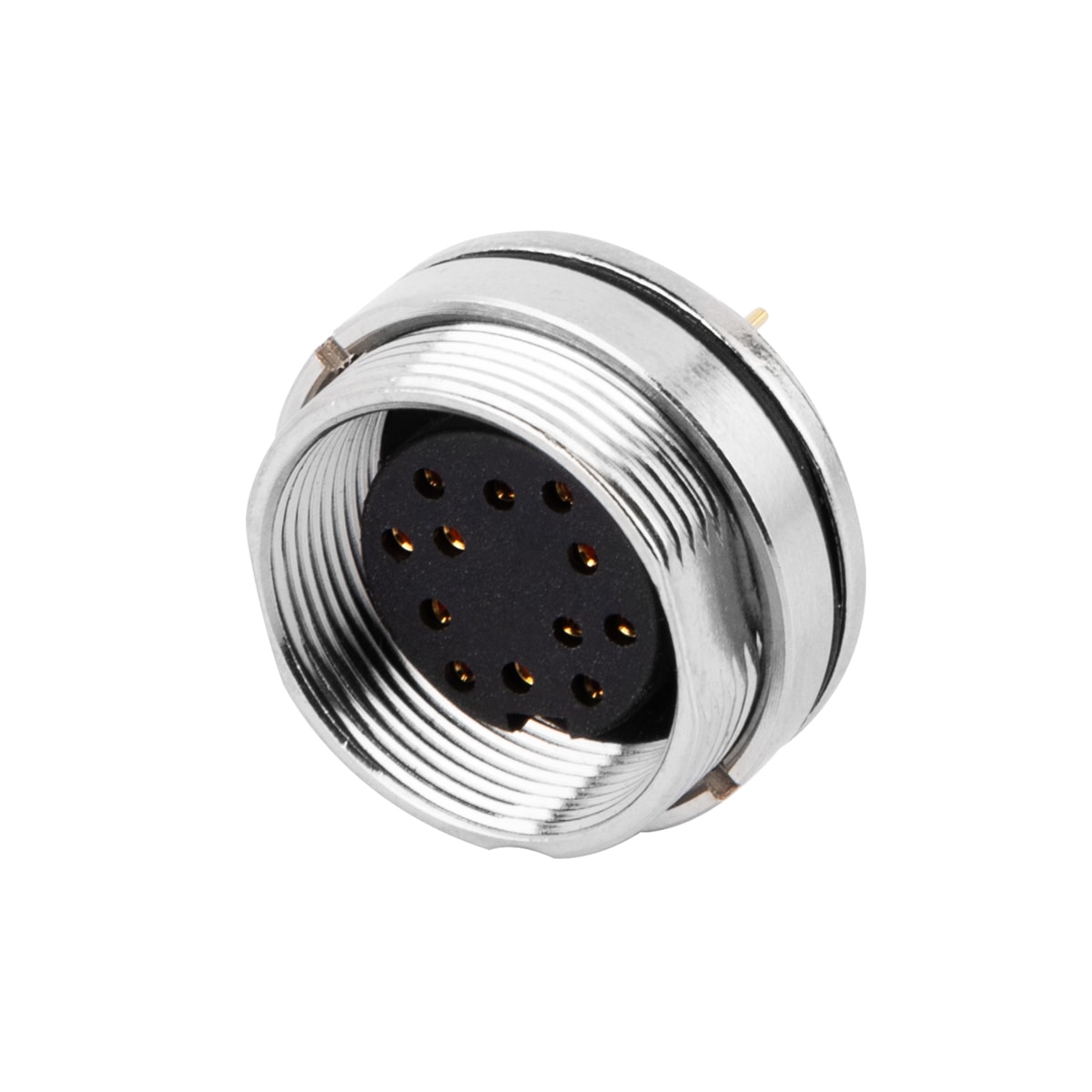

P/N: AM16F2422A001
M16 panel receptacle,rear mount,Female, contacts:24, PCB dip- solder connection,straight,IP67,UL certifiedView All -
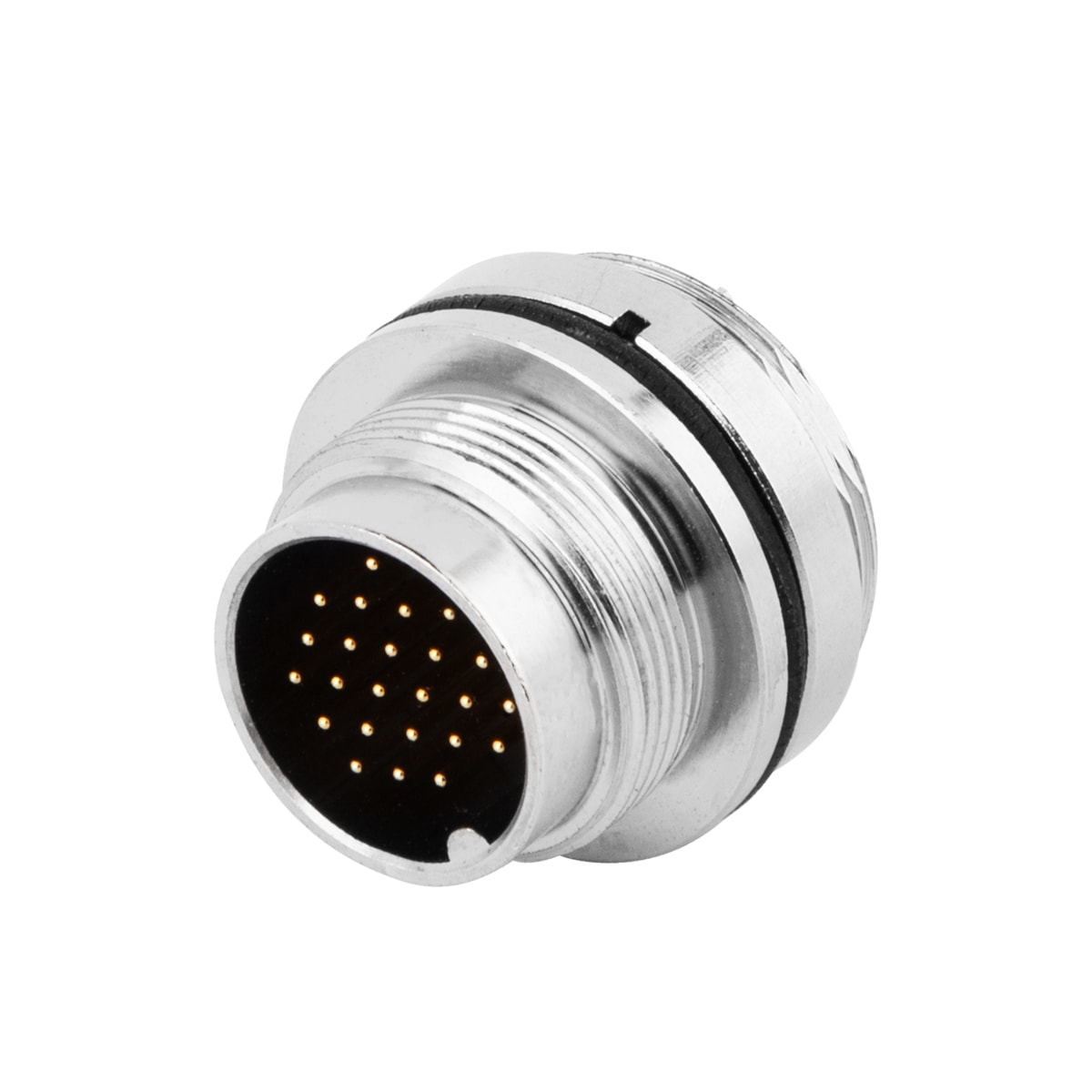

P/N: AM16M2422A001
M16 panel receptacle,rear mount,male, contacts:24, PCB dip- solder connection,straight,IP67,UL certifiedView All -
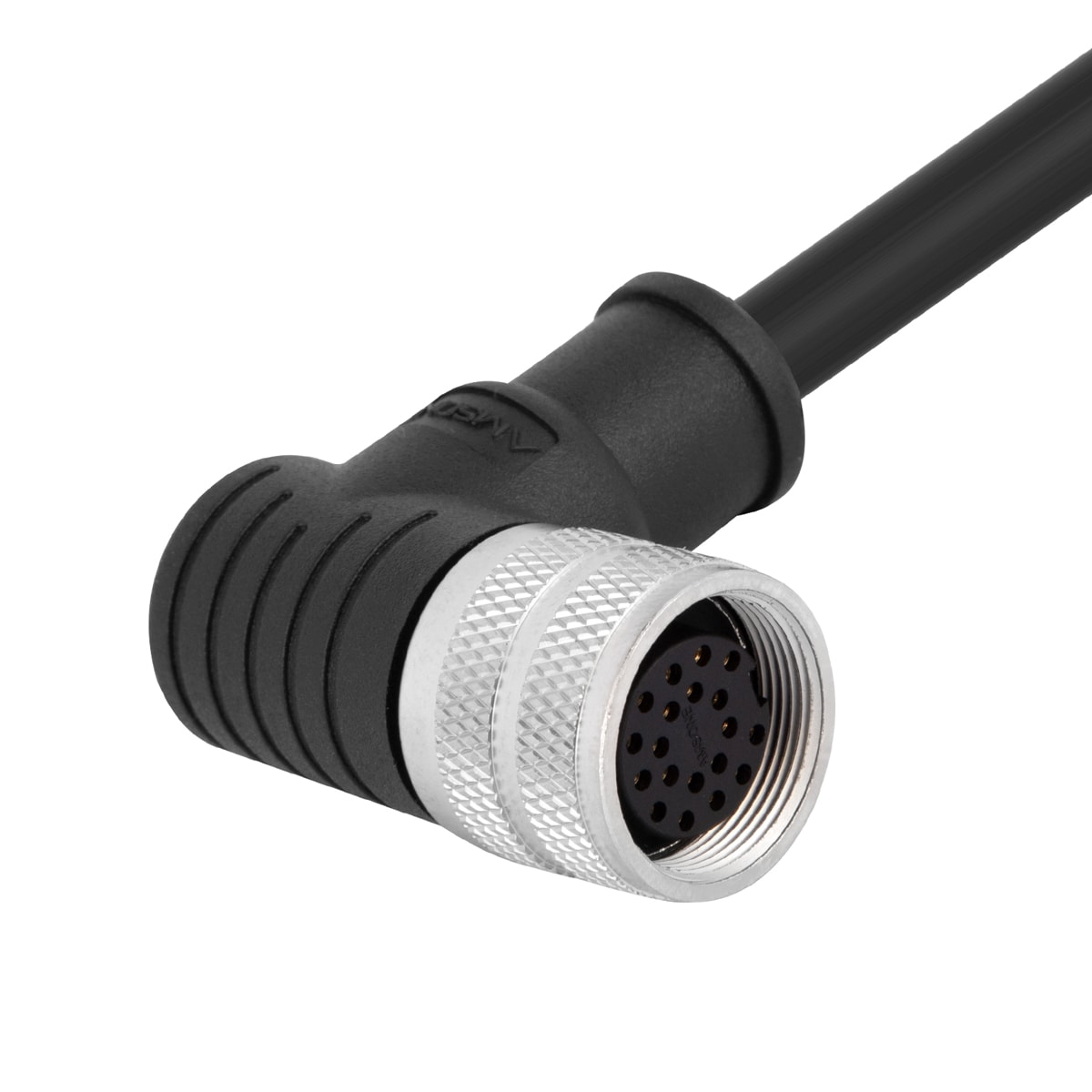

P/N: AM16F2411AXX2-XXX
M16 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:24, solder connection, right angled, IP67, shieldable, UL certifiedView All -
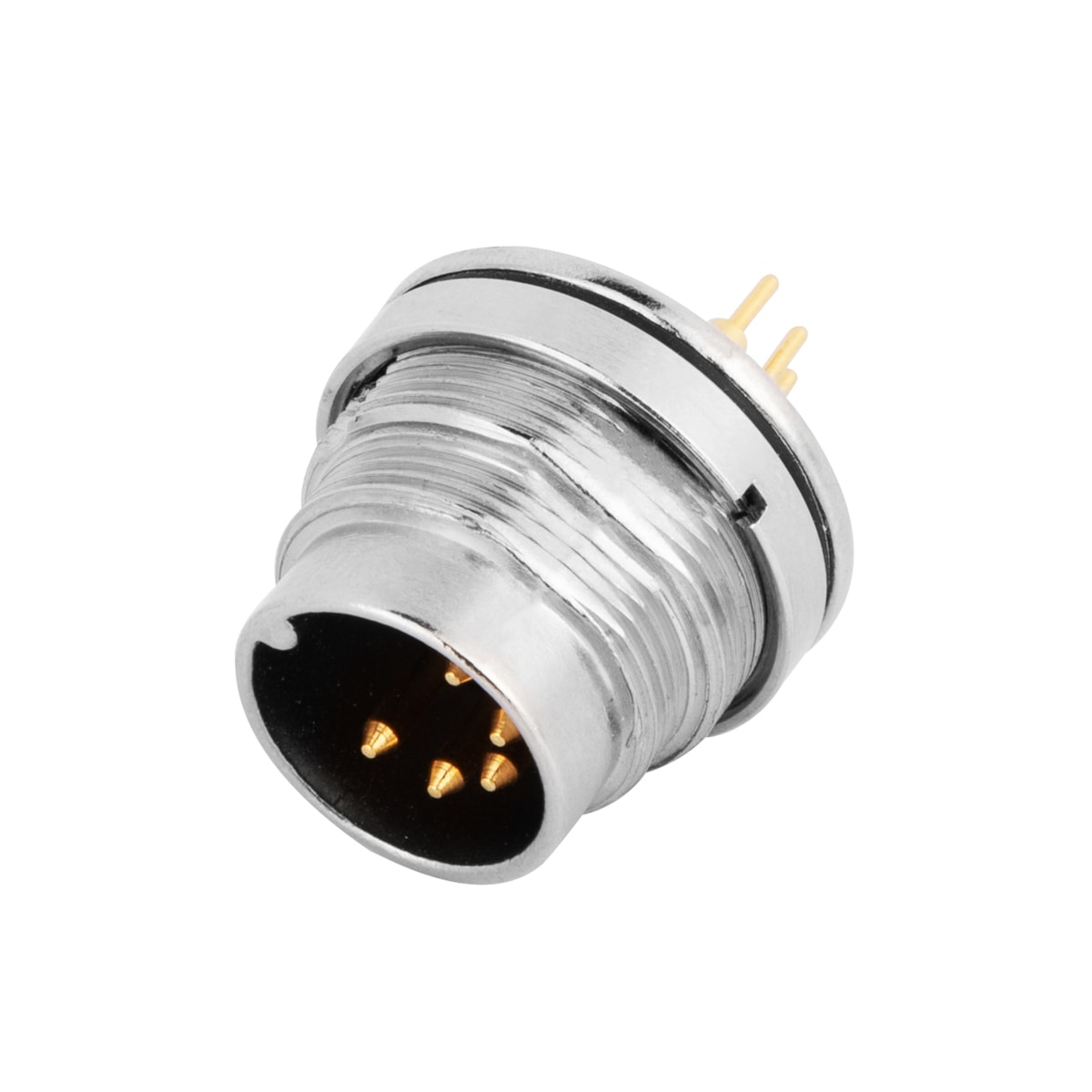

P/N: AM16M0522B001
M1M16 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:5, PCB dip-solderconnection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All -
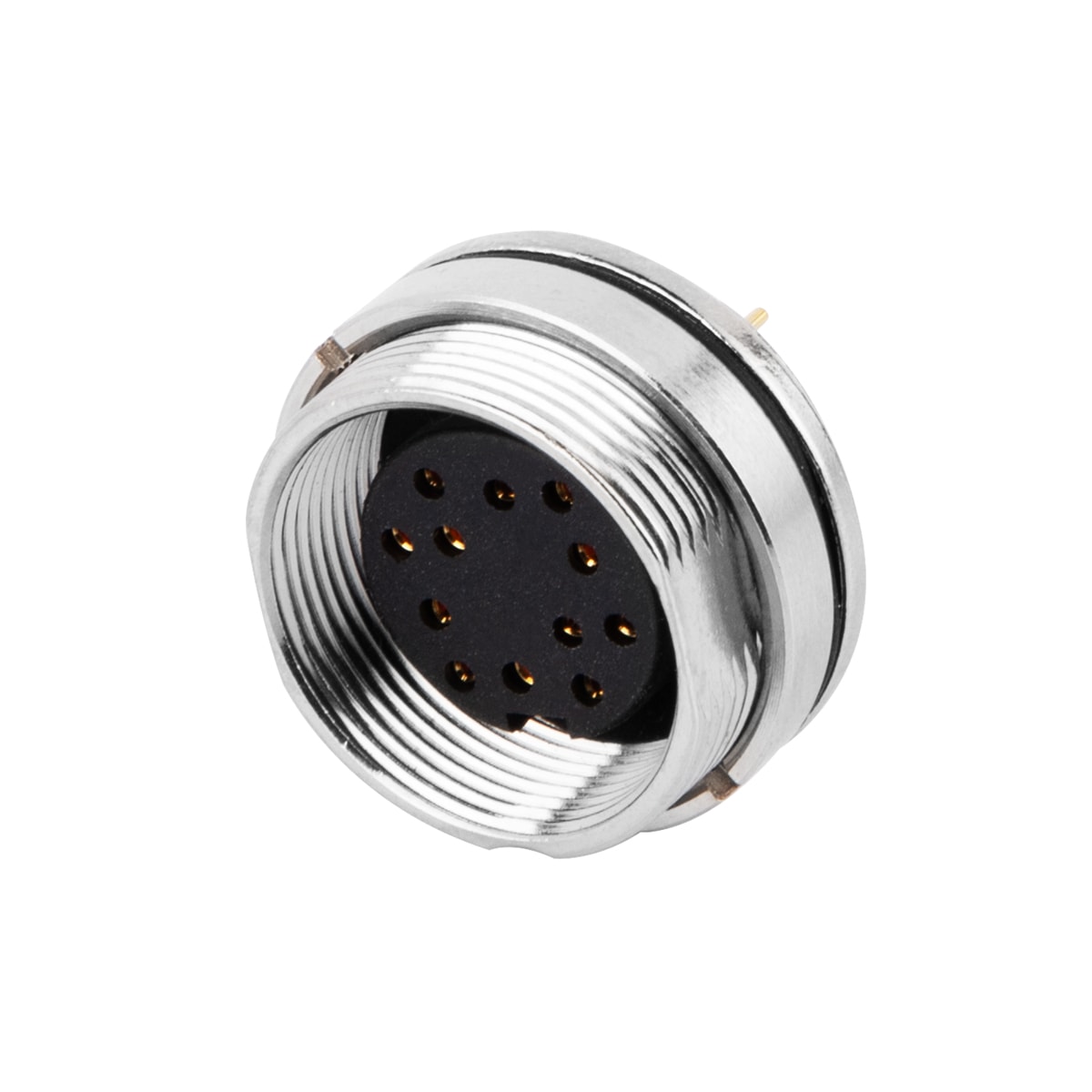

P/N: AM16F1222A001
M16 panel receptacle, rear mount, female, contacts:12,PCB connection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All -
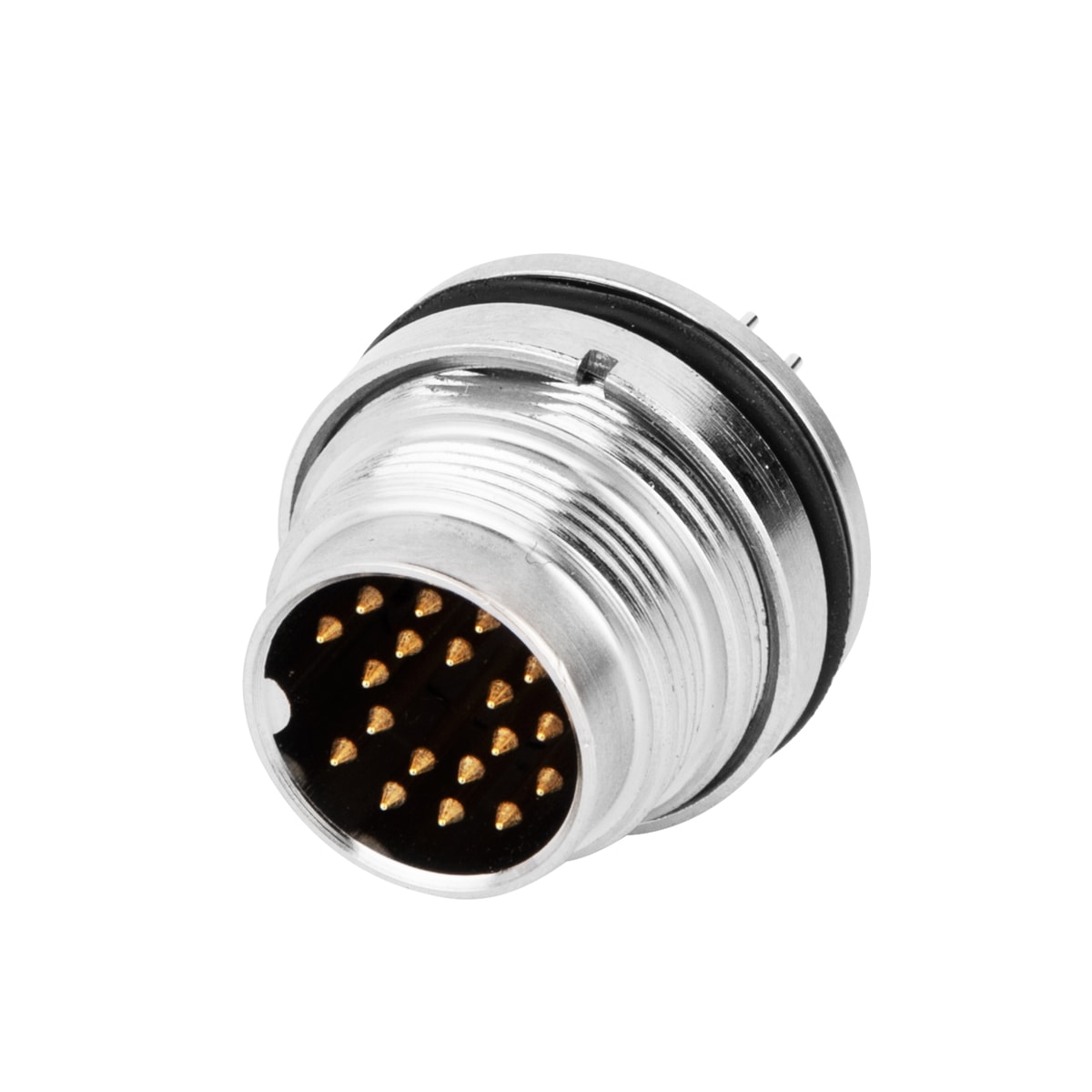

P/N: AM16M1222A001
M16 panel receptacle, rear mount, male, contacts:12,PCB dip-solder connection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All -

P/N: AM16M2411AXX1-XXX
M16 pre-molded cable connector, male, contacts:24, solder connection, straight, IP67, shieldableView All -
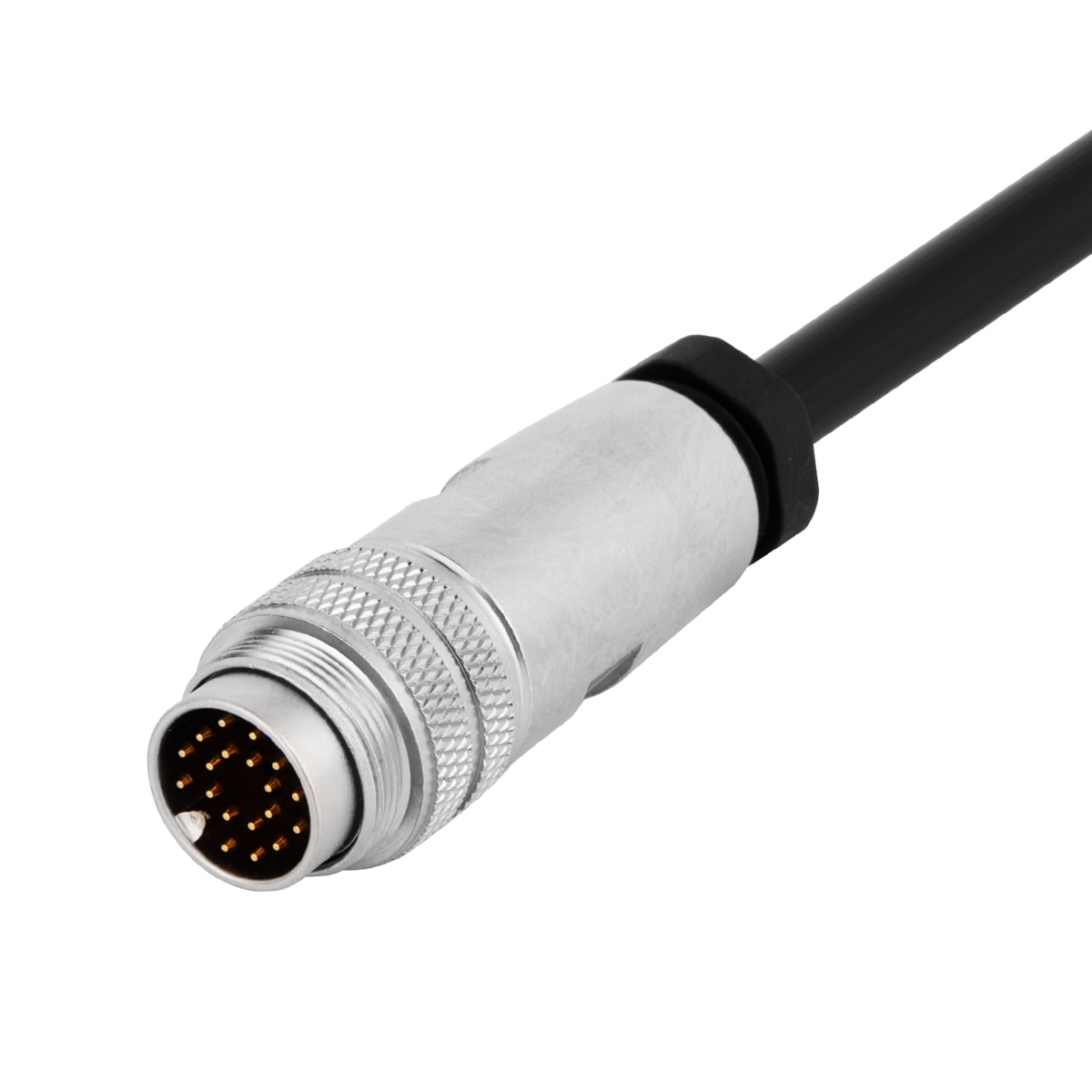

P/N: AM16M1214A001
M16 cable connector, male, contacts:12,field assembly type, solder connection, straight, IP67, UL certifiedView All
-
P/N: AM78F0511A162-010
MINI-Change 7/8View All -
P/N: AM78M0522A001
MINI-Change 7/8-16UNF Panel Rear Mount Receptacle Male 5Pin PCB ConnectorView All -
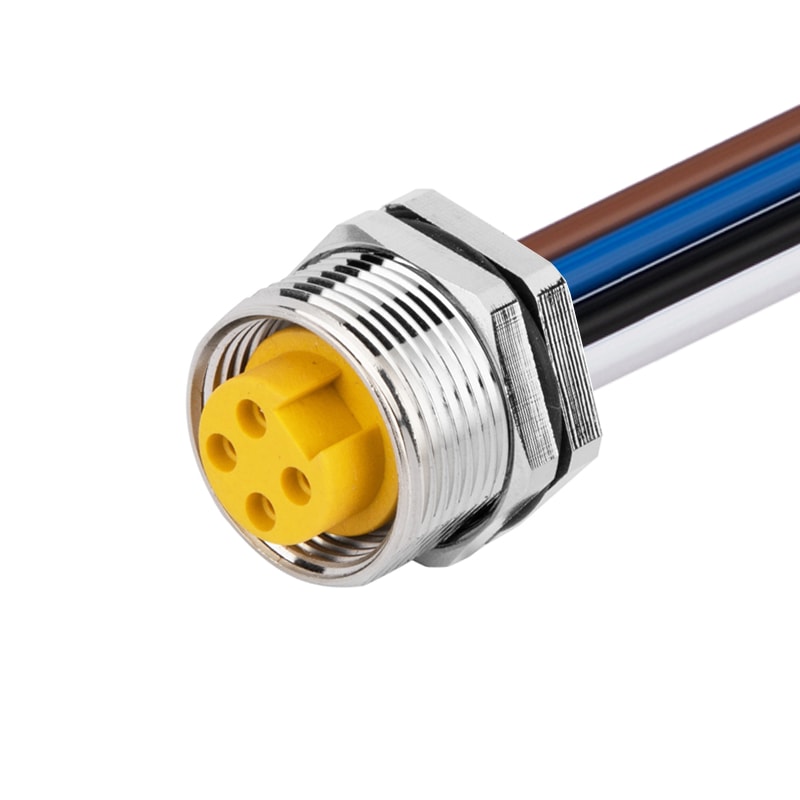

P/N: AM78F0412A371-050
7/8View All -
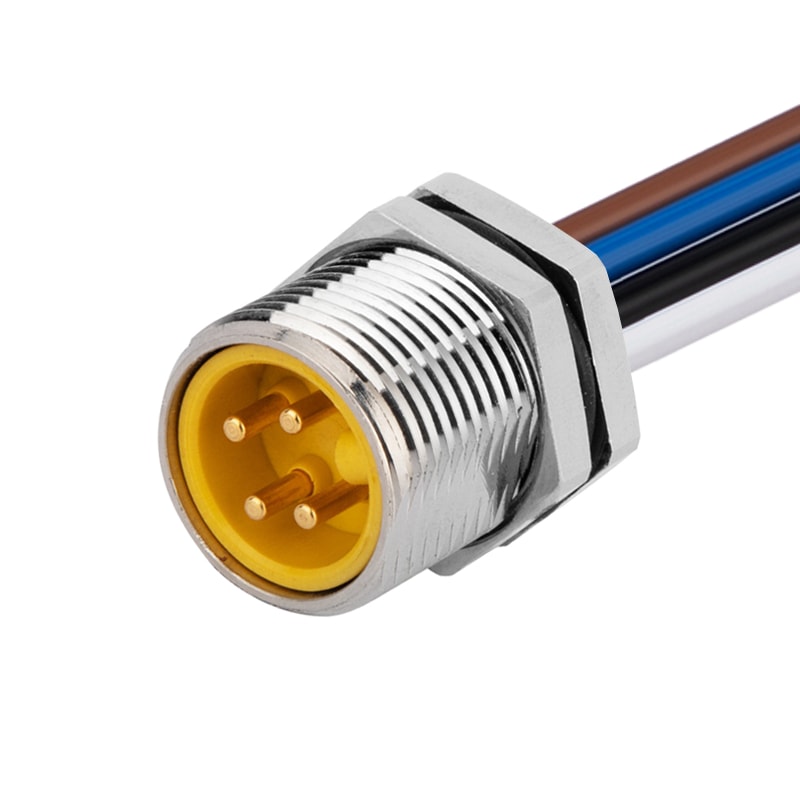

P/N: AM78M0412A371-050
7/8View All -
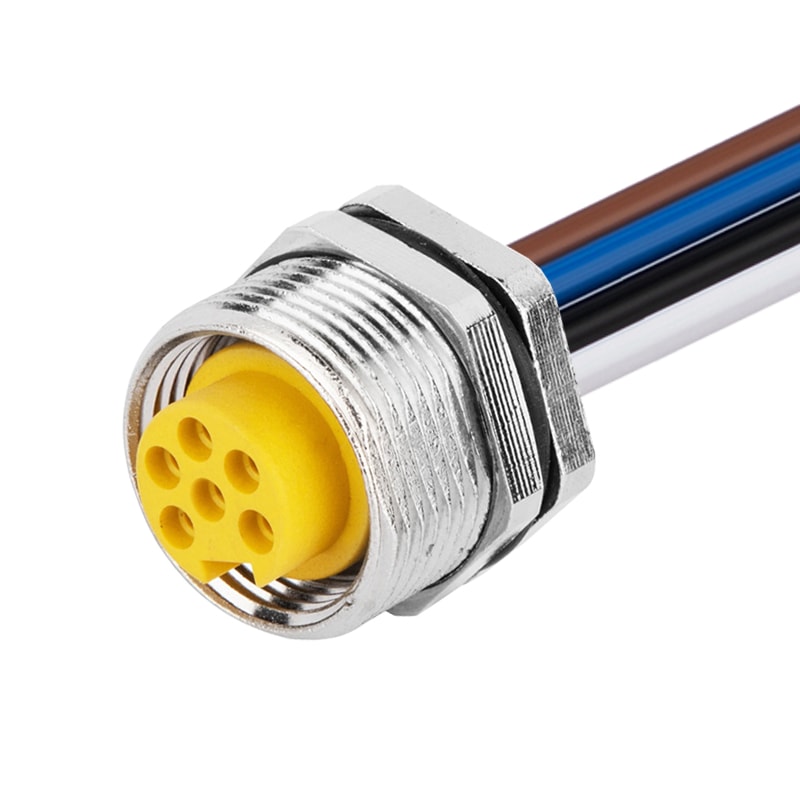

P/N: AM78F0512A371-050
7/8View All -
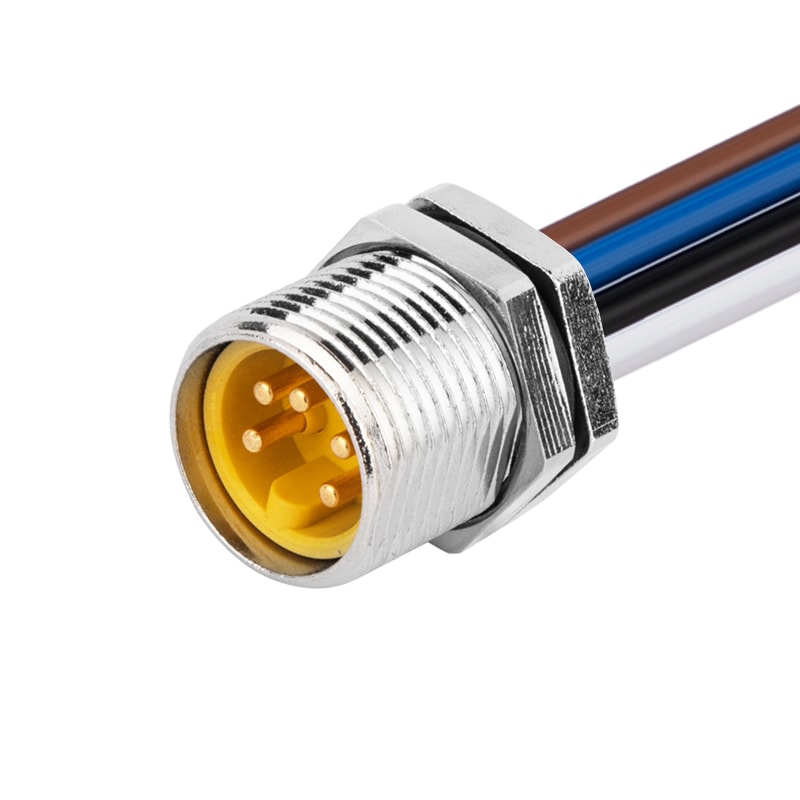

P/N: AM78M0512A371-050
7/8View All -
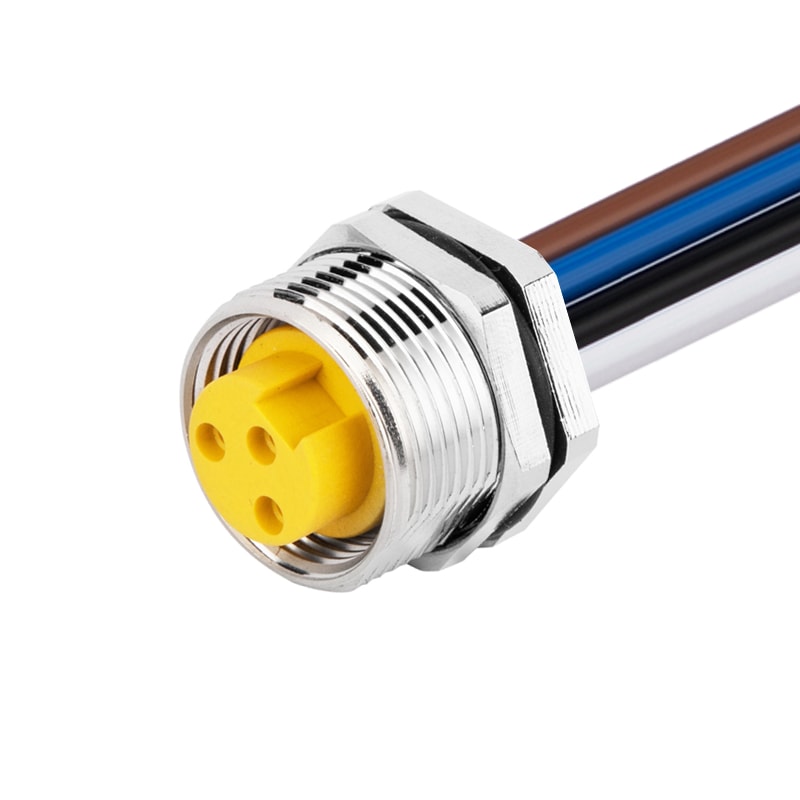

P/N: AM78F0312A371-050
7/8View All -
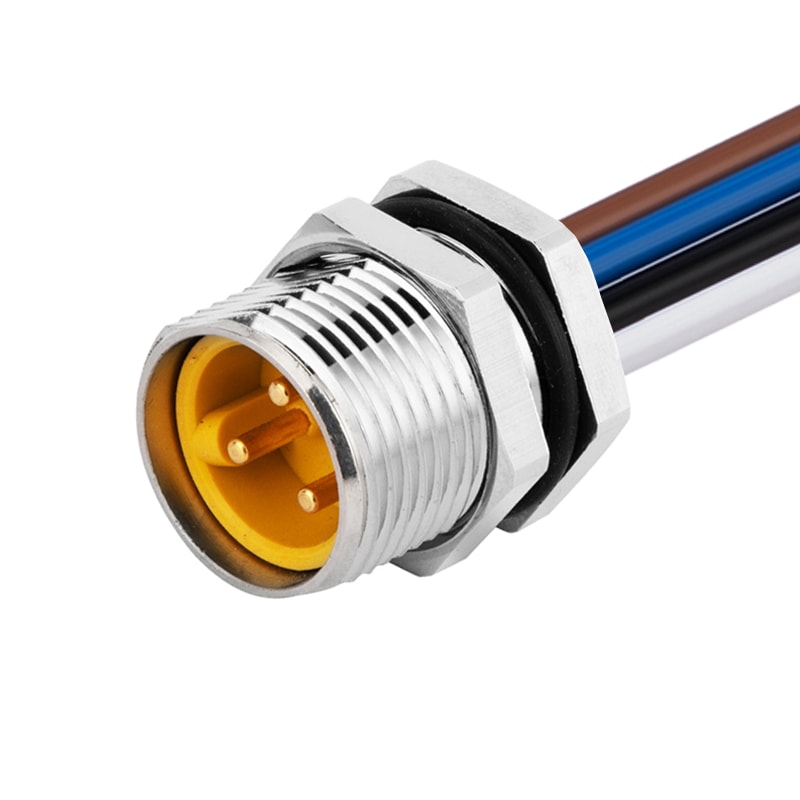

P/N: AM78M0312A371-050
7/8View All
-
P/N: AM23M1912A002
M23 Panel Receptacle Rear Mount Male 19P(16+3) Solder Connection For Wires Straight IP67View All -
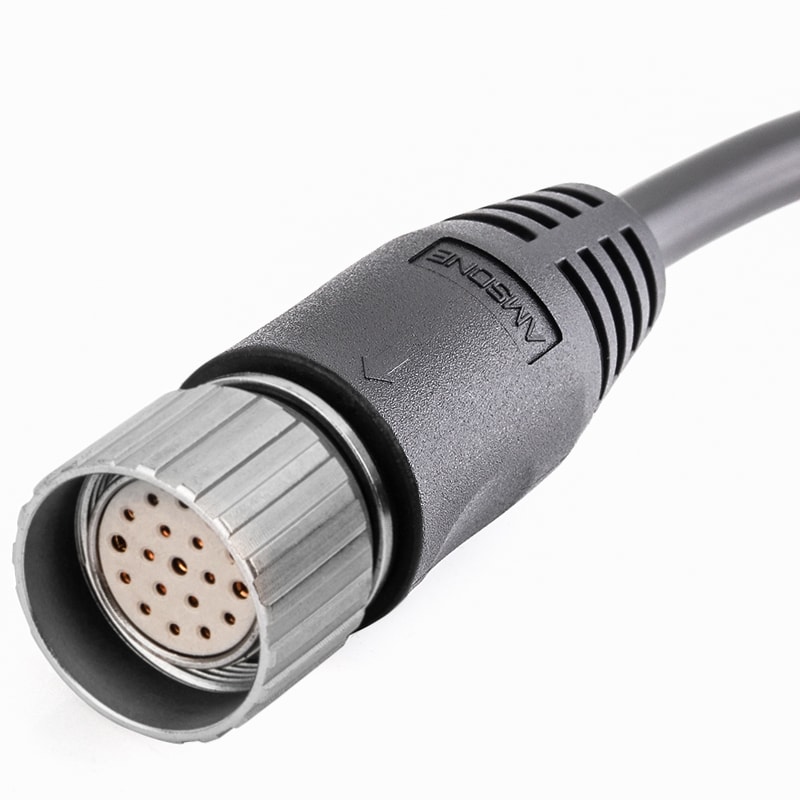

P/N: AM23F1911AXX1-XXX
M23 Pre-molded Cable Connector Female 19P(16+3) Solder Connection Straight IP67View All -
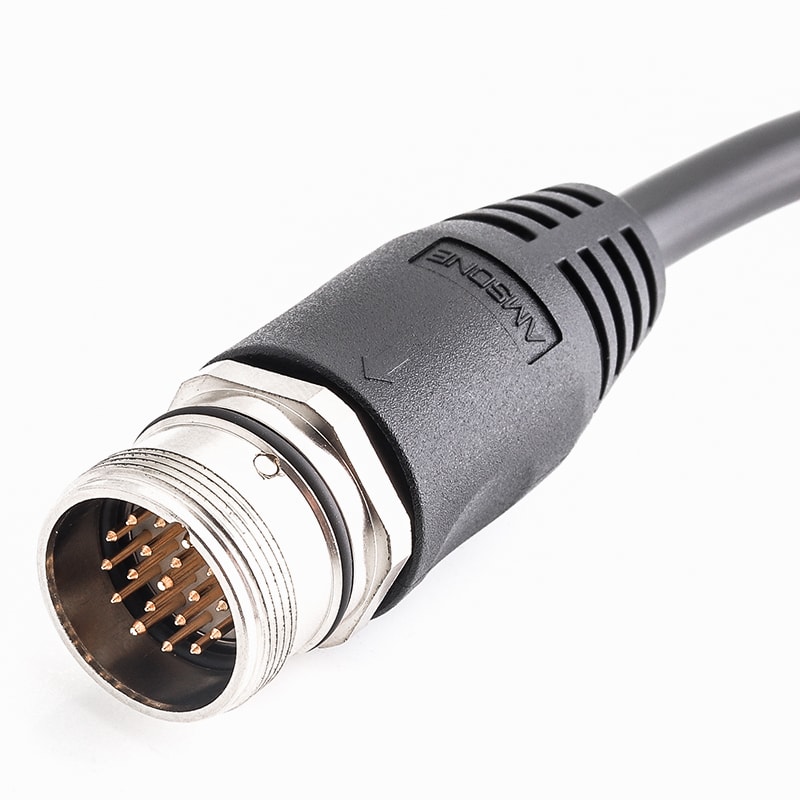

P/N: AM23M1911AXX1-XXX
M23 Pre-molded Cable Connector Male 19P(16+3) Solder Connection Straight IP67View All
-
P/N: BM24F0212A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 2P Receptacle Panel Mount Solder ConnectView All -
P/N: BM24M0214A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 2P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24M0314A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 3P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24F0312A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 3P Receptacle Panel Mount Solder ConnectView All -
P/N: BM24M0414A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 4P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24F0412A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 4P Receptacle Panel Mount Solder ConnectView All -
P/N: BM24M1214A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 12P Plug Connector Field InstallationView All -
P/N: BM24F1222A001
Bayonet Connector BM24 12P Receptacle Panel Mount PCB ConnectView All
Industrial Cable Harnesses
-

P/N: AM12F0411D241-010
M12 4P D Code Pre-molded Cable Connector Female Straight IP67View All -

P/N: AM12M0411D241-010
M12 pre-molded cable connector male solder connection D code straight IP67View All -
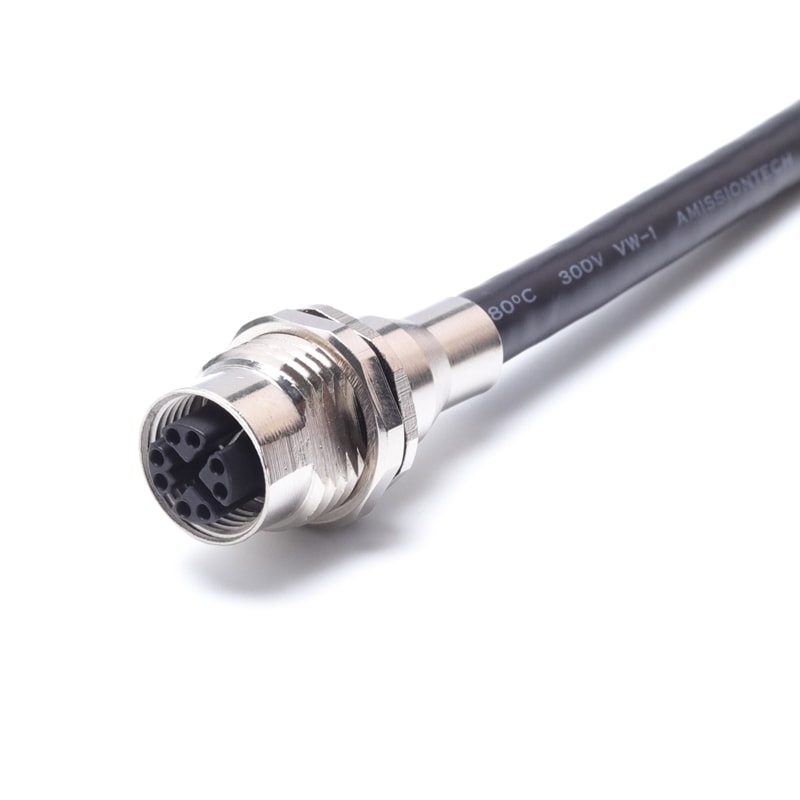

P/N: AM12F0812X003
M12 Device Connector X Code Female EMC Shielded Panel Rear Mount ReceptacleView All -
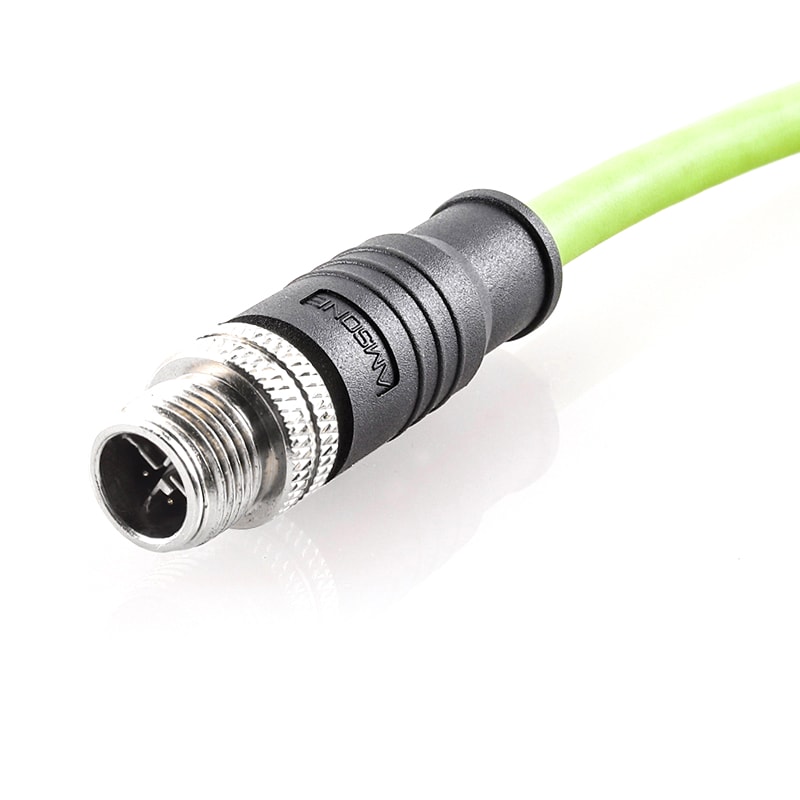

P/N: AM12M0811X231-030
M12 Pre-molded Cable Connector 8Pole Male X Code Cable StraightView All -
P/N: AM12F0411BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -
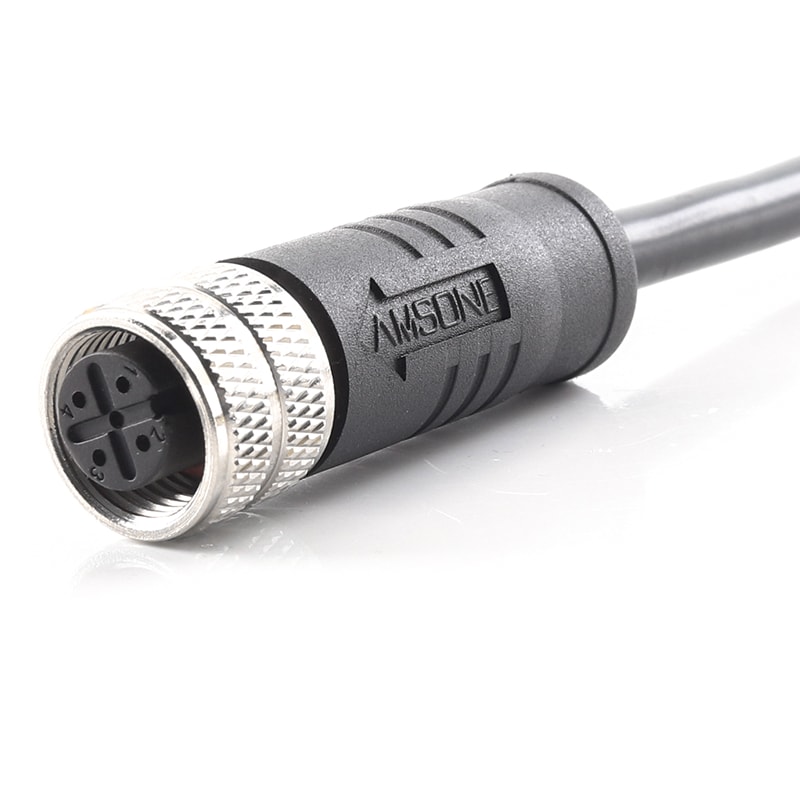

P/N: AM12F0511A241-010
M12 FieldBUS Cable Industrial Automation DeviceNet CanOpen CableView All -
P/N: EhterNet Cable
EhterNet Cable CAT5/CAT6/CAT7 PROFIBUS Industrial Network cableView All -

P/N: AM12M0814X221-010
M12 X Code Male ProfiNET/EtherNET Cable M12 Connector X CodedView All
-

P/N: AM12F0411D241-010
M12 4P D Code Pre-molded Cable Connector Female Straight IP67View All -

P/N: AM78M0411A272-050
DeviceNET 7/8View All -
P/N: AM12F0411BXX1-XXX
M12 pre-molded cable connector, female, contacts:4, solder connection, B code, straight, IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0511A241-010
M12 FieldBUS Cable Industrial Automation DeviceNet CanOpen CableView All -

P/N: AM78M0511A172-030
MINI-Change 7/8View All
-

P/N: AM12M0411D241-010
M12 pre-molded cable connector male solder connection D code straight IP67View All -

P/N: AM12F0812X003
M12 Device Connector X Code Female EMC Shielded Panel Rear Mount ReceptacleView All -

P/N: AM12M0811X231-030
M12 Pre-molded Cable Connector 8Pole Male X Code Cable StraightView All -
P/N: EhterNet Cable
EhterNet Cable CAT5/CAT6/CAT7 PROFIBUS Industrial Network cableView All -

P/N: AM12M0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Male,M12 Y-Coded Power Signal Ethernet CableView All -

P/N: AM12F0811YXX1-XXX
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Power Signal,M12 Y-Coded CablesView All -

P/N: AM12F0812Y003
M12 Hybrid Connector,Female,Panel Mount Shielded,M12 Y-CodedView All
-

P/N: AM78H0511A433-XXX
Electrical Automation Power Supply Connector Cable 7/8-16UNF Pre-molded H-SplitterView All -
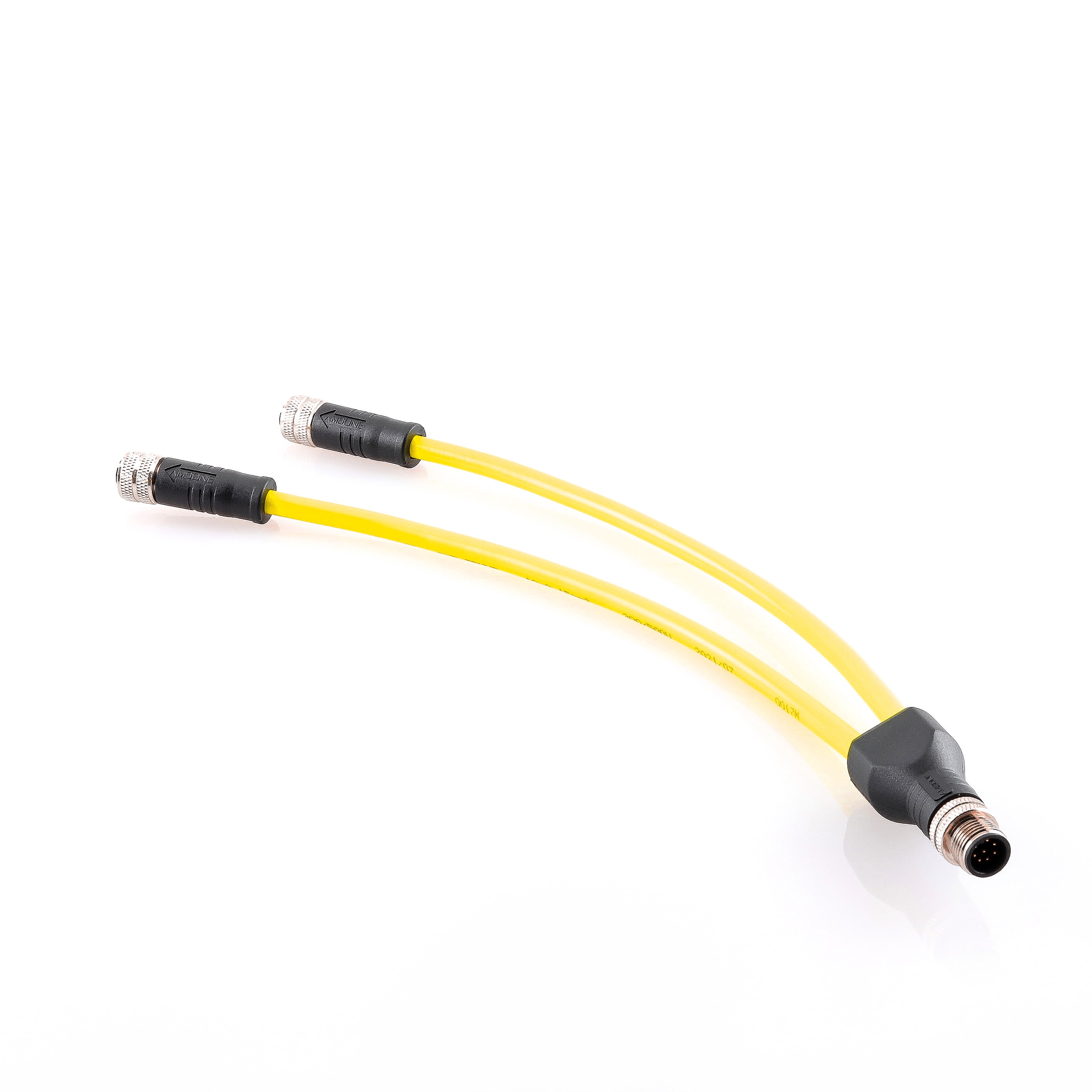

P/N: AM12H0811AXX1-XXX
M12 A Code 8P/4P Connector Y-Splitter Industrial Automation Sensor CableView All -
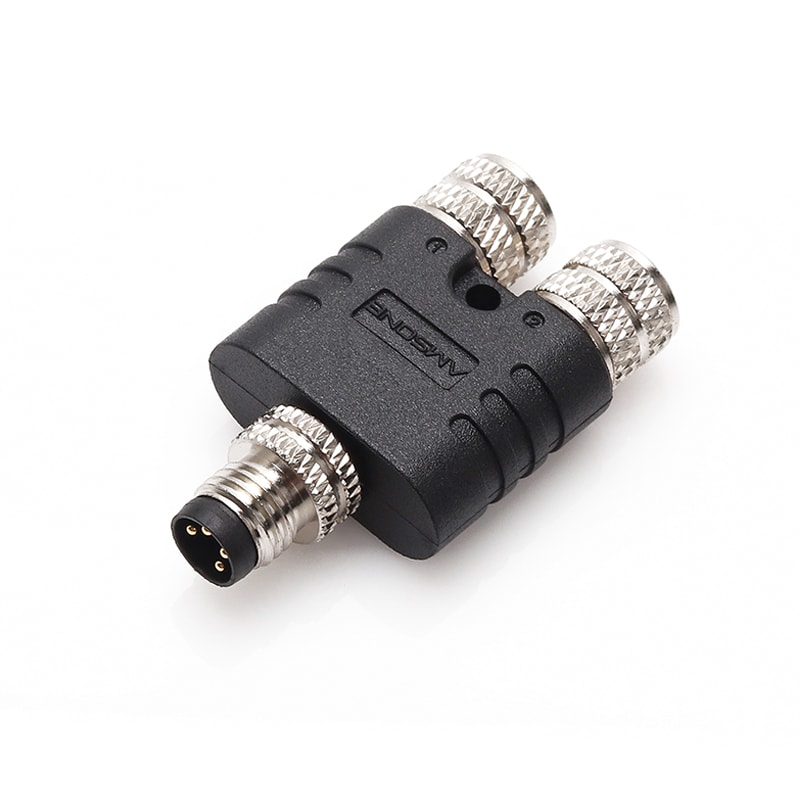

P/N: AM08Y0411A001-000
M8 Y-Splitter Electrical Automation Sensor Connector AdapterView All
Underwater Connectors and Cables
-

P/N: RMK5F
RMK5F 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 And 8 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: MCDLS-F
MCDLS-F 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 8 contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: MCBH5MTI
MCBH5MTI 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 And 8 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: HPBH9M
HPBH9M 9 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: HF75 50CXBH6F
HF75 50CXBH6F 6 Contacts Deepsea Watertight ConnectorsView All -

P/N: DMCIL13F M
DMCIL13F M 13 contacts Underwater cable connectorView All -

P/N: AWQ7-42
AWQ7-42 24, 28, 32, 36, 42 contacts Underwater cable connectorView All -

P/N: 1L25F M
1L25F M Circular 12, 16, 25 Contacts Underwater ConnectorView All
company
News
-
 Amissiontech to Showcase Smart Interconnection Solutions at SPS 2025 in NurembergView All
Amissiontech to Showcase Smart Interconnection Solutions at SPS 2025 in NurembergView All -
 2025 Tokyo International Manufacturing Expo: A Perfect ConclusionView All
2025 Tokyo International Manufacturing Expo: A Perfect ConclusionView All -
 Amissiontech to Showcase Advanced Industrial Connectors and I/O Solutions at Manufacturing World Japan 2025View All
Amissiontech to Showcase Advanced Industrial Connectors and I/O Solutions at Manufacturing World Japan 2025View All -
 Amissiontech Reflects on a Successful Participation at ProPak China 2025View All
Amissiontech Reflects on a Successful Participation at ProPak China 2025View All -
 Amissiontech Team-Building Activity at Hailing IslandView All
Amissiontech Team-Building Activity at Hailing IslandView All -
 Dragon Boat Festival Greetings: Celebrating Tradition with AmissiontechView All
Dragon Boat Festival Greetings: Celebrating Tradition with AmissiontechView All -
 Celebrating Women at Amissiontech on International Women’s DayView All
Celebrating Women at Amissiontech on International Women’s DayView All -
 Amissiontech Invites You to HANNOVER MESSE 2025View All
Amissiontech Invites You to HANNOVER MESSE 2025View All
-
 Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All
Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All -
 What is an M12 A coded connector?View All
What is an M12 A coded connector?View All -
 What Do You Know M12 B Coded?View All
What Do You Know M12 B Coded?View All -
 Revolutionizing Field I/O Signal Transmission with Amissiontech's IO-Link HUBView All
Revolutionizing Field I/O Signal Transmission with Amissiontech's IO-Link HUBView All -
 Exploring the Technology Behind Underwater Connectors and CablesView All
Exploring the Technology Behind Underwater Connectors and CablesView All -
 Amissiontech's IO-LINK Modules Shine at HANNOVER MESSE 2024View All
Amissiontech's IO-LINK Modules Shine at HANNOVER MESSE 2024View All -
 Circular ConnectorView All
Circular ConnectorView All -
 IO-Link Module - Connects Future Digital CommunicationsView All
IO-Link Module - Connects Future Digital CommunicationsView All
-
 Understanding Ethernet MHz Speed and Its Impact on Network PerformanceView All
Understanding Ethernet MHz Speed and Its Impact on Network PerformanceView All -
 Top 10 Cable Types and Their UsesView All
Top 10 Cable Types and Their UsesView All -
 HDMI vs VGA: Understanding the Key Differences for Industrial & Custom Cable ApplicationsView All
HDMI vs VGA: Understanding the Key Differences for Industrial & Custom Cable ApplicationsView All -
 Complete Guide to Ethernet Cable CategoriesView All
Complete Guide to Ethernet Cable CategoriesView All -
 Wire Harness Production ExplainedView All
Wire Harness Production ExplainedView All -
 Industrial HDMI Shielded Cable Technology InterpretationView All
Industrial HDMI Shielded Cable Technology InterpretationView All -
 Revolutionize Automation with DeviceNet-Compatible ToolsView All
Revolutionize Automation with DeviceNet-Compatible ToolsView All -
 Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All
Amissiontech IO-Link Modules: Versatility in Connection MethodsView All
Industries and Solutions
Solutions
Industries
News And Events
RG58 vs. RG59 Coaxial Cable — Which One Is Right for You?
When it comes to coaxial cables, RG58 and RG59 are two of the most commonly used types in a variety of low-frequency applications. Though they may look similar at first glance, their differences in impedance, conductor size, and intended use make them suitable for very different purposes.
In this article, we’ll break down what sets RG58 cable and RG59 cable apart, compare their performance, and help you choose the right one based on your specific needs.
Understanding RG58 and RG59: What’s the Same?
Before diving into the differences, it's important to understand what these two coaxial cables have in common:
Both are low-power RF cables, designed for short-range signal transmission.
They feature polyethylene insulation, which provides good dielectric properties.
Both come with a PVC outer jacket, offering basic protection against physical damage and environmental exposure.
Neither is ideal for high-speed or broadband applications due to higher signal loss over long distances.
These similarities make them both suitable for entry-level or budget-conscious applications where high-frequency performance isn’t critical.
Key Differences Between RG58 and RG59
While RG58 and RG59 share some structural traits, their main differences lie in impedance, conductor thickness, and application focus.
| Feature | RG58 | RG59 |
|---|---|---|
| Impedance | 50 Ohms | 75 Ohms |
| Center Conductor Size | 20 AWG | 22 AWG (thinner) |
| Typical Use | Radio communications, amateur radio, lab equipment | TV antennas, CCTV, analog video systems |
| Signal Performance | Better for low-loss RF signals | Better for baseband video signals |
Impedance Matters
RG58 (50Ω): This impedance is ideal for RF signal transmission, especially in environments like ham radio setups, mobile transmitters, and laboratory instruments where signal integrity matters more than distance.
RG59 (75Ω): The standard impedance for video and TV applications, making it the go-to choice for cable TV, satellite receivers, and CCTV security systems.
When to Choose RG58
If your application involves radio frequency signals, especially in the HF to UHF range, RG58 is likely your best bet. It's widely used in:
Amateur radio (HAM radio)
Mobile communication devices
RF test equipment
Short-range antenna connections
However, due to its smaller diameter and higher resistance, RG58 is not recommended for long-distance runs, as signal loss becomes significant beyond 50 feet.

When to Choose RG59
RG59 cable shines in analog video signal transmission, particularly for:
Closed-circuit television (CCTV)
Cable TV installations
Satellite dish to receiver connections
Home AV systems
Its 75Ω impedance matches perfectly with most consumer-grade video equipment, ensuring minimal signal reflection and interference. That said, it's not suitable for digital or high-definition video, where modern alternatives like HD-SDI or fiber are preferred.
Why Not Just Use RG6 Instead?
You may be wondering: why even consider RG58 or RG59 when RG6 is more modern and widely used?
Here’s how RG6 compares:
| Feature | RG58 / RG59 | RG6 |
|---|---|---|
| Conductor Size | Thinner (20–22 AWG) | Thicker (18 AWG) |
| Shielding | Basic shielding | Double or quad shielding available |
| Impedance | 50/75Ω | 75Ω only |
| Use Case | Low-frequency, short-run | High-definition, long-run |
RG6 offers superior performance for digital TV, satellite, and internet services, especially over longer distances. If you're setting up a new system or need high-bandwidth connectivity, RG6 is usually the better investment.
But if cost is a concern and your application doesn't require high frequencies or long cable runs, RG58 or RG59 can still offer a practical and affordable solution.
Choosing the Right Cable: A Quick Guide
To help you decide between RG58 and RG59, here’s a simple decision framework:
Choose RG58 if:
Your setup involves radio or RF signals
You're using ham radio equipment or mobile transceivers
Signal efficiency matters more than distance
Budget is tight but you still want decent RF performance
Choose RG59 if:
You're connecting TV antennas, CCTV cameras, or cable boxes
You're working with standard definition analog video
Cost is a major factor and performance demands are modest
Avoid RG58/RG59 if:
You need high-definition video or broadband internet
Running cables over long distances
Using modern digital equipment that expects low signal loss
Final Thoughts
While newer cables like RG6 and fiber optics have taken center stage in many industries, RG58 and RG59 remain relevant in niche but essential applications. Whether you're setting up a ham radio station or installing a basic surveillance system, understanding the strengths and limitations of each will ensure you get the most out of your coaxial cable investment.
Always remember to match the impedance of your cable with your equipment and avoid cheap knock-offs that can degrade performance. Invest in quality from a trusted supplier for reliable results.
Ready to Find the Right Coaxial Cable?
Looking for high-quality RG58 or RG59 coaxial cables for your next project? At Amissiontech, we offer a wide selection of durable, tested coax solutions tailored for RF, CCTV, and analog video applications. Our cables are built to last and perform consistently in real-world conditions.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and find the perfect coaxial cable for your setup.







































